
What is the IUPAC name for the amide whose common name is acetamide ?
(A) Methylamide
(B) Ethanamide
(C) Ethylamine
(D) Ethanamide
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: Amide is a derivative of the carboxylic acid. So, if we can remember the nomenclature of carboxylic acid it makes us easy to remember the nomenclature of amide, whether it may by IUPAC name or common name.
Complete Solution :
Amide is one of the derivatives of carboxylic acid.
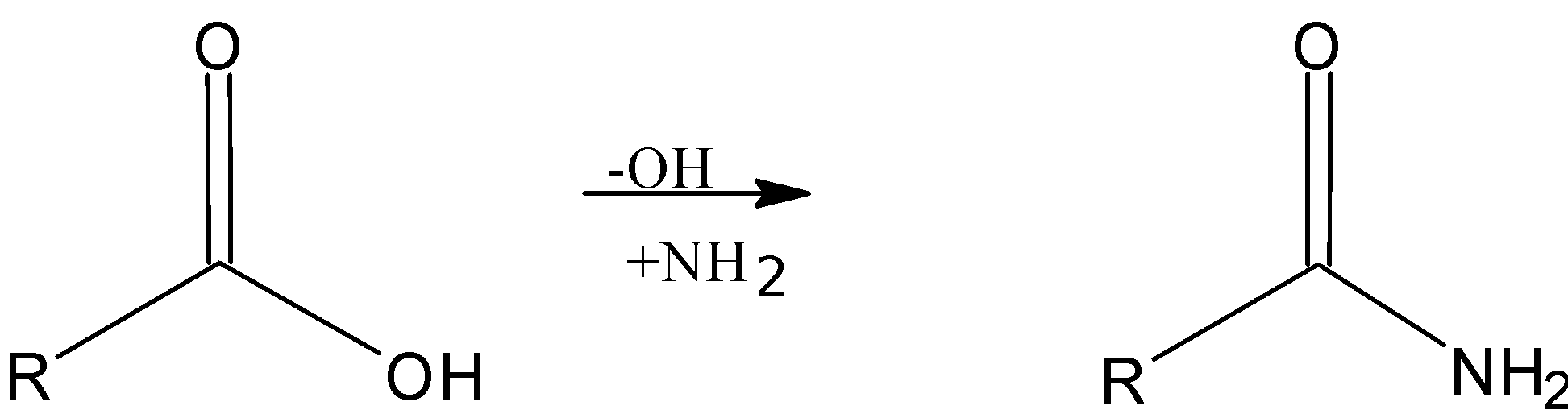
Here we can observe that the -OH function of the -COOH group has been replaced by an amino group -$N{{H}_{2}}$ are called amides.
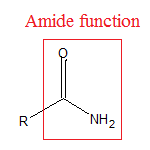
- The -$CON{{H}_{2}}$ is the amide function or the amide group.
Firstly let's know the IUPAC nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
The final -e of the name of the alkane corresponding to the longest chain in the acid and adding -oic acid.
For example:
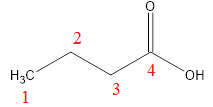
IUPAC name - Butanoic acid
- Now, let's see the IUPAC nomenclature of amides
In the IUPAC system the ending -e of the parent hydrocarbon is replaced by amide. Just like the nomenclature of carboxylic acid.
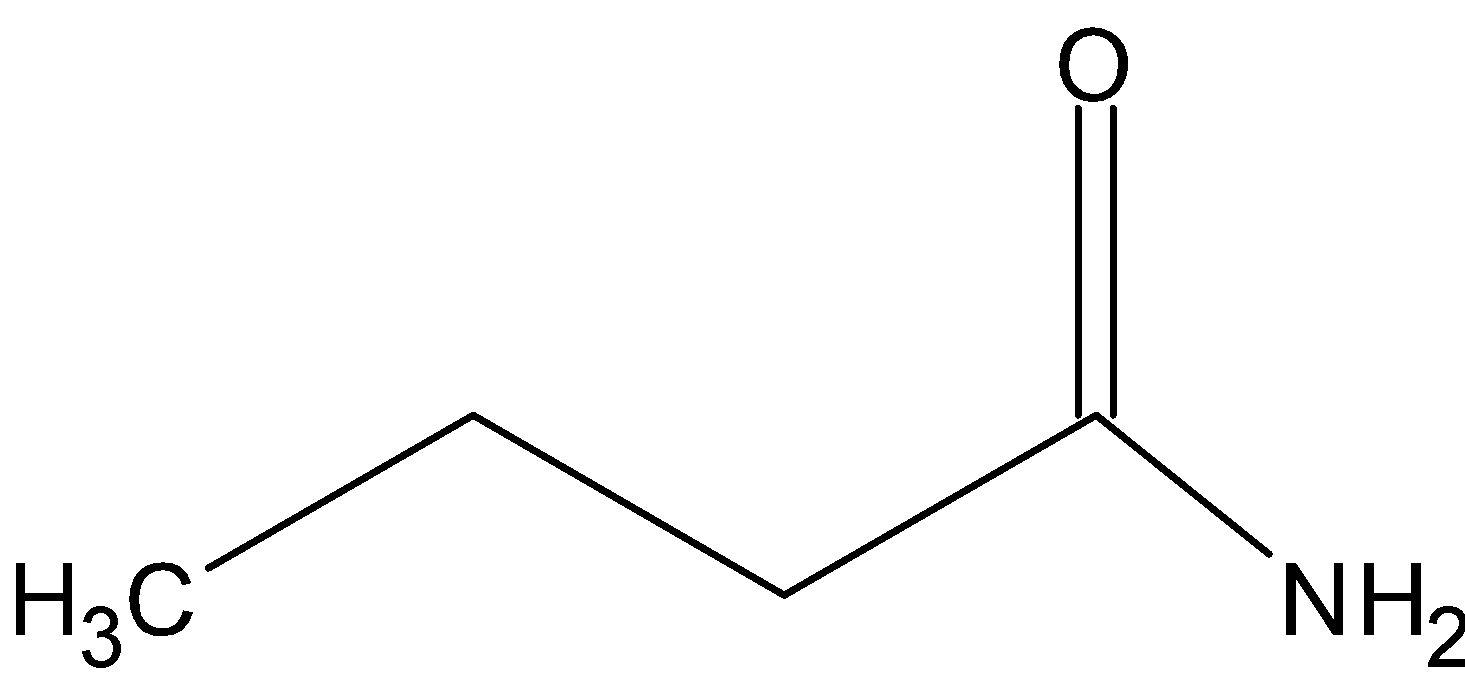
IUPAC name - Butanamide
Common name $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
Their names are derived from the common name of the corresponding parent carboxylic acid by dropping the suffix 'ic acid' and adding amide. The common name of carboxylic acid does not have any particular pattern to follow.
The common names of carboxylic acid and amides are:
From this above table, we write the structure of acetamide and follow by naming it according to the above discussion.
Acetamide - $C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}$
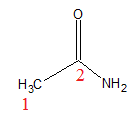
According to IUPAC norms, the ending -e of the parent hydrocarbon is replaced by amide.
So, Ethane has two carbon.
IUPAC name of acetamide is Ethanamide.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Remember the IUPAC nomenclature of carboxylic thoroughly because it may help us remember the pattern of all of its derivatives. The carboxylic derivatives are acid chloride, acid anhydride, amide, and ester. Just depending on the function the ending may change. For common names only carboxylic acid and amide have almost the same naming.
Complete Solution :
Amide is one of the derivatives of carboxylic acid.

