
Most acidic hydrogen is present in
A.
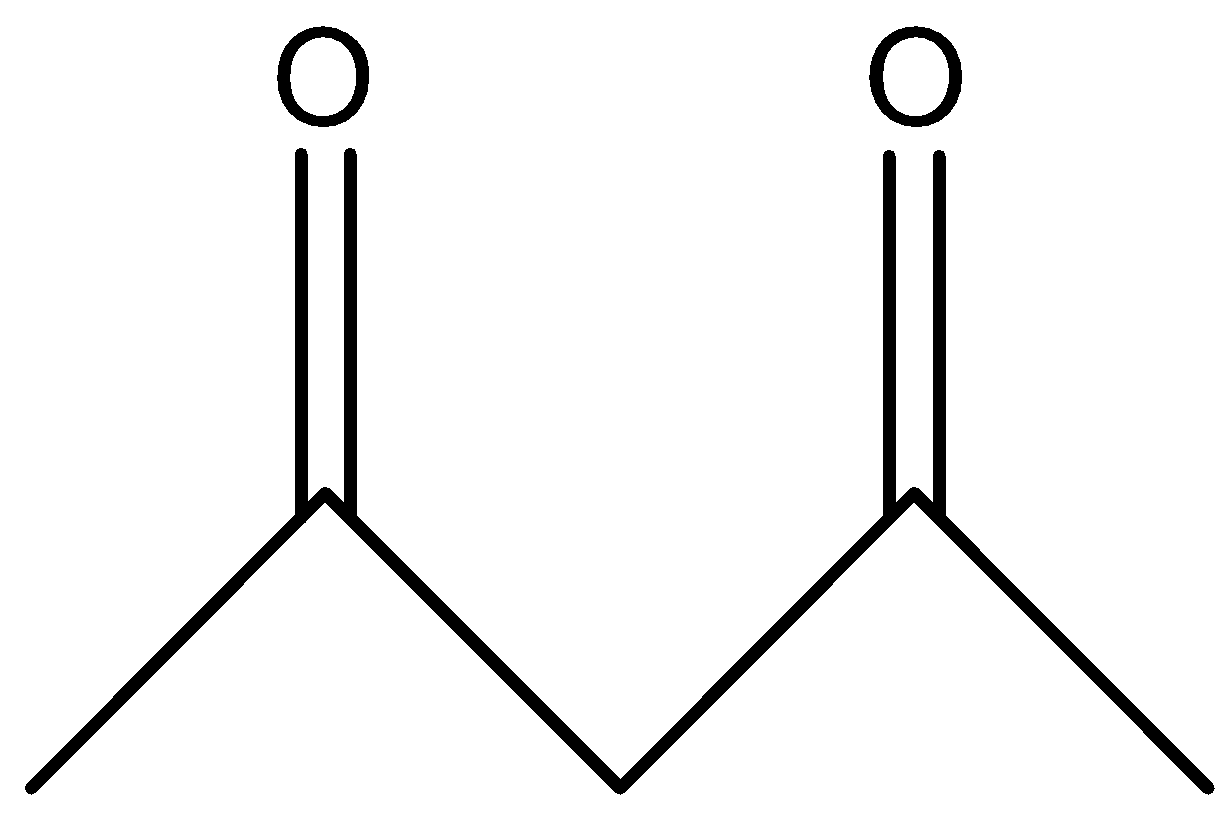
B.
