
Find the differential equation of all the ellipse whose centre at origin and axis are along the coordinate axis.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: We will start by using the fact that the general equation of an ellipse with centre at (h, k) is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$. Then we will write the equation of the ellipse for the centre at origin and differentiate it twice because for forming a differential equation we have removed arbitrary constants which are two in this case.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we have to find the differential equation of all the ellipses whose centre is at origin and axes are along the coordinate axes.
Now, we know that the equation of an ellipse whose centre is at origin is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.
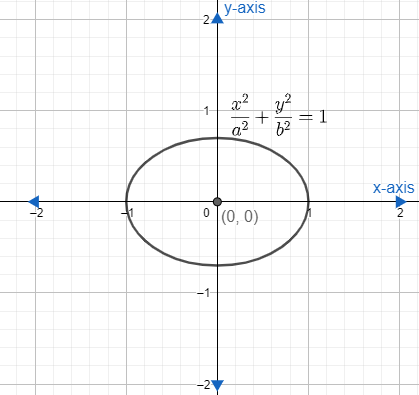
Now, since to form a differential equation we have to eliminate the arbitrary constant and to remove. Then we have to differentiate the equation as many time as the number of constant since the equation has 2 constant. So, we have to differentiate is two times.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}} \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \text{constant} \right)=0$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{2y}{{{b}^{2}}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{2y}{{{b}^{2}}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2y}{{{b}^{2}}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=-\dfrac{2x}{{{a}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2y}{2x}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Now again we will differentiate both sides with respect to x. So, we have,
\[\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{y}{x}.y' \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( -\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)\]
Now we know that,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{f\left( x \right)}{g\left( x \right)} \right)=\dfrac{g\left( x \right)f'\left( x \right)-f\left( x \right)g'\left( x \right)}{g{{\left( x \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( f\left( x \right).g\left( x \right) \right)=f\left( x \right)g'\left( x \right)+g\left( x \right)f'\left( x \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x}\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( y' \right)+y'\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{y}{x} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x}{{y}^{“}}+y'\left( \dfrac{xy'-y\times 1}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x}{{y}^{“}}+y'\left( \dfrac{xy'-y}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow xy{{y}^{‘’}}+x{{\left( y' \right)}^{2}}-y{{y}^{‘}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
is the required differential equation.
Note: To solve such types of questions it is important to note that we have differentiated the equation twice to remove all the arbitrary constants from the differential equation. Generally the number of times an equation has to be differentiated depends on the number of arbitrary constants it has.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we have to find the differential equation of all the ellipses whose centre is at origin and axes are along the coordinate axes.
Now, we know that the equation of an ellipse whose centre is at origin is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.

Now, since to form a differential equation we have to eliminate the arbitrary constant and to remove. Then we have to differentiate the equation as many time as the number of constant since the equation has 2 constant. So, we have to differentiate is two times.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}} \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \text{constant} \right)=0$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{2y}{{{b}^{2}}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{2y}{{{b}^{2}}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2y}{{{b}^{2}}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=-\dfrac{2x}{{{a}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2y}{2x}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Now again we will differentiate both sides with respect to x. So, we have,
\[\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{y}{x}.y' \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( -\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)\]
Now we know that,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{f\left( x \right)}{g\left( x \right)} \right)=\dfrac{g\left( x \right)f'\left( x \right)-f\left( x \right)g'\left( x \right)}{g{{\left( x \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( f\left( x \right).g\left( x \right) \right)=f\left( x \right)g'\left( x \right)+g\left( x \right)f'\left( x \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x}\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( y' \right)+y'\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{y}{x} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x}{{y}^{“}}+y'\left( \dfrac{xy'-y\times 1}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x}{{y}^{“}}+y'\left( \dfrac{xy'-y}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow xy{{y}^{‘’}}+x{{\left( y' \right)}^{2}}-y{{y}^{‘}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
is the required differential equation.
Note: To solve such types of questions it is important to note that we have differentiated the equation twice to remove all the arbitrary constants from the differential equation. Generally the number of times an equation has to be differentiated depends on the number of arbitrary constants it has.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




