
Find the position vector of the circumcentre of a triangle whose vertices are \[A\left( {3,2,5} \right),B\left( {3,4,5} \right),C\left( {3,4,7} \right)\].
Answer
519k+ views
Hint: Here, in the question, we have been given vertices of three points of a triangle and we are asked to find the position vector of its circumcentre. We will first calculate the lengths of all sides of the triangle and try to draw it. After that, we will find the circumcentre and its position vector to get the desired result.
Formula used:
Distance between two points \[{P_1}\left( {{x_1},{y_1},{z_1}} \right)\& {P_2}\left( {{x_2},{y_2},{z_2}} \right)\] is calculated by: \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{z_2} - {z_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
Mid-point formula between two points \[{P_1}\left( {{x_1},{y_1},{z_1}} \right)\& {P_2}\left( {{x_2},{y_2},{z_2}} \right)\] is given by: \[\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{z_1} + {z_2}}}{2}} \right)\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given, Three vertices of a triangle, \[A\left( {3,2,5} \right),B\left( {3,4,5} \right),C\left( {3,4,7} \right)\]
Distance between two points \[A\left( {3,2,5} \right),B\left( {3,4,5} \right)\] is given by,
\[AB = \sqrt {\left| {{{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - 2} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {5 - 5} \right)}^2}} \right|} \\
\Rightarrow AB = 2 \]
Distance between two points \[B\left( {3,4,5} \right),C\left( {3,4,7} \right)\] is given by,
\[BC = \sqrt {{{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - 4} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {7 - 5} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow BC = 2 \]
Distance between two points \[A\left( {3,2,5} \right)\& C\left( {3,4,7} \right)\] is given by,
\[AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - 2} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {7 - 5} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow AC = 2\sqrt 2 \]
If, we observe the magnitude of sides of triangle, we will see that the given triangle is a right angled triangle as it satisfies the Pythagoras Theorem, \[{\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2}\].
Circumcentre: The point of intersection of perpendicular bisectors of all the sides of the triangle is known as the circumcentre.
Let us draw the triangle first.
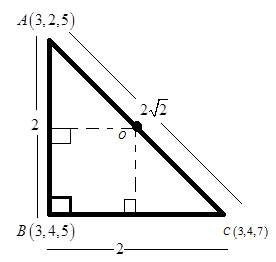
Now, we already know that the circumcentre of a right angled triangle lies on its hypotenuse and is the bisector of the hypotenuse. Therefore, the vertices of the circumcentre will be the same as the midpoint of the hypotenuse i.e. the point \[O\].
Mid-point of \[AC = O\left( {\dfrac{{3 + 3}}{2},\dfrac{{4 + 2}}{2},\dfrac{{7 + 5}}{2}} \right)\]
Or, circumcentre of \[\vartriangle ABC = O\left( {3,3,6} \right)\]
Also, Position vector of a point \[P\left( {x,y,z} \right)\] is given as \[\overrightarrow {OP} = x\hat i + y\hat j + z\hat k\], where \[O\] is the origin
Therefore, the position vector of the circumcentre will be \[3\hat i + 3\hat j + 6\hat k\].
Note: It is important to note here that the concept we used here holds true only in the case of right-angled triangle. It means, in case of right-angled triangle only, the circumcentre lies on the hypotenuse and its vertices are same as the vertices of midpoint of hypotenuse. In other cases, circumcentre can be inside or outside of the triangle.
Formula used:
Distance between two points \[{P_1}\left( {{x_1},{y_1},{z_1}} \right)\& {P_2}\left( {{x_2},{y_2},{z_2}} \right)\] is calculated by: \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{z_2} - {z_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
Mid-point formula between two points \[{P_1}\left( {{x_1},{y_1},{z_1}} \right)\& {P_2}\left( {{x_2},{y_2},{z_2}} \right)\] is given by: \[\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{z_1} + {z_2}}}{2}} \right)\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given, Three vertices of a triangle, \[A\left( {3,2,5} \right),B\left( {3,4,5} \right),C\left( {3,4,7} \right)\]
Distance between two points \[A\left( {3,2,5} \right),B\left( {3,4,5} \right)\] is given by,
\[AB = \sqrt {\left| {{{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - 2} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {5 - 5} \right)}^2}} \right|} \\
\Rightarrow AB = 2 \]
Distance between two points \[B\left( {3,4,5} \right),C\left( {3,4,7} \right)\] is given by,
\[BC = \sqrt {{{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - 4} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {7 - 5} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow BC = 2 \]
Distance between two points \[A\left( {3,2,5} \right)\& C\left( {3,4,7} \right)\] is given by,
\[AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - 2} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {7 - 5} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow AC = 2\sqrt 2 \]
If, we observe the magnitude of sides of triangle, we will see that the given triangle is a right angled triangle as it satisfies the Pythagoras Theorem, \[{\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2}\].
Circumcentre: The point of intersection of perpendicular bisectors of all the sides of the triangle is known as the circumcentre.
Let us draw the triangle first.

Now, we already know that the circumcentre of a right angled triangle lies on its hypotenuse and is the bisector of the hypotenuse. Therefore, the vertices of the circumcentre will be the same as the midpoint of the hypotenuse i.e. the point \[O\].
Mid-point of \[AC = O\left( {\dfrac{{3 + 3}}{2},\dfrac{{4 + 2}}{2},\dfrac{{7 + 5}}{2}} \right)\]
Or, circumcentre of \[\vartriangle ABC = O\left( {3,3,6} \right)\]
Also, Position vector of a point \[P\left( {x,y,z} \right)\] is given as \[\overrightarrow {OP} = x\hat i + y\hat j + z\hat k\], where \[O\] is the origin
Therefore, the position vector of the circumcentre will be \[3\hat i + 3\hat j + 6\hat k\].
Note: It is important to note here that the concept we used here holds true only in the case of right-angled triangle. It means, in case of right-angled triangle only, the circumcentre lies on the hypotenuse and its vertices are same as the vertices of midpoint of hypotenuse. In other cases, circumcentre can be inside or outside of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




