
Explain the structure and functions of cholesterol.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: The molecular formula of cholesterol is \[{{C}_{27}}{{H}_{46}}O\]. Cholesterol contains 4 rings in its structure, one double bond, one hydroxyl group and one hydrocarbon chain. Cholesterol is also known as a "sterol" because it contains alcohol and a steroid moiety in its structure.
Complete answer:
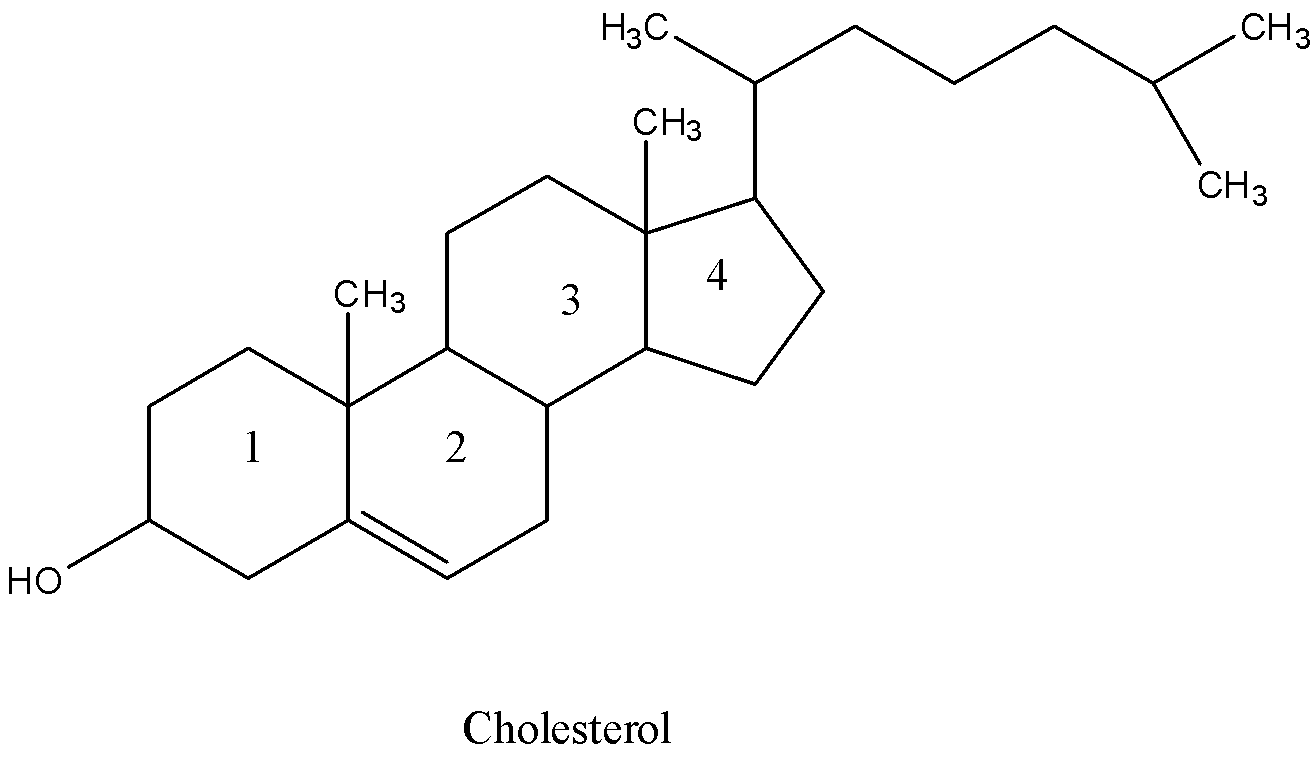
Structure of cholesterol:
We know that Cholesterol is a lipid having a structure consisting of four hydrocarbon rings forming the bulky steroid structure and they are labeled with numbers 1, 2, 3 and 4. We can see the numbering in the below structure.
There is a hydrocarbon chain containing eight carbon atoms linked to five membered rings of the steroid.
There is a double bond in the ring-2 of the cholesterol.
Cholesterol contains a hydroxyl group linked to the first six membered rings in the structure.
The hydroxyl group of cholesterol is capable of forming hydrogen bonds with the nearby oxygen of the carbonyl group of phospholipid.
Functions of cholesterol:
Cholesterol is a vital constituent of the cell membrane.
Cholesterol is going to maintain proper membrane permeability and fluidity of the cells.
Cholesterol is going to involve the synthesis of Steroid Hormones, Vitamin-D and Bile Acids in the cells.
Note: Cholesterol is not present in prokaryotes like bacteria and archaea. Because prokaryotes do not contain a proper cell wall in their structure. By using sunlight cholesterol present in the skin of eukaryotes prepares vitamin-D which is useful to absorb calcium from the intestine.
Complete answer:
Structure of cholesterol:
We know that Cholesterol is a lipid having a structure consisting of four hydrocarbon rings forming the bulky steroid structure and they are labeled with numbers 1, 2, 3 and 4. We can see the numbering in the below structure.
There is a hydrocarbon chain containing eight carbon atoms linked to five membered rings of the steroid.
There is a double bond in the ring-2 of the cholesterol.
Cholesterol contains a hydroxyl group linked to the first six membered rings in the structure.
The hydroxyl group of cholesterol is capable of forming hydrogen bonds with the nearby oxygen of the carbonyl group of phospholipid.

Functions of cholesterol:
Cholesterol is a vital constituent of the cell membrane.
Cholesterol is going to maintain proper membrane permeability and fluidity of the cells.
Cholesterol is going to involve the synthesis of Steroid Hormones, Vitamin-D and Bile Acids in the cells.
Note: Cholesterol is not present in prokaryotes like bacteria and archaea. Because prokaryotes do not contain a proper cell wall in their structure. By using sunlight cholesterol present in the skin of eukaryotes prepares vitamin-D which is useful to absorb calcium from the intestine.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




