
In the following reaction,
${C_2}{H_2}\xrightarrow[{HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}}]{{{H_2}O}}X \rightleftharpoons C{H_3}CHO$
What is $X$ ?
(a) \[C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\]
(b) ${H_3} - O - C{H_3}$
(c) $C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$
(d) $C{H_2} = CHOH$
Answer
553.5k+ views
Hint: The reactant alkyne reacts with ${H_2}O$ in presence of \[HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}\] and forms a product. So, we have to think about the reaction in which alkyne reacts with ${H_2}O$ in presence of \[HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}\] and then tautomerism because the compound ( $ \rightleftharpoons $ this sign shows that this compound is tautomerising itself) is changing itself.
Complete answer:
So, we have to start with the reaction in which alkyne reacts with ${H_2}O$ in presence of \[HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}\]. So, that reaction is Alkyne Hydration.
Alkyne hydration:
So, we try to learn these reaction with an example,
So, let’s take an example,
$C{H_3} - C \equiv C - H + {H_2}O \to C{H_3}COC{H_3}$
Mechanism:
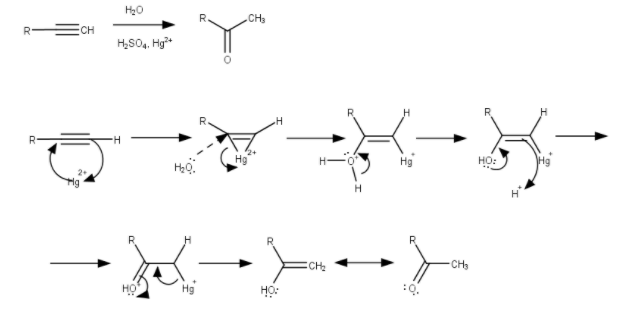
So, in case of unsymmetrical alkynes, the addition of water in the alkyne in according to the Markovnikov’s Rule, which states that the $O - $ atom will attach with the carbon having less number of $H - $ atoms and the two $H - $ atoms will attach with the carbon having greater number of $H - $ atoms.
But In these cases, the alkyne is symmetric.
So, we don’t have to follow any Markovnikov’s Rule,
And the reaction will be,
$H - C \equiv C - H\xrightarrow[{HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}}]{{{H_2}O}}C{H_3}CHO$
Now, the $C{H_3}CHO$ will tautomerise itself,
So, let’s talk about tautomerism,
Tautomerism: When an aldehyde having one hydrogen atom, adjacent to the carbonyl group (i.e, \[\alpha \] carbon), this hydrogen can move to the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group and the double bond between the carbonyl group is shifted to the adjacent to the carbonyl group (i.e, \[\alpha \] carbon). This type of movement of bonds is called tautomerism and the compounds are called tautomers.
So, $C{H_3}CHO$ will tautomerise itself as
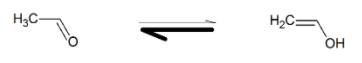
Hence, the complete reaction will be
${C_2}{H_2}\xrightarrow[{HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}}]{{{H_2}O}}C{H_2} = CHOH \rightleftharpoons C{H_3}CHO$
Hence, the correct option is (D) $LiF$.
Note: While alkyne is reacting with ${H_2}O$ in presence of \[HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}\] , we have to use the Markovnikov’s Rule when the alkyne is un-symmetric and when \[\alpha \] carbon is present, we must have to think once about the tautomerism.
Complete answer:
So, we have to start with the reaction in which alkyne reacts with ${H_2}O$ in presence of \[HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}\]. So, that reaction is Alkyne Hydration.
Alkyne hydration:
So, we try to learn these reaction with an example,
So, let’s take an example,
$C{H_3} - C \equiv C - H + {H_2}O \to C{H_3}COC{H_3}$
Mechanism:

So, in case of unsymmetrical alkynes, the addition of water in the alkyne in according to the Markovnikov’s Rule, which states that the $O - $ atom will attach with the carbon having less number of $H - $ atoms and the two $H - $ atoms will attach with the carbon having greater number of $H - $ atoms.
But In these cases, the alkyne is symmetric.
So, we don’t have to follow any Markovnikov’s Rule,
And the reaction will be,
$H - C \equiv C - H\xrightarrow[{HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}}]{{{H_2}O}}C{H_3}CHO$
Now, the $C{H_3}CHO$ will tautomerise itself,
So, let’s talk about tautomerism,
Tautomerism: When an aldehyde having one hydrogen atom, adjacent to the carbonyl group (i.e, \[\alpha \] carbon), this hydrogen can move to the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group and the double bond between the carbonyl group is shifted to the adjacent to the carbonyl group (i.e, \[\alpha \] carbon). This type of movement of bonds is called tautomerism and the compounds are called tautomers.
So, $C{H_3}CHO$ will tautomerise itself as

Hence, the complete reaction will be
${C_2}{H_2}\xrightarrow[{HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}}]{{{H_2}O}}C{H_2} = CHOH \rightleftharpoons C{H_3}CHO$
Hence, the correct option is (D) $LiF$.
Note: While alkyne is reacting with ${H_2}O$ in presence of \[HgS{O_4}/{H_2}S{O_4}\] , we have to use the Markovnikov’s Rule when the alkyne is un-symmetric and when \[\alpha \] carbon is present, we must have to think once about the tautomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




