
Hunsdiecker reaction is first notated by _ _ _ _ _ _ in 1961.
A.Borodin
B.Hunsdiecker
C.Clare
D. None of these
Answer
593.1k+ views
HintHunsdiecker reaction is a decarboxylation and halogenation reaction in which silver salts of carboxylic acids are used to form alkyl halides by reacting them with a halogen.
Complete step by step answer
-Hunsdiecker reaction is also known as Borodin reaction.
-It is a name reaction where the silver salts of carboxylic acids are reacted with a halogen to produce an organic halide. In this reaction both decarboxylation (removal of $C{O_2}$) and halogenations (addition of halogen) takes place at the same time.
This reaction is as follows:
$RCO{O^ - }A{g^ + }\xrightarrow[{CC{l_4}}]{{B{r_2}}}R - Br$
-In 1861, Alexander Borodin was the first one to demonstrate this reaction, when he prepared methyl bromide ($C{H_3}Br$) using silver acetate ($C{H_3}CO{O^ - }A{g^ + }$).
$C{H_3}COOAg + B{r_2} \to C{H_3}Br + C{O_2} + AgBr$
But now it is known as Hunsdiecker reaction because this process was developed into a general method for preparation of organic halide by Clare Hunsdiecker and her husband Heinz Hunsdiecker.
-We can say that this is a decarboxylation reaction because the product has 1 less carbon in it as compared to the parent molecules and a carbon dioxide molecule is released. Since a halogen atom is added to it, it is a halogenations reaction.
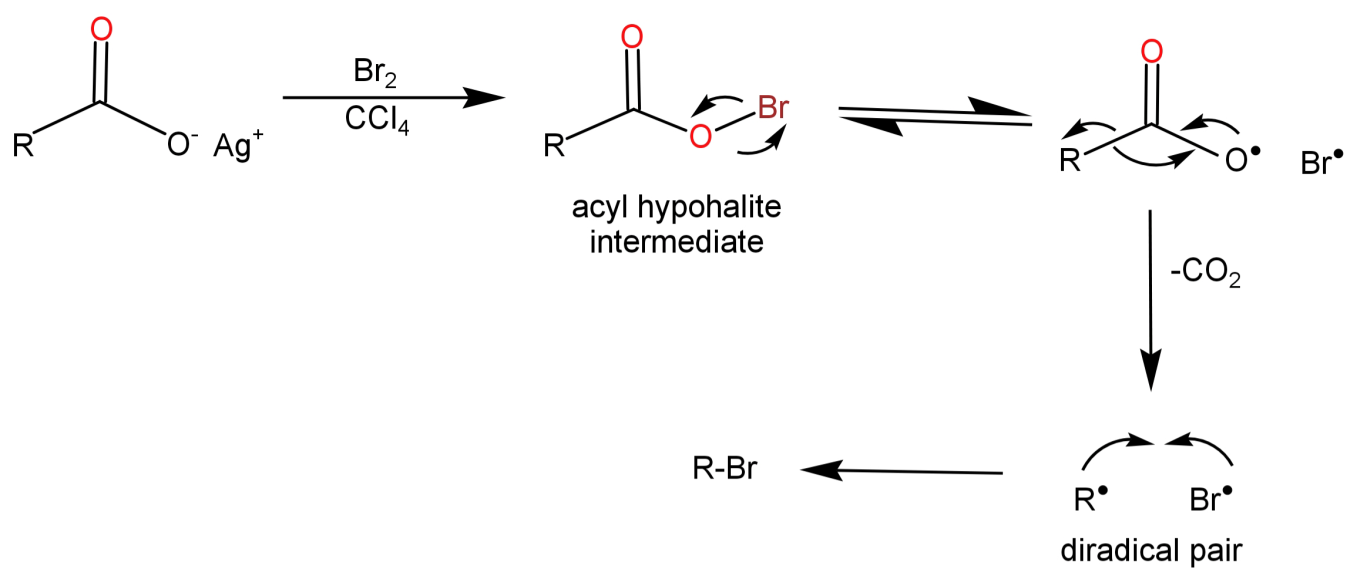
-In this reaction radical intermediates are formed. When the silver salt of carboxylic acid reacts with bromine an acyl hypohalite intermediate is formed. Then the O and Br in this hypohalite intermediate leave each other keeping their own electrons to themselves to form a diradical pair. This is followed by decarboxylation resulting in the formation of R free radical (${R^ \bullet }$) and Br free radical ($B{r^ \bullet }$), which combine quickly with each other to form alkyl halide.
This mechanism is shown below:
So, the correct option is: (A) Borodin.
Note:
Although the reaction is named after Hunsdiecker, they were not the first one to demonstrate this reaction. They made it a general reaction but it was first demonstrated by Borodin. Also if we take carboxylate to iodine (as a halide) ratio of 1:1 then we obtain alkyl halide as product, but if we take them in a ratio of 2:1 we obtain an ester product and for a 3:1 ratio we obtain a mixture of both alkyl halide and an ester.
Complete step by step answer
-Hunsdiecker reaction is also known as Borodin reaction.
-It is a name reaction where the silver salts of carboxylic acids are reacted with a halogen to produce an organic halide. In this reaction both decarboxylation (removal of $C{O_2}$) and halogenations (addition of halogen) takes place at the same time.
This reaction is as follows:
$RCO{O^ - }A{g^ + }\xrightarrow[{CC{l_4}}]{{B{r_2}}}R - Br$
-In 1861, Alexander Borodin was the first one to demonstrate this reaction, when he prepared methyl bromide ($C{H_3}Br$) using silver acetate ($C{H_3}CO{O^ - }A{g^ + }$).
$C{H_3}COOAg + B{r_2} \to C{H_3}Br + C{O_2} + AgBr$
But now it is known as Hunsdiecker reaction because this process was developed into a general method for preparation of organic halide by Clare Hunsdiecker and her husband Heinz Hunsdiecker.
-We can say that this is a decarboxylation reaction because the product has 1 less carbon in it as compared to the parent molecules and a carbon dioxide molecule is released. Since a halogen atom is added to it, it is a halogenations reaction.
-In this reaction radical intermediates are formed. When the silver salt of carboxylic acid reacts with bromine an acyl hypohalite intermediate is formed. Then the O and Br in this hypohalite intermediate leave each other keeping their own electrons to themselves to form a diradical pair. This is followed by decarboxylation resulting in the formation of R free radical (${R^ \bullet }$) and Br free radical ($B{r^ \bullet }$), which combine quickly with each other to form alkyl halide.
This mechanism is shown below:

So, the correct option is: (A) Borodin.
Note:
Although the reaction is named after Hunsdiecker, they were not the first one to demonstrate this reaction. They made it a general reaction but it was first demonstrated by Borodin. Also if we take carboxylate to iodine (as a halide) ratio of 1:1 then we obtain alkyl halide as product, but if we take them in a ratio of 2:1 we obtain an ester product and for a 3:1 ratio we obtain a mixture of both alkyl halide and an ester.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




