
In the following electron dot structure, calculate the formal charge from left to right nitrogen atom (shown)
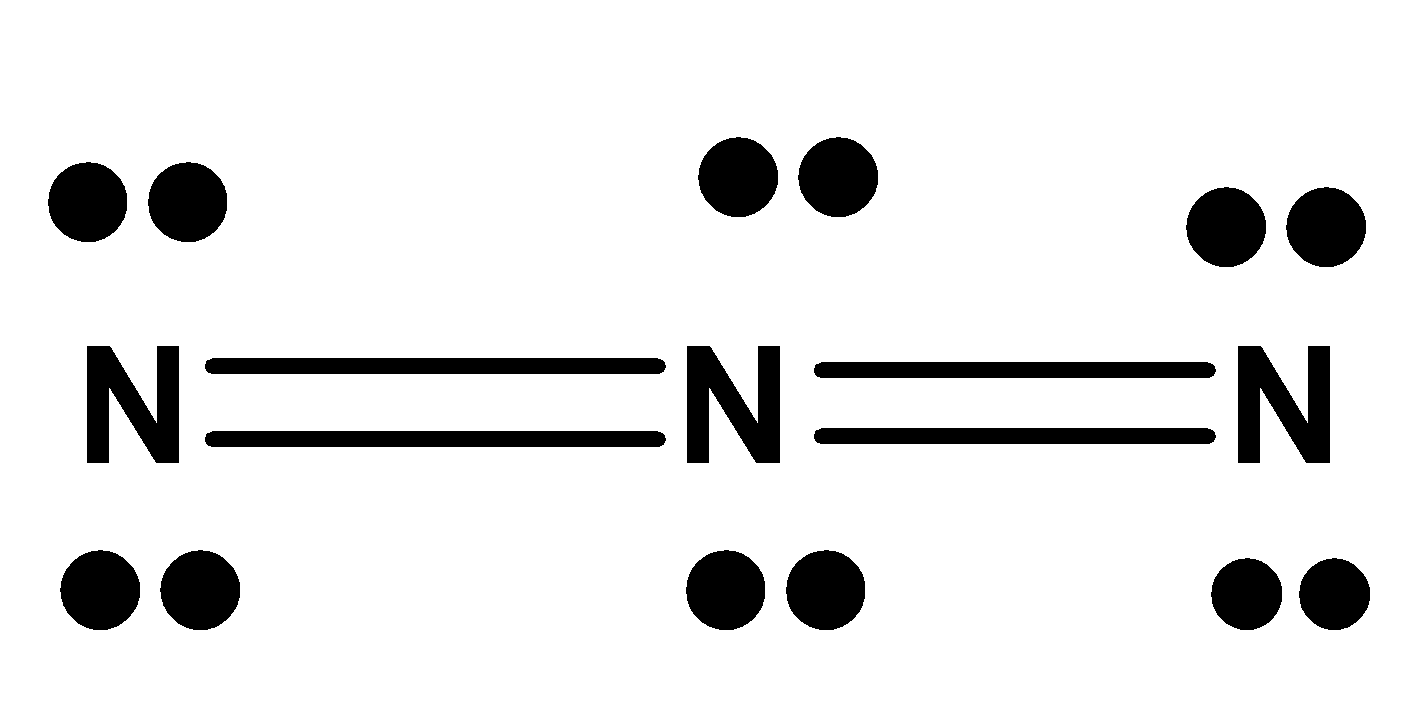

A. ${{ - 1, - 1, + 1}}$
B.\[{{ - 1, + 1, - 1}}\]
C.${{ + 1, - 1, - 1}}$
D.${{ + 1, - 1, + 1}}$


Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:Charge assigned to an atom in a molecule is the formal charge. It is also called a fake charge. We know that when an atom gives away its electrons, it gains a positive charge, and when an atom accepts electrons, it gains a negative charge. Even if it is a neutral molecule, the atom may possess a charge.
Complete step by step answer:
-The formal charge can be calculated by the formula:-
\[\text{formal charge = valence electrons - Non bonding valence electrons - }\dfrac{{{{bonding electrons}}}}{{{2}}}\]
-Let us take a simple example to understand this.
