
Froth flotation process used for the concentration of sulphide ore:
(This question has multiple correct options)
A. is based on the difference in wettability of different minerals
B. uses sodium ethyl xanthate (${{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{OC}{{\text{S}}_{2}}\text{Na}$) as a collector
C. uses $\text{NaCN}$ as depressant in the mixture of $\text{ZnS}$and $\text{PbS}$ when $\text{ZnS}$ forms soluble complex and $\text{PbS}$ forms froth
D. uses pine oil as frothing agent
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: The term froth flotation needs to be cleared first. Froth flotation is a process for separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. Froth flotation can be easily understood by its diagram:
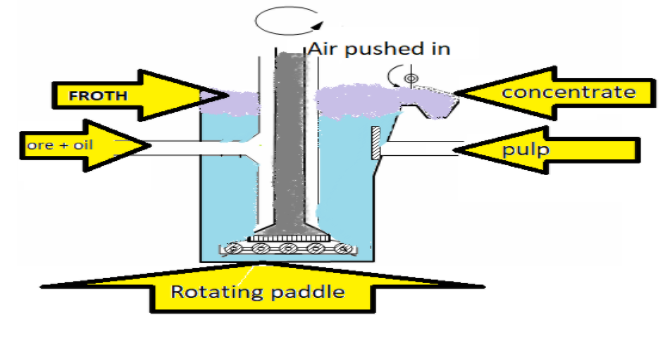
Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss some basic information about froth flotation:
> Principle involved in froth flotation is: A technique used in the mining industry. In this technique, particles required are physically separated from a liquid phase as a result of difference in their ability of air bubbles to adhere to the surface of the particles/materials, based upon their hydrophobicity.
> Pine oil is used in the froth flotation process because of the hydrophobic chemicals due to which it does not have affinity towards water constituents and it attracts impurities so that it can be washed away. In the froth-flotation process, pine oil functions as a foaming agent. Other frothing agents are eucalyptus oil, xanthates. The frothing agent forms froth with air.
> Collectors: Collectors are agents that are used to adsorb onto the surfaces of particles. A monolayer is formed by the collectors on the particle’s surface that makes a thin film of non-polar hydrophobic hydrocarbons. Collectors are a type of reagents that increase the hydrophobicity of the surface, increasing the separability of the repelling and liking particles. Collectors either chemically bond via chemisorption with the mineral or adsorb onto the surface via physisorption. The use of Sodium methyl xanthate (${{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{OC}{{\text{S}}_{2}}\text{Na}$) is used as collector in froth flotation method. The characteristic of methyl xanthates is that they promote the flotation of sulphide minerals; they first attack the surface which is most highly flocculated.
> Froth Stabilizers: During this process, substances are used to stabilize the froth so that they can be easily removed and purified. These substances are froth stabilizers. For example: cresol and aniline.
> Depressants: In the froth floatation process, depressants help in separation of two sulphide ores by prevention of froth formation by one ore and by allowing the other to come into froth. For example, to separate two sulphide ores (ZnS and PbS), NaCN is used as a depressant.
The correct answers are options A, B, C and D.
Additional Information Applications of froth flotation:
(1) This process is used for purification of potassium chloride $\text{(KCl)}$ from sodium chloride $\text{(NaCl)}$.
(2) This process is used in paper recycling, mineral processing and waste-water treatment industries.
Note: Not all types of ores can be obtained by the froth flotation process, only sulphide ores are concentrated by it because pine oil used selectively wets the sulphide ores brings up the froth. The ore gets wet with oil and gangues with the water.

Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss some basic information about froth flotation:
> Principle involved in froth flotation is: A technique used in the mining industry. In this technique, particles required are physically separated from a liquid phase as a result of difference in their ability of air bubbles to adhere to the surface of the particles/materials, based upon their hydrophobicity.
> Pine oil is used in the froth flotation process because of the hydrophobic chemicals due to which it does not have affinity towards water constituents and it attracts impurities so that it can be washed away. In the froth-flotation process, pine oil functions as a foaming agent. Other frothing agents are eucalyptus oil, xanthates. The frothing agent forms froth with air.
> Collectors: Collectors are agents that are used to adsorb onto the surfaces of particles. A monolayer is formed by the collectors on the particle’s surface that makes a thin film of non-polar hydrophobic hydrocarbons. Collectors are a type of reagents that increase the hydrophobicity of the surface, increasing the separability of the repelling and liking particles. Collectors either chemically bond via chemisorption with the mineral or adsorb onto the surface via physisorption. The use of Sodium methyl xanthate (${{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{OC}{{\text{S}}_{2}}\text{Na}$) is used as collector in froth flotation method. The characteristic of methyl xanthates is that they promote the flotation of sulphide minerals; they first attack the surface which is most highly flocculated.
> Froth Stabilizers: During this process, substances are used to stabilize the froth so that they can be easily removed and purified. These substances are froth stabilizers. For example: cresol and aniline.
> Depressants: In the froth floatation process, depressants help in separation of two sulphide ores by prevention of froth formation by one ore and by allowing the other to come into froth. For example, to separate two sulphide ores (ZnS and PbS), NaCN is used as a depressant.
The correct answers are options A, B, C and D.
Additional Information Applications of froth flotation:
(1) This process is used for purification of potassium chloride $\text{(KCl)}$ from sodium chloride $\text{(NaCl)}$.
(2) This process is used in paper recycling, mineral processing and waste-water treatment industries.
Note: Not all types of ores can be obtained by the froth flotation process, only sulphide ores are concentrated by it because pine oil used selectively wets the sulphide ores brings up the froth. The ore gets wet with oil and gangues with the water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




