
In the circuit shown below, ${V_A}$and ${V_B}$ are the potential at A and B, R is the equivalent resistance between A and B, ${S_1}$and ${S_2}$ are switches, and the diodes are ideal
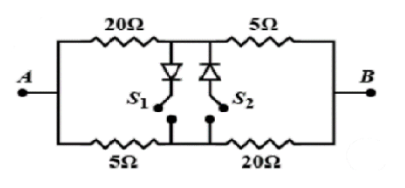
A) If ${V_A} > {V_B}$, ${S_1}$ is open and ${S_2}$is closed then $R = 8\Omega $
B) If ${V_A} > {V_B}$, ${S_1}$ is closed and ${S_2}$is open then $R = 12.5\Omega $
C) If ${V_A} > {V_B}$, ${S_1}$ is open and ${S_2}$is closed then $R = 12.5\Omega $
D) If ${V_A} > {V_B}$, ${S_1}$ is closed and ${S_2}$is open then $R = 8\Omega $

Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint:An electric circuit and each component of the circuit are known as an element. The given circuit is connected from the resistance values $20\Omega $ and$5\Omega $.
The ideal diodes are connected from the ${S_{1{\text{ }}}}{\text{and }}{S_2}$ switches.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given ${V_A} > {V_B},$so current flows from A to B.
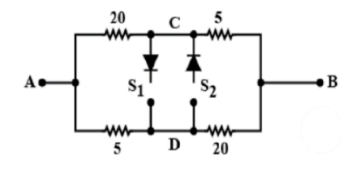
From the below figure when ${S_1}$ is open and ${S_2}$is closed
-The diode at ${S_2}$passes current only from D to C else zero current.
-If the current passes through the diode the voltage will be equal to D and C.
Let us assume that the D and C voltages are equal. Now we can short the ${S_2}$part.
Now in the equivalent circuit as$20\Omega > 5\Omega $current flows from D to C.
So it is satisfying the diode property.
Our circuit equivalent circuit will be the above circuit.
So the equivalent resistance $ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{20}} + \dfrac{1}{5}} \right)}}\Omega $
Here we have to take an LCM on the denominator term we get
$ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{{1 + 4}}{{20}}} \right)}}\Omega $
Let us add the term we get
$ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{5}{{20}}} \right)}}\Omega $
On dividing the term we get
$ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{4}} \right)}}\Omega $
Taking reciprocal of the numerator term and multiply it we get,
$ = 8\Omega $
Now,${S_1}$ is closed and ${S_2}$is open
-The diode at ${S_1}$passes current only from C to D or else zero current.
- If current passes through the diode the voltage will be equal to D and C.
-Let us assume that the D and C voltage is equal. Now in the equivalent circuit as $20\Omega {\text{ > }}5\Omega $current has to flow from D to C. From D to C current does not allow. So our assumption is wrong.
We have to treat ${S_1}$as open.
The equivalent resistance is $ = \dfrac{{20 + 5}}{2}\Omega $
On adding the numerator term we get
$ = \dfrac{{25}}{2}\Omega $
Let us divide the term we get
$ = 12.5\Omega $
Additional information:
Potential difference, when the current flows between two points A and B of an electric circuit.
Where the aggregate resistance connected either in parallel or series is calculated, it is called equivalent resistance. Essentially, either in Series or Parallel is designed in the circuit
Note: A diode that acts like a perfect conductor, ideal diodes, when voltage is applied forward biased and like a perfect insulator, when voltage is applied reverse biased.
So the anode to the cathode when the positive voltage is applied across, the diode conducts forward current instantly.
The ideal diodes are connected from the ${S_{1{\text{ }}}}{\text{and }}{S_2}$ switches.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given ${V_A} > {V_B},$so current flows from A to B.
From the below figure when ${S_1}$ is open and ${S_2}$is closed
-The diode at ${S_2}$passes current only from D to C else zero current.
-If the current passes through the diode the voltage will be equal to D and C.
Let us assume that the D and C voltages are equal. Now we can short the ${S_2}$part.
Now in the equivalent circuit as$20\Omega > 5\Omega $current flows from D to C.
So it is satisfying the diode property.
Our circuit equivalent circuit will be the above circuit.
So the equivalent resistance $ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{20}} + \dfrac{1}{5}} \right)}}\Omega $
Here we have to take an LCM on the denominator term we get
$ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{{1 + 4}}{{20}}} \right)}}\Omega $
Let us add the term we get
$ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{5}{{20}}} \right)}}\Omega $
On dividing the term we get
$ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{4}} \right)}}\Omega $
Taking reciprocal of the numerator term and multiply it we get,
$ = 8\Omega $
Now,${S_1}$ is closed and ${S_2}$is open
-The diode at ${S_1}$passes current only from C to D or else zero current.
- If current passes through the diode the voltage will be equal to D and C.
-Let us assume that the D and C voltage is equal. Now in the equivalent circuit as $20\Omega {\text{ > }}5\Omega $current has to flow from D to C. From D to C current does not allow. So our assumption is wrong.
We have to treat ${S_1}$as open.
The equivalent resistance is $ = \dfrac{{20 + 5}}{2}\Omega $
On adding the numerator term we get
$ = \dfrac{{25}}{2}\Omega $
Let us divide the term we get
$ = 12.5\Omega $
Additional information:
Potential difference, when the current flows between two points A and B of an electric circuit.

Where the aggregate resistance connected either in parallel or series is calculated, it is called equivalent resistance. Essentially, either in Series or Parallel is designed in the circuit
Note: A diode that acts like a perfect conductor, ideal diodes, when voltage is applied forward biased and like a perfect insulator, when voltage is applied reverse biased.
So the anode to the cathode when the positive voltage is applied across, the diode conducts forward current instantly.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