-In ${{C}}{{{H}}_{{4}}}$,
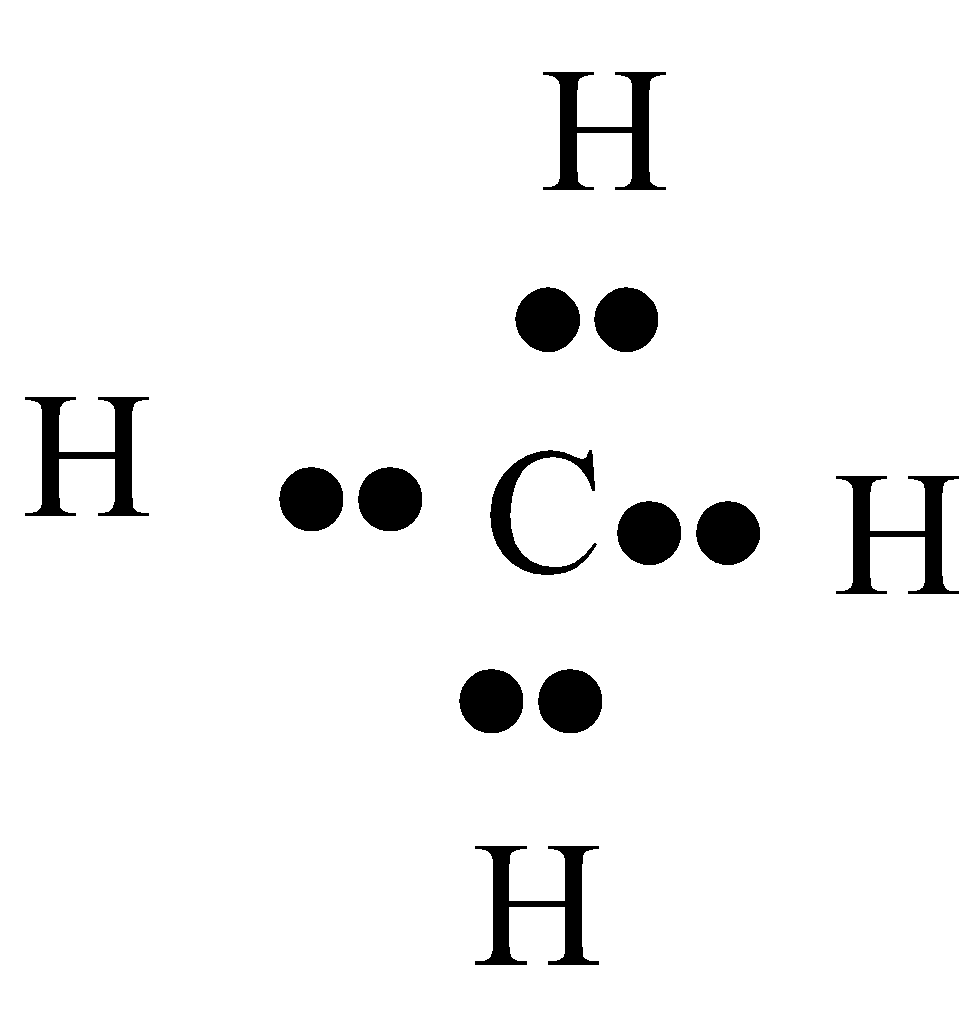 , let us find the formal charge by using the above-mentioned formula. The valence electrons in Carbon is 4. All the 4 valence electrons of carbon in methane are bonded. Thus, there are no nonbonding electrons. The bonding electrons are 8.
, let us find the formal charge by using the above-mentioned formula. The valence electrons in Carbon is 4. All the 4 valence electrons of carbon in methane are bonded. Thus, there are no nonbonding electrons. The bonding electrons are 8.
-On giving these values in the equation,
${{F}}{{.C of C = 4 - 0 - }}\dfrac{8}{{{2}}}$
${{F}}{{.C = 0}}$
-So now let us look at
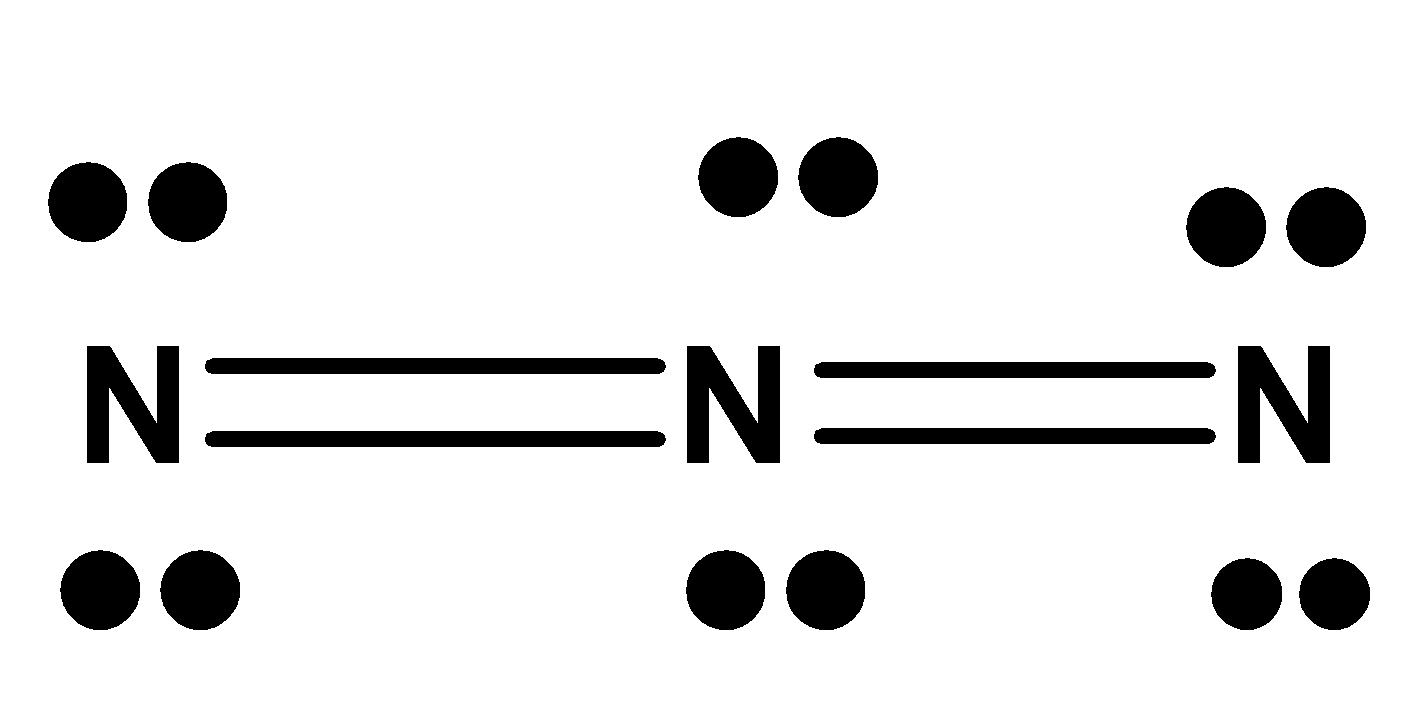
-Let the nitrogen in the left end be considered first.
The valence electrons in Nitrogen is 5. The non-bonding electrons are 4. The bonding electrons are 4.
-On substituting these values to the formal charge formula
${{F}}{{.C = 5 - 4 - }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{ F}}{{.C = - 1}}$
It is the same for the rightmost nitrogen atom.
-On checking the formal charge on the middle nitrogen, the valence electrons on nitrogen as we know is 5. The non-bonding electrons present here is 0 because the octet is satisfied here in the middle nitrogen. The bonding electrons are 8.
${{F}}{{.C = 5 - 0 - }}\dfrac{8}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {{ F}}{{.C = 1}}$
Therefore, the formal charge is in the order ${{ - 1, + 1, - 1}}$
The correct answer is option (B).
Note:
Formal charge helps to find the electrons in a molecule, whether it has more electrons or protons associated with it. In some molecules in which resonance structures are possible, the resonance structure which has the least number of atoms with a non-zero formal charge would be preferred. The lower formal charge would be favored than one with a high formal charge.
