
What is meant by the transverse nature of electromagnetic waves? Draw a diagram showing the propagation of an electromagnetic wave along X-direction, indicating clearly the directions of oscillating electric and magnetic fields associated with it.
Answer
553.2k+ views
Hint:There are two types of waves; which are transverse waves as well as longitudinal waves. An electromagnetic wave is a combination of an oscillating electric field and an oscillating magnetic field travelling alongside each other. In electromagnetic waves, the vectors of the electric and magnetic field form a right handed system.
Complete answer:
Transverse Nature of Electromagnetic Waves: In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic field vectors would oscillate perpendicular to the direction of the propagation of the electromagnetic wave. This property of an electromagnetic wave is known as the transverse nature of an electromagnetic wave. In an electromagnetic wave, the three vectors $E$,$B$ and $K$ form a right handed system.
Accordingly if a wave is propagating along X-axis, the electric field vector oscillates along Y-axis and magnetic field vector oscillates along Z-axis. The diagram showing the propagation of an electromagnetic wave along X-direction is shown in the figure below. There can be a phase difference between the electric fields and the magnetic field passing in an electromagnetic wave.
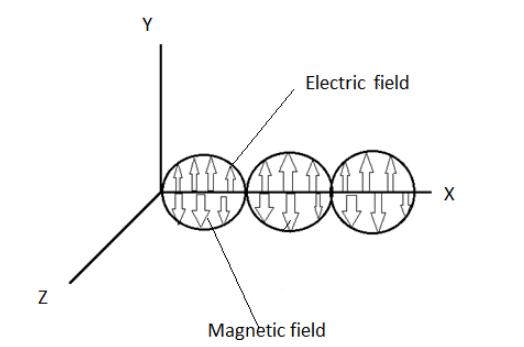
Here, the upper envelope in the diagram is that of the electric field when started from the origin, while the lower envelope is that of the magnetic field and then they start oscillating.Here, in the diagram, the phase difference is zero.
Note:An electromagnetic wave travels with the speed of light in vacuum. In fact, light itself is an electromagnetic wave. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, while sound waves are longitudinal waves. Sound waves travel through compressions and rarefactions which causes vibrations in the medium.
Complete answer:
Transverse Nature of Electromagnetic Waves: In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic field vectors would oscillate perpendicular to the direction of the propagation of the electromagnetic wave. This property of an electromagnetic wave is known as the transverse nature of an electromagnetic wave. In an electromagnetic wave, the three vectors $E$,$B$ and $K$ form a right handed system.
Accordingly if a wave is propagating along X-axis, the electric field vector oscillates along Y-axis and magnetic field vector oscillates along Z-axis. The diagram showing the propagation of an electromagnetic wave along X-direction is shown in the figure below. There can be a phase difference between the electric fields and the magnetic field passing in an electromagnetic wave.

Here, the upper envelope in the diagram is that of the electric field when started from the origin, while the lower envelope is that of the magnetic field and then they start oscillating.Here, in the diagram, the phase difference is zero.
Note:An electromagnetic wave travels with the speed of light in vacuum. In fact, light itself is an electromagnetic wave. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, while sound waves are longitudinal waves. Sound waves travel through compressions and rarefactions which causes vibrations in the medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