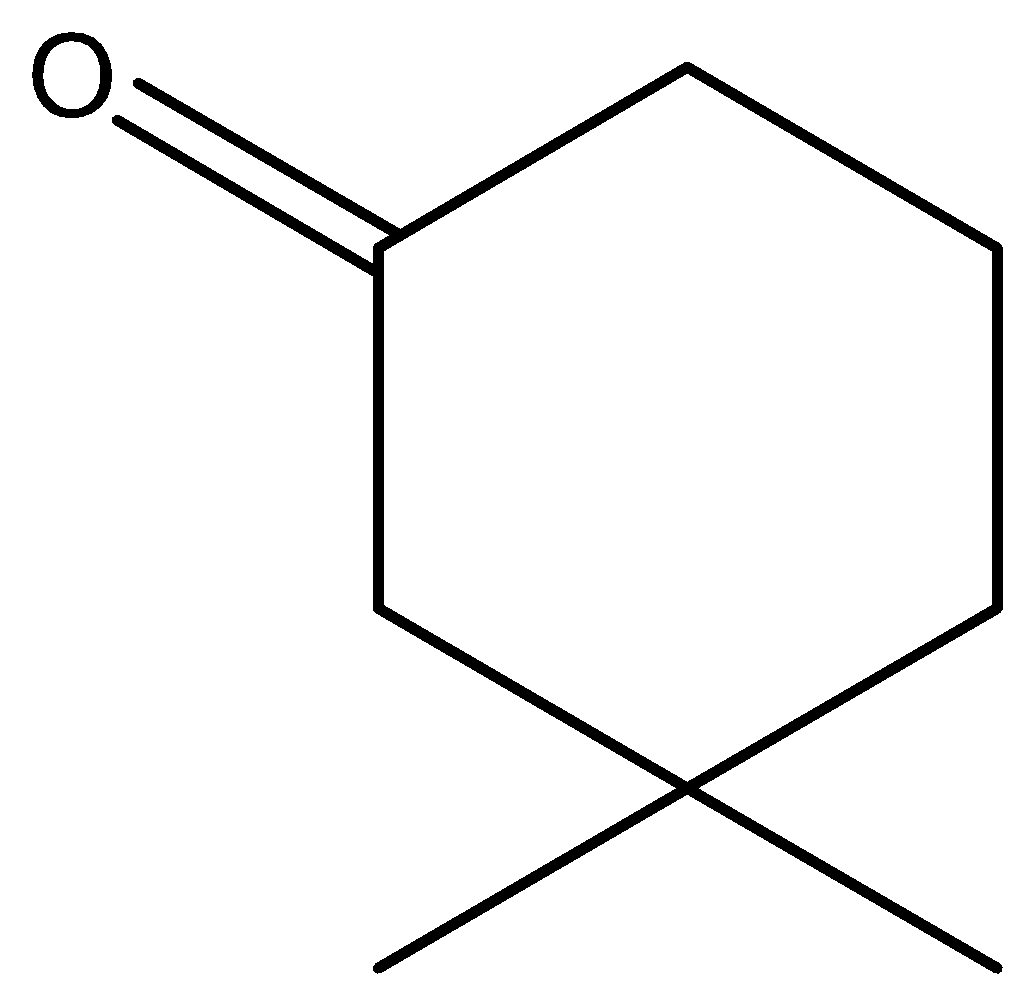
C.\[{{(C{{H}_{3}}CO)}_{3}}CH\]
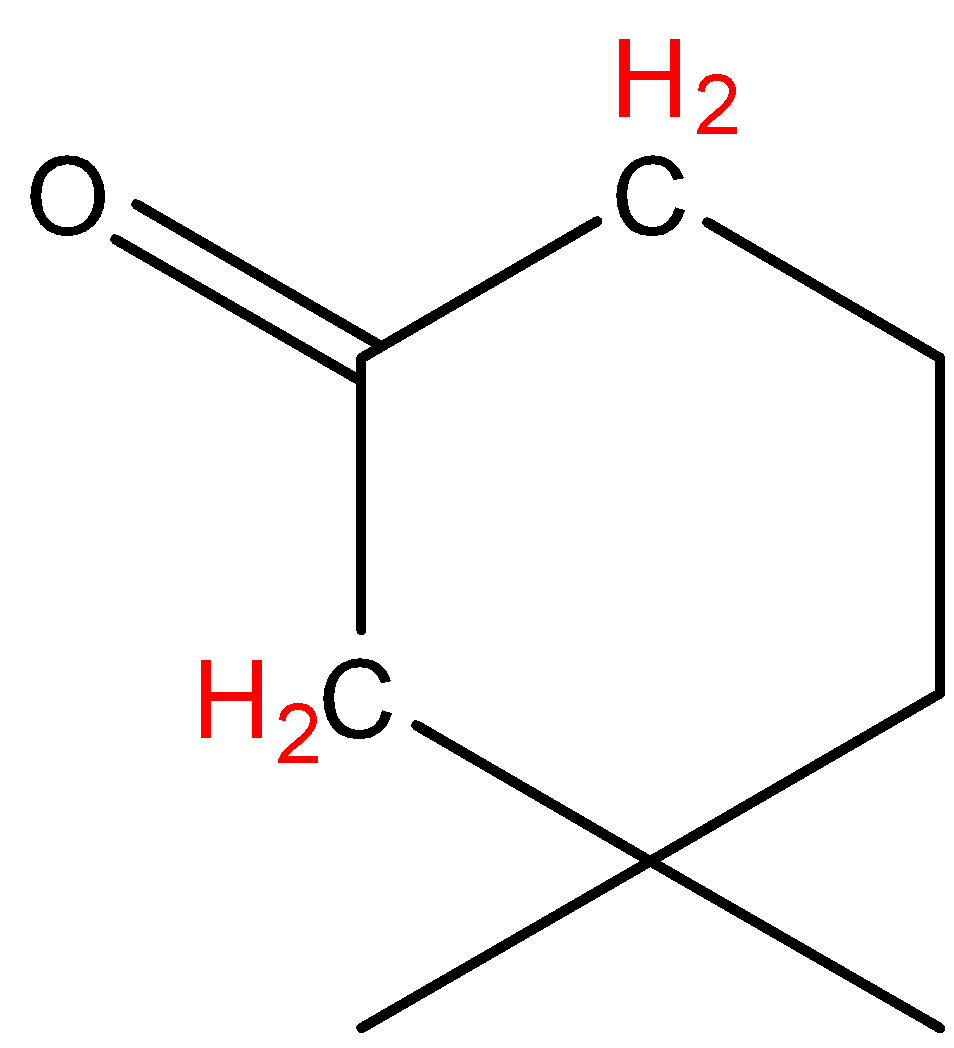
D.\[{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}COH\]


Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: “Acidic hydrogen means it has a tendency to be released as \[{{H}^{+}}\] ion. So, if any H-atom is attached to another atom or group of atoms with higher electronegativity, that H-atom can be released very easily as \[{{H}^{+}}\] ion.”
Complete step by step answer:
In option A, the hydrogen marked with red color is an acidic hydrogen, due to the presence of hydrogens in between electron withdrawing groups .

In option B, the hydrogens marked with red color are acidic hydrogens, due to the presence of hydrogens in between electron withdrawing groups .
In option C, the hydrogen marked with red color is acidic hydrogen, due to the presence of hydrogens in between electron withdrawing groups .
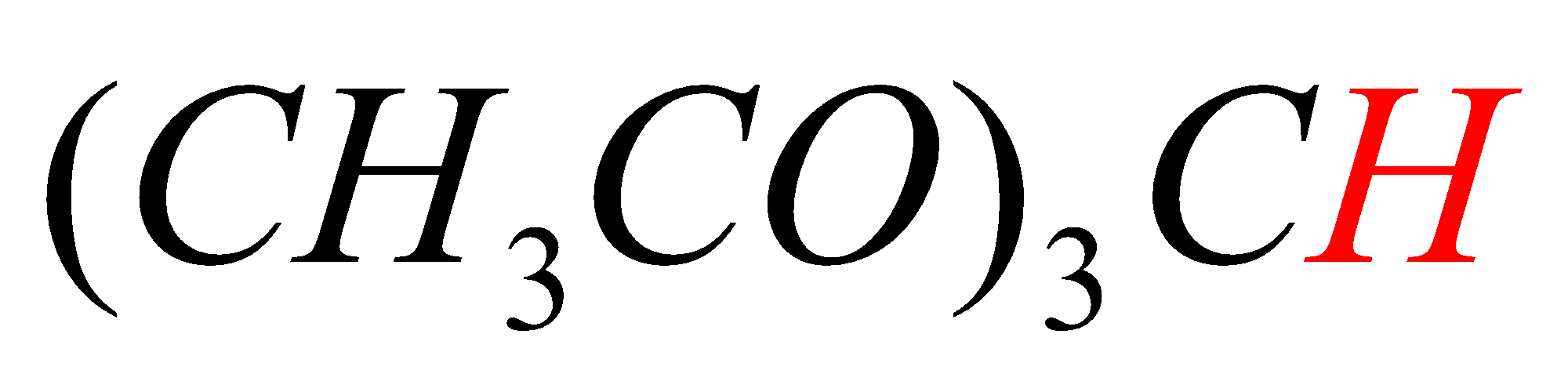
In option D, the hydrogen marked with red color is acidic hydrogen, due to the attachment of hydrogen directly to the oxygen.