Complete step by step answer:
-The formal charge can be calculated by the formula:-
\[\text{formal charge = valence electrons - Non bonding valence electrons - }\dfrac{{{{bonding electrons}}}}{{{2}}}\]
-Let us take a simple example to understand this.
-In ${{C}}{{{H}}_{{4}}}$,

-On giving these values in the equation,
${{F}}{{.C of C = 4 - 0 - }}\dfrac{8}{{{2}}}$
${{F}}{{.C = 0}}$
-So now let us look at

-Let the nitrogen in the left end be considered first.
The valence electrons in Nitrogen is 5. The non-bonding electrons are 4. The bonding electrons are 4.
-On substituting these values to the formal charge formula
${{F}}{{.C = 5 - 4 - }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{ F}}{{.C = - 1}}$
It is the same for the rightmost nitrogen atom.
-On checking the formal charge on the middle nitrogen, the valence electrons on nitrogen as we know is 5. The non-bonding electrons present here is 0 because the octet is satisfied here in the middle nitrogen. The bonding electrons are 8.
${{F}}{{.C = 5 - 0 - }}\dfrac{8}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {{ F}}{{.C = 1}}$
Therefore, the formal charge is in the order ${{ - 1, + 1, - 1}}$
The correct answer is option (B).
Note:
Formal charge helps to find the electrons in a molecule, whether it has more electrons or protons associated with it. In some molecules in which resonance structures are possible, the resonance structure which has the least number of atoms with a non-zero formal charge would be preferred. The lower formal charge would be favored than one with a high formal charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




