
Explain the following reactions:
(i) Reimer- Tiemann Reaction
(ii) Williamson’s ether synthesis.
Answer
529.4k+ views
Hint: The Reimer- Tiemann reaction is carried out on phenols in presence of chloroform and we obtain a hydroxybenzaldehyde as the end product. It proceeds through electrophilic substitution pathway.In the Williamson’s synthesis, a primary alkyl halide and an alkoxide ion is used and the product thus formed is ether. It proceeds through nucleophilic substitution pathway.
Complete Step by Step Solution: At first, we will discuss the Reimer- Tiemann Reaction-
When we treat phenol with chloroform and an aqueous hydroxide, an aldehyde group –CHO is introduced onto the aromatic ring. Generally, the aldehyde is introduced at the ortho-position with respect to the –OH group. This reaction is named as Reimer- Tiemann Reaction. Let us take an example-
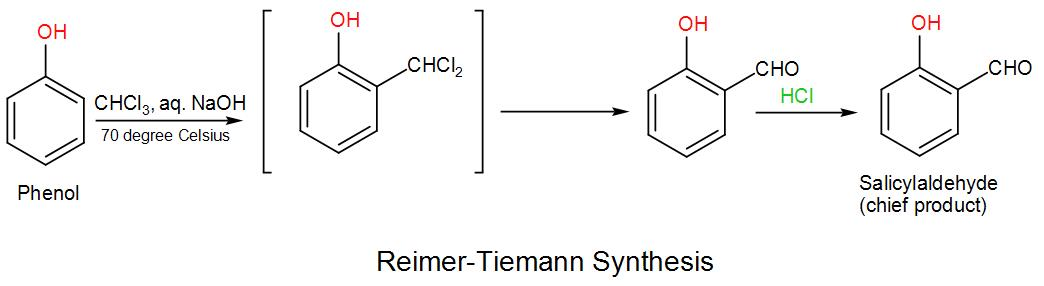
Here, a substituted benzal chloride is formed initially, but it is hydrolysed by the alkaline reaction medium.
The Riemer-Tiemann synthesis reaction involves electrophilic substitution on the highly reactive phenoxide ring. Here, the electrophilic reagent is dichlorocarbene ($:CC{{l}_{2}}$), which is generated from chloroform through the action of base. Although dichlorocarbene is electrically neutral but it contains carbon with only a sextet of electrons which makes it highly electrophilic-
\[O{{H}^{-}}+CHC{{l}_{3}}\rightleftarrows {{H}_{2}}O{{+}^{-}}:CC{{l}_{3}}\to C{{l}^{-}}+:CC{{l}_{2}}\]
Now, we will discuss the Williamson ether synthesis-
As we can understand from the name itself, the end product in this synthesis is ether.
In this synthesis, an alkoxide anion undergoes substitution nucleophilic bimolecular reaction with an alkyl halide and forms ether. We generally carry out this reaction for the formation of unsymmetrical ethers. We will take an example to understand the mechanism of this reaction-
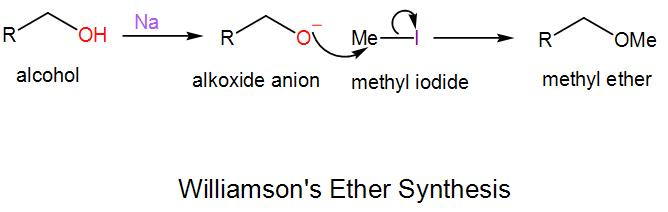
Here we have to use a strong base, NaH to form the alkoxide anion as alcohols are a weak acid and methyl iodide is used here which is the electrophile.
Here, the reaction proceeds via ${{S}_{N}}_2$ pathway.
Note:
(i) In the Riemer-Tiemann reaction, the phenoxide ion formed will show mesomeric and inductive effect hence, the reaction might take place at ortho or para position. But as we know, +I effect decreases with increasing distance, therefore the ortho position will be electron rich and the incoming electrophile will attack at the ortho position. Therefore, formylation will take place at the ortho position.
(ii) The simple alkyl groups, methyl groups and primary alkyl groups always react by the ${{S}_{N}}_2$ mechanism. This is due to the fact that if it proceeds via ${{S}_{N}}_1$ pathway, the cations formed will not be stable.
Complete Step by Step Solution: At first, we will discuss the Reimer- Tiemann Reaction-
When we treat phenol with chloroform and an aqueous hydroxide, an aldehyde group –CHO is introduced onto the aromatic ring. Generally, the aldehyde is introduced at the ortho-position with respect to the –OH group. This reaction is named as Reimer- Tiemann Reaction. Let us take an example-

Here, a substituted benzal chloride is formed initially, but it is hydrolysed by the alkaline reaction medium.
The Riemer-Tiemann synthesis reaction involves electrophilic substitution on the highly reactive phenoxide ring. Here, the electrophilic reagent is dichlorocarbene ($:CC{{l}_{2}}$), which is generated from chloroform through the action of base. Although dichlorocarbene is electrically neutral but it contains carbon with only a sextet of electrons which makes it highly electrophilic-
\[O{{H}^{-}}+CHC{{l}_{3}}\rightleftarrows {{H}_{2}}O{{+}^{-}}:CC{{l}_{3}}\to C{{l}^{-}}+:CC{{l}_{2}}\]
Now, we will discuss the Williamson ether synthesis-
As we can understand from the name itself, the end product in this synthesis is ether.
In this synthesis, an alkoxide anion undergoes substitution nucleophilic bimolecular reaction with an alkyl halide and forms ether. We generally carry out this reaction for the formation of unsymmetrical ethers. We will take an example to understand the mechanism of this reaction-
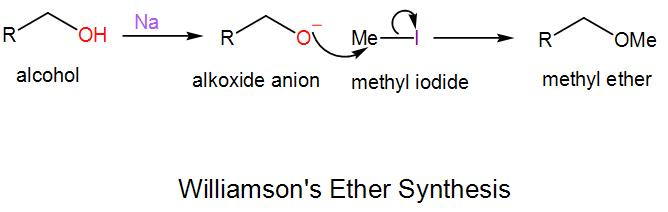
Here we have to use a strong base, NaH to form the alkoxide anion as alcohols are a weak acid and methyl iodide is used here which is the electrophile.
Here, the reaction proceeds via ${{S}_{N}}_2$ pathway.
Note:
(i) In the Riemer-Tiemann reaction, the phenoxide ion formed will show mesomeric and inductive effect hence, the reaction might take place at ortho or para position. But as we know, +I effect decreases with increasing distance, therefore the ortho position will be electron rich and the incoming electrophile will attack at the ortho position. Therefore, formylation will take place at the ortho position.
(ii) The simple alkyl groups, methyl groups and primary alkyl groups always react by the ${{S}_{N}}_2$ mechanism. This is due to the fact that if it proceeds via ${{S}_{N}}_1$ pathway, the cations formed will not be stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




