
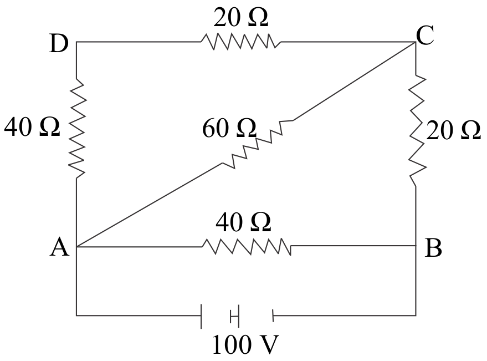
What is Kirchoff's current law of electric circuit? Calculate the potential difference between A and C from the given figure

Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint:-The Kirchoff’s current law is basically conservation of charge which states that the total current entering and leaving a junction has to be zero.
Apply Kirchoff’s current law at the node C i.e. the sum of all outgoing (or incoming) current is zero.
Also, current $I = \dfrac{{PD}}{R}$ where $PD$ is the potential difference between any two points and $R$ is the resistance between these two points. Remember current flows from higher potential to lower potential.
Complete step-by-step solution:-
The Kirchoff’s current law states that the total current entering a junction or a node is equal to the charge leaving the node.
In other words, the algebraic sum of every current entering and leaving the junction has to be zero. This property of Kirchhoff law is commonly called Conservation of charge.
Now, in the question we are asked to find the potential difference between A and C.
For this, we have to first calculate the absolute potential of point A and point C.
As the voltage of the battery is given as $100V$ and the positive terminal is connected to point A.
So let us take ${V_A} = 110V$ and ${V_B} = 0$
We know that the current flows from higher potential to lower potential. Also, current $I = \dfrac{{PD}}{R}$ where $PD$ is the potential difference between any two points and $R$ is the resistance between these two points.
Therefore we first calculate equivalent resistance between A and C
$40\Omega $ and $20\Omega $ are in series which gives $40\Omega + 20\Omega = 60\Omega $ which is again parallel with $60\Omega $.
So, ${R_{AC}} = \dfrac{{60}}{2} = 30\Omega $ and ${R_{AB}} = 20\Omega $
Now in order to find the potential of point C, we apply Kirchoff’s current law at the node C i.e. the sum of all outgoing (you can also take incoming) current is zero.
$\dfrac{{{V_C} - {V_A}}}{{{R_{AC}}}} + \dfrac{{{V_C} - {V_B}}}{{{R_{AB}}}} = 0$
On substituting the values we have
$\dfrac{{{V_C} - 110}}{{30}} + \dfrac{{{V_C} - 0}}{{20}} = 0$
On simplifying the equation we get
${V_C} = 44\Omega $
Hence, the potential difference between A and C
${V_C} - {V_A} = 110V - 44V = 66V$ . This is the final answer.
Note:- Kirchhoff’s Current Law is also known as Kirchhoff’s First Law or Kirchhoff’s Junction Rule. According to the Junction rule the algebraic sum of the currents into a junction is equal to the sum of currents outside the junction.
The term Node or a junction is just a connection of two or more conductors like cables and other components. Kirchhoff’s current law can also be used to analyze parallel circuits.
Apply Kirchoff’s current law at the node C i.e. the sum of all outgoing (or incoming) current is zero.
Also, current $I = \dfrac{{PD}}{R}$ where $PD$ is the potential difference between any two points and $R$ is the resistance between these two points. Remember current flows from higher potential to lower potential.
Complete step-by-step solution:-
The Kirchoff’s current law states that the total current entering a junction or a node is equal to the charge leaving the node.
In other words, the algebraic sum of every current entering and leaving the junction has to be zero. This property of Kirchhoff law is commonly called Conservation of charge.
Now, in the question we are asked to find the potential difference between A and C.
For this, we have to first calculate the absolute potential of point A and point C.
As the voltage of the battery is given as $100V$ and the positive terminal is connected to point A.
So let us take ${V_A} = 110V$ and ${V_B} = 0$
We know that the current flows from higher potential to lower potential. Also, current $I = \dfrac{{PD}}{R}$ where $PD$ is the potential difference between any two points and $R$ is the resistance between these two points.
Therefore we first calculate equivalent resistance between A and C
$40\Omega $ and $20\Omega $ are in series which gives $40\Omega + 20\Omega = 60\Omega $ which is again parallel with $60\Omega $.
So, ${R_{AC}} = \dfrac{{60}}{2} = 30\Omega $ and ${R_{AB}} = 20\Omega $
Now in order to find the potential of point C, we apply Kirchoff’s current law at the node C i.e. the sum of all outgoing (you can also take incoming) current is zero.
$\dfrac{{{V_C} - {V_A}}}{{{R_{AC}}}} + \dfrac{{{V_C} - {V_B}}}{{{R_{AB}}}} = 0$
On substituting the values we have
$\dfrac{{{V_C} - 110}}{{30}} + \dfrac{{{V_C} - 0}}{{20}} = 0$
On simplifying the equation we get
${V_C} = 44\Omega $
Hence, the potential difference between A and C
${V_C} - {V_A} = 110V - 44V = 66V$ . This is the final answer.
Note:- Kirchhoff’s Current Law is also known as Kirchhoff’s First Law or Kirchhoff’s Junction Rule. According to the Junction rule the algebraic sum of the currents into a junction is equal to the sum of currents outside the junction.
The term Node or a junction is just a connection of two or more conductors like cables and other components. Kirchhoff’s current law can also be used to analyze parallel circuits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