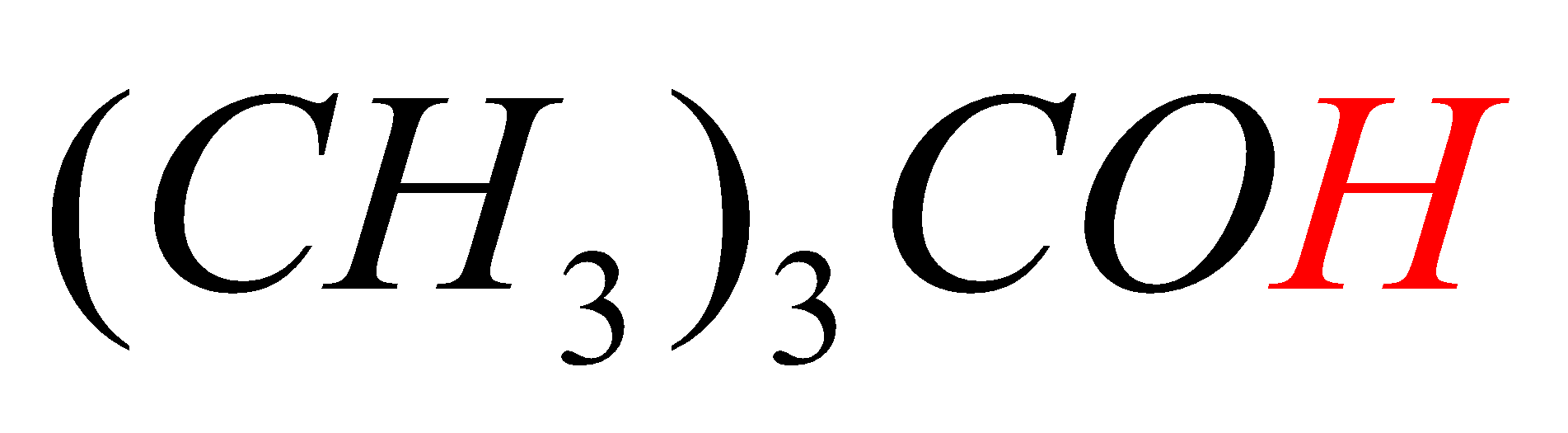
-In all the first three options (A, B, C) the acidic hydrogens (Red in color) are not directly attached to electron withdrawing groups (attached to carbon directly) but in option D, the acidic hydrogen (Red in color) is directly attached to the Oxygen atom (have high electronegativity).
-Oxygen atoms have higher electronegativity than carbon.
-So, the hydrogen which is attached to oxygen is more acidic than the hydrogen atoms that are attached to carbon atoms (carbon atoms later attached to electron withdrawing groups).
So, the correct option is Option D.
Note:
The hydrogen atom which lies between two electron withdrawing groups is acidic (in the options A, B, C). Even though the hydrogen atom lies between the electron withdrawing groups are acidic, the hydrogen which is directly attached to the more electronegative atom is more acidic (in option D).
Complete step by step answer:
In option A, the hydrogen marked with red color is an acidic hydrogen, due to the presence of hydrogens in between electron withdrawing groups .

In option B, the hydrogens marked with red color are acidic hydrogens, due to the presence of hydrogens in between electron withdrawing groups .

In option C, the hydrogen marked with red color is acidic hydrogen, due to the presence of hydrogens in between electron withdrawing groups .
