
Lycopodium is
a) Heterosporous
b) Homosporous
c) Water firm
d) Both Band C
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Lycopodium is a genus of creeping cedars or ground pines. They come under the class of tracheophytes with the same kind of spores. Lycopodium is of great benefit as it is used as an herb.
Complete answer:
Homosporous is a condition in which a plant produces only a single type of spore. Lycopodium is a flowerless plant and has a needle like a leaf present. The leaf is the microphylls. The sporangia produce the only homospory on the upper surface of the leaf blade in the sporophylls which are arranged in the cone-like strobilus at the end of the stem. Lycopodium usually reproduces asexually by spores. They also have an underground sexual stage where they produce gametes.
Additional information:
- Heterosporous is a condition in which different types of spores are produced. The spores differ in size and shape greatly. The small spore is the male gametophyte and the large spore is the female gametophyte. All the seed-bearing plants are heterosporous in nature. This condition in plants is known as heterospory.
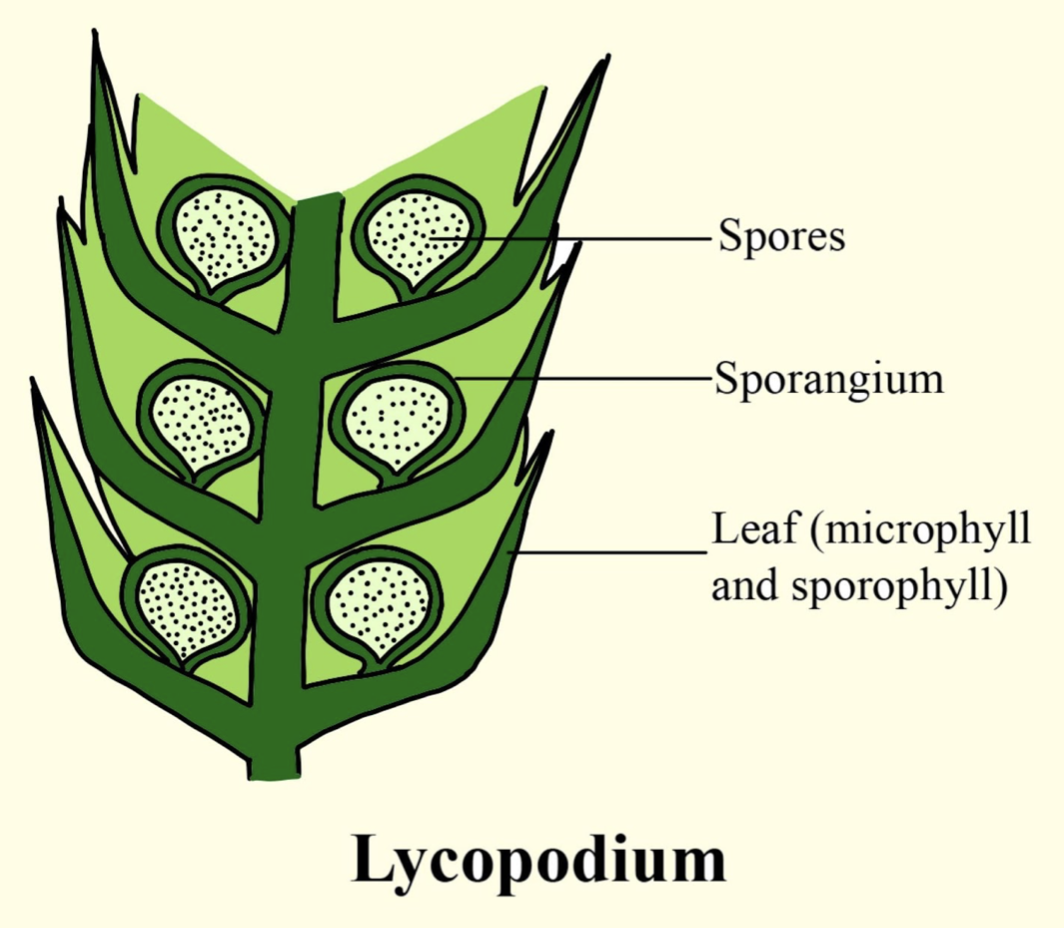
- Homosporous is a condition where only one type of spores is produced. They occur only in the bryophytes and lower pteridophytes. The spores are morphologically similar. They can be bisexual or unisexual. The spores may germinate to produce either both male and female gametophyte. This condition of producing only one kind of spore is called homospory.
The answer is ‘(b) Homosporous’.
Note: Lycopodium plant is of great economic value. It is used to cure diarrhea, dysentery, gout, and rheumatism. It is also used in homeopathic medicines for liver and urinary related diseases. It is also beneficial in dementia disorder.
Complete answer:
Homosporous is a condition in which a plant produces only a single type of spore. Lycopodium is a flowerless plant and has a needle like a leaf present. The leaf is the microphylls. The sporangia produce the only homospory on the upper surface of the leaf blade in the sporophylls which are arranged in the cone-like strobilus at the end of the stem. Lycopodium usually reproduces asexually by spores. They also have an underground sexual stage where they produce gametes.
Additional information:
- Heterosporous is a condition in which different types of spores are produced. The spores differ in size and shape greatly. The small spore is the male gametophyte and the large spore is the female gametophyte. All the seed-bearing plants are heterosporous in nature. This condition in plants is known as heterospory.

- Homosporous is a condition where only one type of spores is produced. They occur only in the bryophytes and lower pteridophytes. The spores are morphologically similar. They can be bisexual or unisexual. The spores may germinate to produce either both male and female gametophyte. This condition of producing only one kind of spore is called homospory.
The answer is ‘(b) Homosporous’.
Note: Lycopodium plant is of great economic value. It is used to cure diarrhea, dysentery, gout, and rheumatism. It is also used in homeopathic medicines for liver and urinary related diseases. It is also beneficial in dementia disorder.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




