
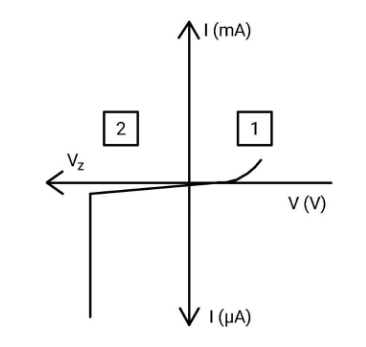
In this I-V characteristic curve of a Zener diode, regions 1 and 2 respectively indicate
A. forward bias and reverse bias regions
B. reverse bias and forward bias regions
C. forward bias regions only
D. reverse bias regions only

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: A Zener diode is a diode which allows the current to flow in the opposite/backward direction when the reverse voltage is reached. Consider the behavior of Zener diodes in both forward and reverse biasing.
Complete answer:
In the forward bias, the behavior of the Zener diode is ordinary like a silicon diode. In reverse bias, when the reverse bias voltage is greater than a particular voltage, the breakdown of the Zener voltage occurs, denoted by ${V_Z}$. The reverse current suddenly increases at a certain value of reverse voltage. According to this, we can conclude that region 1 represents the forward bias which is a normal behaviour and region 2 represents the reverse bias condition where the breakdown occurs.
Hence, in this I-V characteristic curve of a Zener diode, regions 1 and 2 respectively indicate forward bias and reverse bias regions.
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Additional information:
Zener diodes are usually used in the reverse bias, meaning anode to the negative and cathode to the positive side of the voltage source. A large change in the reverse current brings a slight change in the breakdown voltage.
Note: The breakdown voltage/Zener voltage remains almost constant, variations are negligible. The Zener diode can be used in another way. This constant voltage can be applied across a load. Remember the changes in ${V_Z}$ is negligible and ${V_Z}$ is not constant.
Complete answer:
In the forward bias, the behavior of the Zener diode is ordinary like a silicon diode. In reverse bias, when the reverse bias voltage is greater than a particular voltage, the breakdown of the Zener voltage occurs, denoted by ${V_Z}$. The reverse current suddenly increases at a certain value of reverse voltage. According to this, we can conclude that region 1 represents the forward bias which is a normal behaviour and region 2 represents the reverse bias condition where the breakdown occurs.
Hence, in this I-V characteristic curve of a Zener diode, regions 1 and 2 respectively indicate forward bias and reverse bias regions.
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Additional information:
Zener diodes are usually used in the reverse bias, meaning anode to the negative and cathode to the positive side of the voltage source. A large change in the reverse current brings a slight change in the breakdown voltage.
Note: The breakdown voltage/Zener voltage remains almost constant, variations are negligible. The Zener diode can be used in another way. This constant voltage can be applied across a load. Remember the changes in ${V_Z}$ is negligible and ${V_Z}$ is not constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