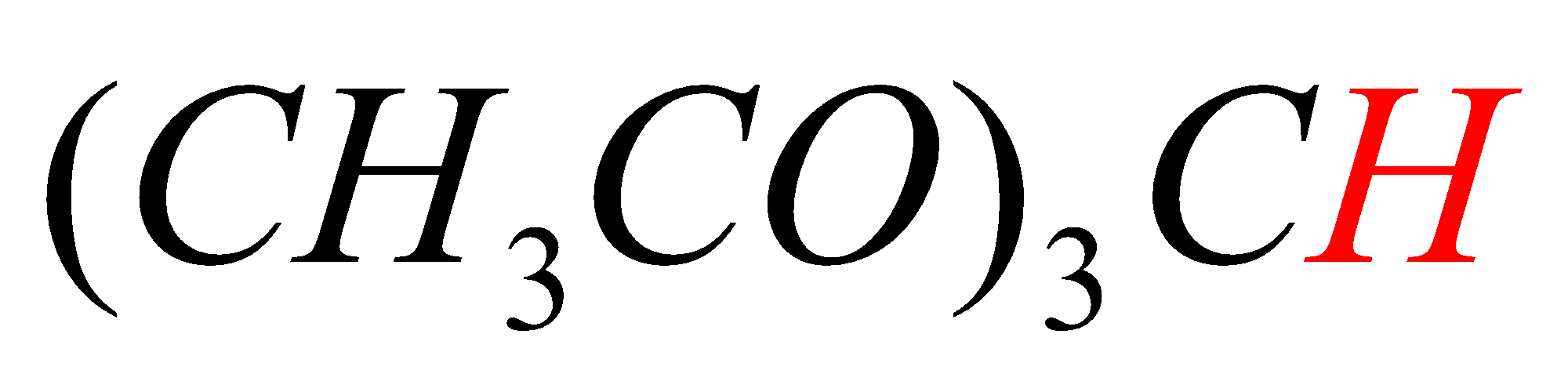
In option D, the hydrogen marked with red color is acidic hydrogen, due to the attachment of hydrogen directly to the oxygen.
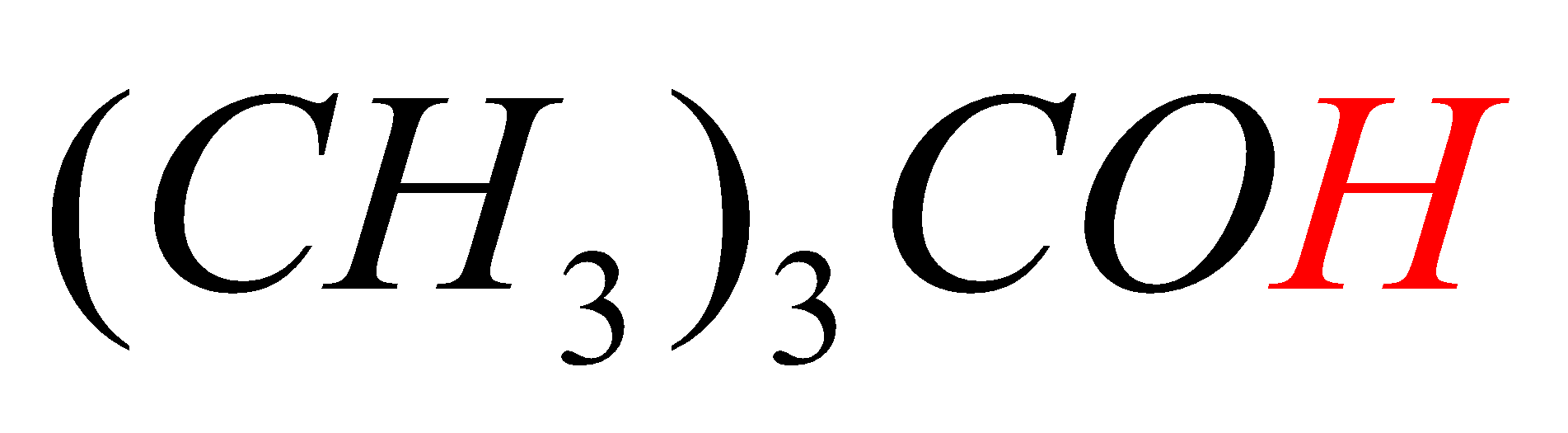
-In all the first three options (A, B, C) the acidic hydrogens (Red in color) are not directly attached to electron withdrawing groups (attached to carbon directly) but in option D, the acidic hydrogen (Red in color) is directly attached to the Oxygen atom (have high electronegativity).
-Oxygen atoms have higher electronegativity than carbon.
-So, the hydrogen which is attached to oxygen is more acidic than the hydrogen atoms that are attached to carbon atoms (carbon atoms later attached to electron withdrawing groups).
So, the correct option is Option D.
Note:
The hydrogen atom which lies between two electron withdrawing groups is acidic (in the options A, B, C). Even though the hydrogen atom lies between the electron withdrawing groups are acidic, the hydrogen which is directly attached to the more electronegative atom is more acidic (in option D).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




