
If OP = r, d.c’s of \[\overrightarrow{OP}\] are l, m and n then $P=(lr,mr,nr)$.
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will first write the values of direction cosines in the Cartesian form. After that, we will find the length of line OP which passes through point P ( x, y z ) and origin. After that, we will substitute the value of length OP = r in values of direction cosines and hence obtain the coordinates of P in terms of cosines of line OP.
Complete step-by-step solution
Before we solve this question, let us see what direction cosines are.
In three – dimension geometry, we have three axes which are the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis. Now, let us assume that line OP passes through the origin in the three – dimensional space. Then, it is obvious that the line will make an angle each with the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis respectively.
Now, cosines of each of these three angles that the line makes with the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis respectively are called direction cosines of the line in three-dimensional space. In general, these direction cosines are denoted by using letters l, m, and n.
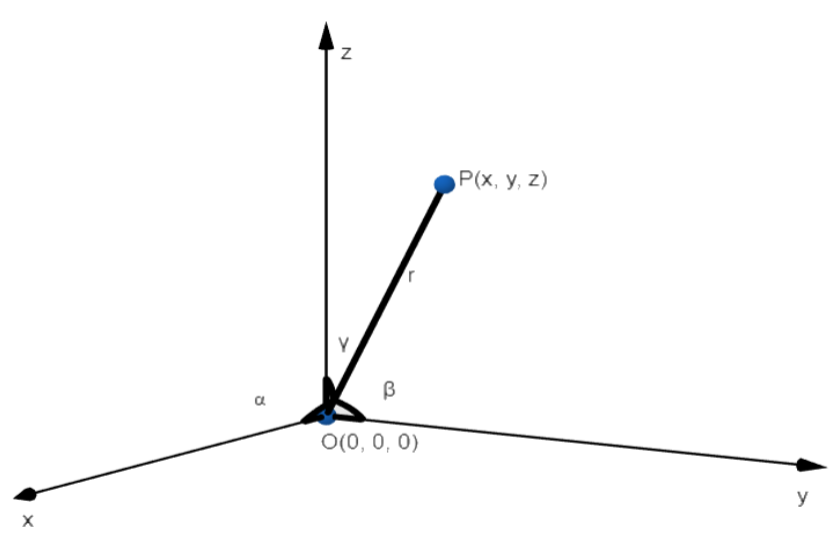
Now, we know that if l, m and n are direction cosines of a line passing through origin to point P(x, y, z), then $l=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$ , $m=\dfrac{y}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$, $n=\dfrac{z}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$
Now as OP passes from O( 0, 0, 0 ) and P( x, y, z )
So, using distance formula
$OP=\sqrt{{{(x-0)}^{2}}+{{(y-0)}^{2}}+{{(z-0)}^{2}}}$
On simplifying, we get
$OP=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$
As, given that OP = r
So, $r=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$
Substituting value of $r=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$ in values of direction cosines, we get
$l=\dfrac{x}{r}$ , $m=\dfrac{y}{r}$, $n=\dfrac{z}{r}$
Multiplying, both sides by r, we get
x = lr, y = mr and z = nr
Now, as (x, y, z ) are the coordinates of point P.
So, P ( lr, mr, nr )
Note: Always remember that if line passes through origin and point P ( x, y, z ) then direction cosines of line OP are equals to $l=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$ , $m=\dfrac{y}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$, $n=\dfrac{z}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$. Also remember that length of line passing through points L( a, b, c ) and M( x, y, z ) is equals to $LM=\sqrt{{{(x-a)}^{2}}+{{(y-b)}^{2}}+{{(z-c)}^{2}}}$. Try not to make any error while solving the question.
Complete step-by-step solution
Before we solve this question, let us see what direction cosines are.
In three – dimension geometry, we have three axes which are the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis. Now, let us assume that line OP passes through the origin in the three – dimensional space. Then, it is obvious that the line will make an angle each with the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis respectively.
Now, cosines of each of these three angles that the line makes with the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis respectively are called direction cosines of the line in three-dimensional space. In general, these direction cosines are denoted by using letters l, m, and n.

Now, we know that if l, m and n are direction cosines of a line passing through origin to point P(x, y, z), then $l=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$ , $m=\dfrac{y}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$, $n=\dfrac{z}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$
Now as OP passes from O( 0, 0, 0 ) and P( x, y, z )
So, using distance formula
$OP=\sqrt{{{(x-0)}^{2}}+{{(y-0)}^{2}}+{{(z-0)}^{2}}}$
On simplifying, we get
$OP=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$
As, given that OP = r
So, $r=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$
Substituting value of $r=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$ in values of direction cosines, we get
$l=\dfrac{x}{r}$ , $m=\dfrac{y}{r}$, $n=\dfrac{z}{r}$
Multiplying, both sides by r, we get
x = lr, y = mr and z = nr
Now, as (x, y, z ) are the coordinates of point P.
So, P ( lr, mr, nr )
Note: Always remember that if line passes through origin and point P ( x, y, z ) then direction cosines of line OP are equals to $l=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$ , $m=\dfrac{y}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$, $n=\dfrac{z}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}}$. Also remember that length of line passing through points L( a, b, c ) and M( x, y, z ) is equals to $LM=\sqrt{{{(x-a)}^{2}}+{{(y-b)}^{2}}+{{(z-c)}^{2}}}$. Try not to make any error while solving the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