Here we can observe that the -OH function of the -COOH group has been replaced by an amino group -$N{{H}_{2}}$ are called amides.

- The -$CON{{H}_{2}}$ is the amide function or the amide group.
Firstly let's know the IUPAC nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
The final -e of the name of the alkane corresponding to the longest chain in the acid and adding -oic acid.
For example:

IUPAC name - Butanoic acid
- Now, let's see the IUPAC nomenclature of amides
In the IUPAC system the ending -e of the parent hydrocarbon is replaced by amide. Just like the nomenclature of carboxylic acid.

IUPAC name - Butanamide
Common name $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
Their names are derived from the common name of the corresponding parent carboxylic acid by dropping the suffix 'ic acid' and adding amide. The common name of carboxylic acid does not have any particular pattern to follow.
The common names of carboxylic acid and amides are:
| S.No | Carboxylic acid | Amide | ||
| 1 | Formic acid | HCOOH | Formamide | HCO$N{{H}_{2}}$ |
| 2 | Acetic acid | $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ | Acetamide | $C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}$ |
| 3 | Propanoic acid | $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH$ | Propionamide | $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}$ |
| 4 | Butyric acid | $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH$ | Butyramide | $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}$ |
From this above table, we write the structure of acetamide and follow by naming it according to the above discussion.
Acetamide - $C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}$

According to IUPAC norms, the ending -e of the parent hydrocarbon is replaced by amide.
So, Ethane has two carbon.
IUPAC name of acetamide is Ethanamide.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Remember the IUPAC nomenclature of carboxylic thoroughly because it may help us remember the pattern of all of its derivatives. The carboxylic derivatives are acid chloride, acid anhydride, amide, and ester. Just depending on the function the ending may change. For common names only carboxylic acid and amide have almost the same naming.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




