
Peroxide effect can be checked by the addition of sufficient amount of:
(A)- diphenylamine
(B)- mono phenylamine
(C)- triphenylamine
(D)- penta phenylamine
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: When unsymmetrical alkene is treated with hydrogen bromide (HBr) in the presence of peroxides, the regioselectivity of the reaction is reversed and the product obtained does not follow Markovnikov’s rule. This anti-Markovnikov’s addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes in the presence of peroxides is called peroxide effect.
Complete answer: Markovnikov’s rule for electrophilic addition of alkenes states that the negative part of the reagent adds to that carbon of the carbon-carbon double bond which contains less number of hydrogen atoms.
In the absence of peroxides, HBr addition to alkenes takes place via ionic mechanism whereas HBr addition follows free radical mechanism in the presence of peroxides. The anti-Markovnikov’s addition in the presence of peroxide can be checked with the addition diphenylamine.
Peroxides are mild oxidizing agents. Therefore, peroxides oxidize N, N-diphenylamine to give a blue-violet coloured compound called quinoneimine.
In a reaction where peroxide is not present, the colour of the reaction mixture does not change on the addition of N, N-diphenylamine. N, N-diphenylamine is widely used as an antioxidant. It inhibits or prevents the reaction brought about by peroxides.
Structure of diphenylamine (DPA) is shown below:
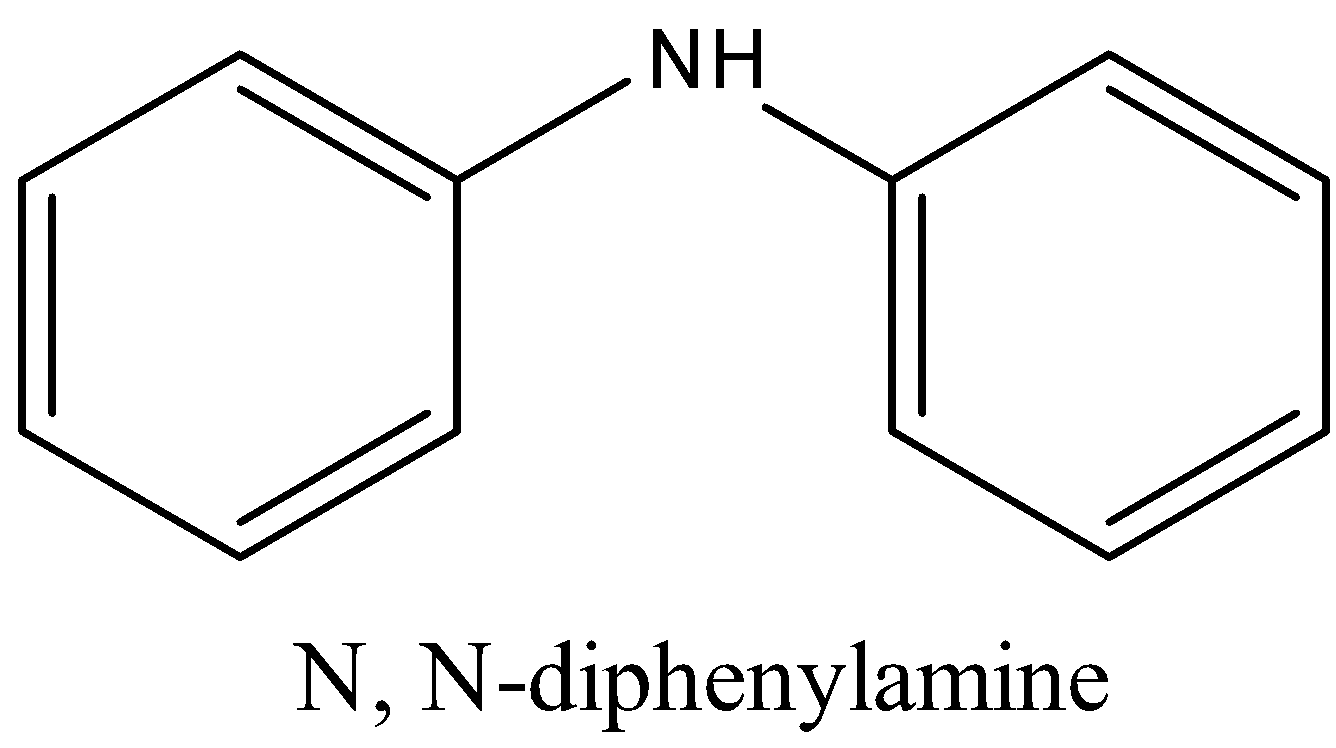
Diphenylamine is used to check the peroxide effect.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: Peroxide effect is also known as kharasch effect. Peroxides are generally used as radical initiators. They have weak $O-O$ bond which cleaves homolytically to generate free radicals.
Note: Peroxide effect is only observed with HBr. The regioselectivity of other electrophilic addition reactions like with HF, HCl and HI, is not changed in the presence of peroxides. This is due to the reason that HF and HCl bonds are strong and do not cleave easily. However, HI bond is relatively weak and undergoes homolytic cleavage in presence of peroxide but iodine radicals couple to form iodine immediately.
Complete answer: Markovnikov’s rule for electrophilic addition of alkenes states that the negative part of the reagent adds to that carbon of the carbon-carbon double bond which contains less number of hydrogen atoms.
In the absence of peroxides, HBr addition to alkenes takes place via ionic mechanism whereas HBr addition follows free radical mechanism in the presence of peroxides. The anti-Markovnikov’s addition in the presence of peroxide can be checked with the addition diphenylamine.
Peroxides are mild oxidizing agents. Therefore, peroxides oxidize N, N-diphenylamine to give a blue-violet coloured compound called quinoneimine.
In a reaction where peroxide is not present, the colour of the reaction mixture does not change on the addition of N, N-diphenylamine. N, N-diphenylamine is widely used as an antioxidant. It inhibits or prevents the reaction brought about by peroxides.
Structure of diphenylamine (DPA) is shown below:

Diphenylamine is used to check the peroxide effect.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: Peroxide effect is also known as kharasch effect. Peroxides are generally used as radical initiators. They have weak $O-O$ bond which cleaves homolytically to generate free radicals.
Note: Peroxide effect is only observed with HBr. The regioselectivity of other electrophilic addition reactions like with HF, HCl and HI, is not changed in the presence of peroxides. This is due to the reason that HF and HCl bonds are strong and do not cleave easily. However, HI bond is relatively weak and undergoes homolytic cleavage in presence of peroxide but iodine radicals couple to form iodine immediately.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




