
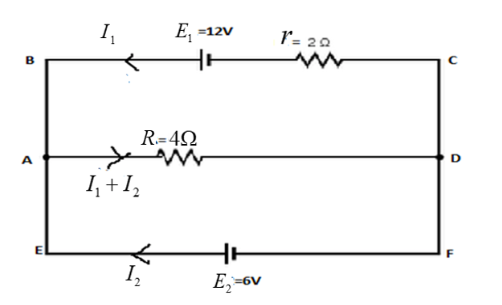
In the electric network shown in the figure, use Kirchhoff’s rules to calculate the power consumed by the resistance$R = 4\Omega $

Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint:Ohm’s law gives current-voltage relation in simple electrical circuits. But when the circuit is complicated, it will be difficult to find the current distribution by ohm’s law. Kirchhoff’s formulated the two laws which enable us to find the distribution of current in complicated electrical circuits.
Complete step by step answer:
Kirchhoff’s first law is also called junction law or current law. it states that, at any junction, the sum of the currents entering the junction is equal to the sum of current leaving the junction.
Mathematically it is represented as,$\sum {I = 0} $
Kirchhoff’s second law is also called loop law or voltage law. It says that the algebraic sum of changes in potential around any closed loop involving resistors and cells in the loop is zero.
Mathematically represented as, $\sum {V = 0} $ or$\sum {\left( {IR} \right)} + \sum {E = 0} $
Now in this problem we will be using Kirchhoff’s second law for solving the given circuit.
For loop ABCDA, apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law,
$ \Rightarrow - 12 + 2{I_1} + 4\left( {{I_1} + {I_2}} \right) = 0$
We can simplify the given equations we get,
$ \Rightarrow 3{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 6$ ………………………(!)
For loop AREA, apply Kirchhoff’s voltage rule, we get
$ \Rightarrow - 4\left( {{I_1} + {I_2}} \right) + 6 = 0$
We can simplify the given equations we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 3$……………………(2)
Subtract equation (1) and (2) we get
$
3{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 6 \\
\left( - \right) \\
2{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 3 \\
$
Now we have,$ \Rightarrow {I_1} = 3A$
Next to find ${I_2}$substitute the value of${I_1}$ in equation (1) we get
$ \Rightarrow 3{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 6$
We can substitute the value of ${I_1}$ in the given equation, we get.
$ \Rightarrow 3 \times 3 + 2{I_2} = 6$
Solving the above equation,
$ \Rightarrow 2{I_2} = 6 - 9$
$ \Rightarrow {I_2} = - \dfrac{3}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow - 1.5A$
Total amount of current flowing in the circuit is given by,
$ \Rightarrow I = {I_1} + {I_2}$
$ \Rightarrow I = 3 - 1.5$
$ \Rightarrow 1.5A$
Hence, power consumed by the resistor is given by,
$P = {I^2}R$
Substitute the given values we get,
$ \Rightarrow P = {\left( {1.5} \right)^2} \times 4$
$\therefore P = 9W$
$\therefore $ The power consumed by the resistance$R = 4\Omega $ is 9W.
Note: Sign conventions for Kirchhoff’s second law:
-The change in potential in traversing a resistance in the direction of current is$ - IR$ while in the opposite direction$ + IR$.
-The change in voltage in traversing an emf source from negative to positive is \[ + e\] while in the opposite direction \[-e\] irrespective of the direction of current in the circuit.
-Kirchhoff’s second law follows the principle of conservation of energy.
Complete step by step answer:
Kirchhoff’s first law is also called junction law or current law. it states that, at any junction, the sum of the currents entering the junction is equal to the sum of current leaving the junction.
Mathematically it is represented as,$\sum {I = 0} $
Kirchhoff’s second law is also called loop law or voltage law. It says that the algebraic sum of changes in potential around any closed loop involving resistors and cells in the loop is zero.
Mathematically represented as, $\sum {V = 0} $ or$\sum {\left( {IR} \right)} + \sum {E = 0} $
Now in this problem we will be using Kirchhoff’s second law for solving the given circuit.
For loop ABCDA, apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law,
$ \Rightarrow - 12 + 2{I_1} + 4\left( {{I_1} + {I_2}} \right) = 0$
We can simplify the given equations we get,
$ \Rightarrow 3{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 6$ ………………………(!)
For loop AREA, apply Kirchhoff’s voltage rule, we get
$ \Rightarrow - 4\left( {{I_1} + {I_2}} \right) + 6 = 0$
We can simplify the given equations we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 3$……………………(2)
Subtract equation (1) and (2) we get
$
3{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 6 \\
\left( - \right) \\
2{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 3 \\
$
Now we have,$ \Rightarrow {I_1} = 3A$
Next to find ${I_2}$substitute the value of${I_1}$ in equation (1) we get
$ \Rightarrow 3{I_1} + 2{I_2} = 6$
We can substitute the value of ${I_1}$ in the given equation, we get.
$ \Rightarrow 3 \times 3 + 2{I_2} = 6$
Solving the above equation,
$ \Rightarrow 2{I_2} = 6 - 9$
$ \Rightarrow {I_2} = - \dfrac{3}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow - 1.5A$
Total amount of current flowing in the circuit is given by,
$ \Rightarrow I = {I_1} + {I_2}$
$ \Rightarrow I = 3 - 1.5$
$ \Rightarrow 1.5A$
Hence, power consumed by the resistor is given by,
$P = {I^2}R$
Substitute the given values we get,
$ \Rightarrow P = {\left( {1.5} \right)^2} \times 4$
$\therefore P = 9W$
$\therefore $ The power consumed by the resistance$R = 4\Omega $ is 9W.
Note: Sign conventions for Kirchhoff’s second law:
-The change in potential in traversing a resistance in the direction of current is$ - IR$ while in the opposite direction$ + IR$.
-The change in voltage in traversing an emf source from negative to positive is \[ + e\] while in the opposite direction \[-e\] irrespective of the direction of current in the circuit.
-Kirchhoff’s second law follows the principle of conservation of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




