
Find the coordination number of $N{{a}^{+}}$ in $N{{a}_{2}}O$.
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: Disodium oxide has an anti-fluorite structure. The cations take up the void here. If we can find the type of void in the anti-fluorite structure, we can find the number of atoms which surround the sodium cation.
Complete answer:
We know that coordination number is the number of ions or atoms the central metal ion holds. In the given question, we have to find out the coordination number of sodium cation in disodium oxide.
Here, we have to know that disodium oxide forms an anti-fluorite structure. In an anti-fluorite structure, the position of the cations and anions is exchanged from their original positions in the fluorite structure.
In fluorite structure, the cations are in the fcc lattice and the anion take up the tetrahedral voids whereas in anti-fluorite structure, the cations lie in the tetrahedral voids and the anions will be packed in the fcc.
In disodium oxide, we have $N{{a}^{+}}\text{ and }{{\text{O}}^{2-}}$. As it has an anti-fluorite structure, the superoxide anion will lie in fcc and the sodium cation will take up the tetrahedral voids.
We know that a tetrahedral void is formed when one more atom is placed on top of the triangular void i.e. the ion which will lie in this tetrahedral void will have 4 surrounding atoms or ions.
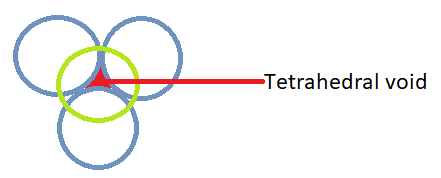
As the sodium cation will lie in the tetrahedral voids, surrounded by 4 oxygen atoms so its coordination number will be 4.
Therefore, the correct answer is the coordination number of $N{{a}^{+}}$ in $N{{a}_{2}}O$ is 4.
Note: The alkali metals oxides with the structure ${{M}_{2}}O$ crystallize in fluorite or anti-fluorite structure. The Bravais lattice of fluorite or anti-fluorite structure is fcc i.e. face centered cubic. In such lattice, the lattice points are at every corner of the cube and also on each face centre.
Complete answer:
We know that coordination number is the number of ions or atoms the central metal ion holds. In the given question, we have to find out the coordination number of sodium cation in disodium oxide.
Here, we have to know that disodium oxide forms an anti-fluorite structure. In an anti-fluorite structure, the position of the cations and anions is exchanged from their original positions in the fluorite structure.
In fluorite structure, the cations are in the fcc lattice and the anion take up the tetrahedral voids whereas in anti-fluorite structure, the cations lie in the tetrahedral voids and the anions will be packed in the fcc.
In disodium oxide, we have $N{{a}^{+}}\text{ and }{{\text{O}}^{2-}}$. As it has an anti-fluorite structure, the superoxide anion will lie in fcc and the sodium cation will take up the tetrahedral voids.
We know that a tetrahedral void is formed when one more atom is placed on top of the triangular void i.e. the ion which will lie in this tetrahedral void will have 4 surrounding atoms or ions.

As the sodium cation will lie in the tetrahedral voids, surrounded by 4 oxygen atoms so its coordination number will be 4.
Therefore, the correct answer is the coordination number of $N{{a}^{+}}$ in $N{{a}_{2}}O$ is 4.
Note: The alkali metals oxides with the structure ${{M}_{2}}O$ crystallize in fluorite or anti-fluorite structure. The Bravais lattice of fluorite or anti-fluorite structure is fcc i.e. face centered cubic. In such lattice, the lattice points are at every corner of the cube and also on each face centre.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




