
Explain Malus law for polaroids.
Answer
609.9k+ views
Hint: When a plane-polarized light ray is passed through a Polaroid, the intensity of the light ray is affected as some parts of the electric vector of light are removed by the Polaroid. Malus’ law gives us the expression for the intensity of light obtained from a Polaroid.
Detailed step by step solution:
The light waves are electromagnetic waves. Such waves are transverse and have an electric field vector and magnetic field vector which are perpendicular to each other.
An unpolarized wave is one that has its vectors vibrating in all directions. A source of light like the sun or an electric bulb emits unpolarized light waves. We can convert an unpolarized and polarized light by passing the unpolarized light through a polarizer. The polarizer allows only certain components of the field vector to pass through while other components are removed. The result is that we get light which is polarized in a certain direction. This process is called polarization.
The intensity of light depends on its vibrations. When light is passed through a polarizer, its intensity is decreased due to the removal of some vibrations. Malus’ law gives a mathematical relation between the intensity of the light incident on the polaroid and the intensity of light obtained after passing it through the polaroid.
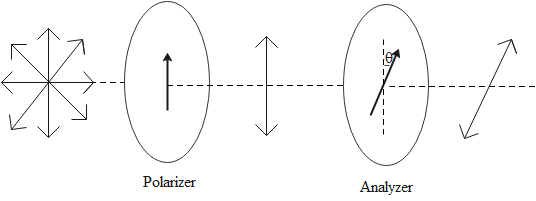
Malus’ law states that the intensity of plane-polarized light passing through a polarizer is directly proportional to the square of the cosine of the angle between the transmission axis of the analyzer and polarizer.
\[
I \propto {\cos ^2}\theta \\
I = {I_0}{\cos ^2}\theta \\
\]
Note: An analyzer is also a polarizer that is placed after a polarizer and rotating the analyzer affects the intensity of the polarized light. It is used to further reduce the intensity of light and also adjust it by adjusting the angle of the analyser with respect to the polarizer.
Detailed step by step solution:
The light waves are electromagnetic waves. Such waves are transverse and have an electric field vector and magnetic field vector which are perpendicular to each other.
An unpolarized wave is one that has its vectors vibrating in all directions. A source of light like the sun or an electric bulb emits unpolarized light waves. We can convert an unpolarized and polarized light by passing the unpolarized light through a polarizer. The polarizer allows only certain components of the field vector to pass through while other components are removed. The result is that we get light which is polarized in a certain direction. This process is called polarization.
The intensity of light depends on its vibrations. When light is passed through a polarizer, its intensity is decreased due to the removal of some vibrations. Malus’ law gives a mathematical relation between the intensity of the light incident on the polaroid and the intensity of light obtained after passing it through the polaroid.

Malus’ law states that the intensity of plane-polarized light passing through a polarizer is directly proportional to the square of the cosine of the angle between the transmission axis of the analyzer and polarizer.
\[
I \propto {\cos ^2}\theta \\
I = {I_0}{\cos ^2}\theta \\
\]
Note: An analyzer is also a polarizer that is placed after a polarizer and rotating the analyzer affects the intensity of the polarized light. It is used to further reduce the intensity of light and also adjust it by adjusting the angle of the analyser with respect to the polarizer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




