
Name two monosaccharide present in sucrose.
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: Saccharides are basically a group of organic compounds. The general formula of saccharide is \[{C_n}{H_{2n}}{O_n}\]. The ratio of hydrogen and oxygen is always \[2:1\]. Saccharides are also called carbohydrates. These are biomolecules.
On the basis of number of saccharide molecules attached with each other saccharides are classified into four different types These are,
Mono saccharides, disaccharides, trisaccharide, and polysaccharide etc.
The common example of disaccharide is sucrose. Sucrose contains glucose and fructose in one molecule . The structure of sucrose is shown below.
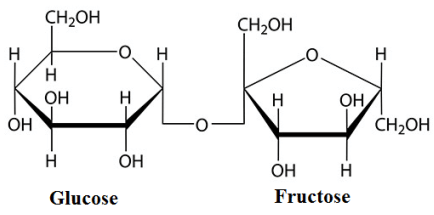
In this structure the bonding between glucose and fructose is called glycosidic linkage. And this glycosidic linkage is at \[{C_1}\] carbon of glucose and \[{C_5}\] carbon of fructose.
Additional information:
There is another classification of saccharides on the basis of reducible character of the saccharide. If the anomeric -OH group is free in the structure of the saccharide it is called reducible saccharide and if it is not then it is called non- reducible saccharide .
The example of reducible saccharide are, glucose, fructose, sucrose etc. the example of non-reducible saccharide is cellulose, starch etc.
Note:
Sucrose is dextrorotatory in nature i.e it rotates the plane polarised light towards right.But on hydrolysis it yields glucose and fructose, fructose show higher degree of laevorotation than glucose dextrorotation.So on hydrolysis sucrose is laevorotatory in nature.
On the basis of number of saccharide molecules attached with each other saccharides are classified into four different types These are,
Mono saccharides, disaccharides, trisaccharide, and polysaccharide etc.
The common example of disaccharide is sucrose. Sucrose contains glucose and fructose in one molecule . The structure of sucrose is shown below.

In this structure the bonding between glucose and fructose is called glycosidic linkage. And this glycosidic linkage is at \[{C_1}\] carbon of glucose and \[{C_5}\] carbon of fructose.
Additional information:
There is another classification of saccharides on the basis of reducible character of the saccharide. If the anomeric -OH group is free in the structure of the saccharide it is called reducible saccharide and if it is not then it is called non- reducible saccharide .
The example of reducible saccharide are, glucose, fructose, sucrose etc. the example of non-reducible saccharide is cellulose, starch etc.
Note:
Sucrose is dextrorotatory in nature i.e it rotates the plane polarised light towards right.But on hydrolysis it yields glucose and fructose, fructose show higher degree of laevorotation than glucose dextrorotation.So on hydrolysis sucrose is laevorotatory in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




