
Find the magnetic induction at the centre of a rectangular wire frame whose diagonal is equal to $d = 16cm$ and the angle between the diagonals is equal to $\varphi = 30^\circ $ ; the current in the following frame equals $I = 5.0A$ .

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint:Any current carrying conductor induces a magnetic field around it. The magnetic field at the center of the given wire frame will be the resultant of the magnetic fields due to individual elements of the frame.
Formula Used:
Magnetic induction due to a straight current carrying wire at a point is given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{i}{r}(\sin {\theta _1} + \sin {\theta _2})$
Where, ${\mu _0} = 4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}H{m^{ - 1}}$ is the permeability of free space, $i$ is the current in the wire, $r$ is the perpendicular distance from the wire to the considered point, ${\theta _1}$ is the angle between the line joining the top of the wire to the considered point and the perpendicular from the wire to the considered point, ${\theta _2}$ is the angle between the line joining the bottom of the wire to the considered point and the perpendicular from the wire to the considered point.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
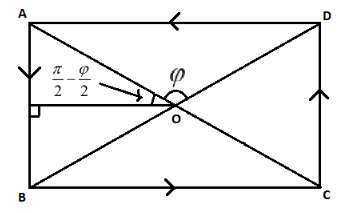
Here, we are given that the diagonal is of length $d = 16cm$ therefore AO $ = \dfrac{d}{2} = 8cm$ . Now by using the vector resolving method, we can find the length of perpendicular from any side of the rectangular wire to the considered point O.
Length of perpendicular from side AB of the wire to the point O $ = \dfrac{d}{2}\cos (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\varphi }{2}) = \dfrac{d}{2}\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}$ $(\cos (90 - \theta ) = \sin \theta )$
Length of perpendicular from side DA of the wire to the point O $ = \dfrac{d}{2}\sin (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\varphi }{2}) = \dfrac{d}{2}\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}$ $(\sin (90 - \theta ) = \cos \theta )$
Hence, the magnetic induction at the centre of the rectangular wire due to side AB will be ${B_{AB}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\sin (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\varphi }{2}) + \sin (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\varphi }{2}))$
On simplifying, ${B_{AB}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2} + \cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2})$
The magnetic induction at the centre of the rectangle due to side CD will be equal to magnetic induction at the centre due to side AB. Hence,
${B_{AB}} = {B_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times 2\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}$
The magnetic induction at the centre of the rectangular wire due to side BC will be ${B_{BC}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2} + \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2})$
The magnetic induction at the centre of the rectangle due to side DA will be equal to magnetic induction at the centre due to side BC. Hence,
${B_{BC}} = {B_{DA}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times 2\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}$
The net magnetic induction at point O due to the rectangular wire will be $ = {B_1} + {B_2} + {B_3} + {B_4}$
$ = 2 \times [\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\cos \frac{\varphi }{2} + \cos \frac{\varphi }{2})] + 2 \times [\frac{{{\mu _ 0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \frac{y}{{\frac{d}{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2} + \sin \frac{\varphi }{2})]$
$ = 2 \times 2 \times \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{d/2}} \times [\dfrac{{\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}}{{\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} + \dfrac{{\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}}{{\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}}]$
$ = \dfrac{{4{\mu _0}i}}{{\pi d\sin \varphi }} = 0.10mT$
Therefore, the magnetic induction at the centre of a rectangular wire frame $ = 0.10mT$
Note:The perpendicular distance from the centre O to side AB will not be equal to the perpendicular distance from centre O to side BC because the angles subtended by the perpendicular and the line joining the end point of the wire to the point O are different.
Formula Used:
Magnetic induction due to a straight current carrying wire at a point is given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{i}{r}(\sin {\theta _1} + \sin {\theta _2})$
Where, ${\mu _0} = 4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}H{m^{ - 1}}$ is the permeability of free space, $i$ is the current in the wire, $r$ is the perpendicular distance from the wire to the considered point, ${\theta _1}$ is the angle between the line joining the top of the wire to the considered point and the perpendicular from the wire to the considered point, ${\theta _2}$ is the angle between the line joining the bottom of the wire to the considered point and the perpendicular from the wire to the considered point.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here, we are given that the diagonal is of length $d = 16cm$ therefore AO $ = \dfrac{d}{2} = 8cm$ . Now by using the vector resolving method, we can find the length of perpendicular from any side of the rectangular wire to the considered point O.
Length of perpendicular from side AB of the wire to the point O $ = \dfrac{d}{2}\cos (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\varphi }{2}) = \dfrac{d}{2}\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}$ $(\cos (90 - \theta ) = \sin \theta )$
Length of perpendicular from side DA of the wire to the point O $ = \dfrac{d}{2}\sin (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\varphi }{2}) = \dfrac{d}{2}\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}$ $(\sin (90 - \theta ) = \cos \theta )$
Hence, the magnetic induction at the centre of the rectangular wire due to side AB will be ${B_{AB}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\sin (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\varphi }{2}) + \sin (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \dfrac{\varphi }{2}))$
On simplifying, ${B_{AB}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2} + \cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2})$
The magnetic induction at the centre of the rectangle due to side CD will be equal to magnetic induction at the centre due to side AB. Hence,
${B_{AB}} = {B_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times 2\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}$
The magnetic induction at the centre of the rectangular wire due to side BC will be ${B_{BC}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2} + \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2})$
The magnetic induction at the centre of the rectangle due to side DA will be equal to magnetic induction at the centre due to side BC. Hence,
${B_{BC}} = {B_{DA}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times 2\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}$
The net magnetic induction at point O due to the rectangular wire will be $ = {B_1} + {B_2} + {B_3} + {B_4}$
$ = 2 \times [\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{\dfrac{d}{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\cos \frac{\varphi }{2} + \cos \frac{\varphi }{2})] + 2 \times [\frac{{{\mu _ 0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \frac{y}{{\frac{d}{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} \times (\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2} + \sin \frac{\varphi }{2})]$
$ = 2 \times 2 \times \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{i}{{d/2}} \times [\dfrac{{\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}}{{\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}} + \dfrac{{\sin \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}}{{\cos \dfrac{\varphi }{2}}}]$
$ = \dfrac{{4{\mu _0}i}}{{\pi d\sin \varphi }} = 0.10mT$
Therefore, the magnetic induction at the centre of a rectangular wire frame $ = 0.10mT$
Note:The perpendicular distance from the centre O to side AB will not be equal to the perpendicular distance from centre O to side BC because the angles subtended by the perpendicular and the line joining the end point of the wire to the point O are different.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




