
Electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius 10cm surrounding the total charge is 25 V-m. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius 20 cm will be:
$A.$ 25V-m
$B.$ 50V-m
$C.$ 100V-m
$D.$ 200V-m
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: The flux through a surface does not depend on its shape and size; it only depends upon the charge enclosed by the sphere of radius 10 cm and the sphere of radius 20 cm is same so the flux through them will also be the same.
Complete answer:
Values given to us are flux through a surface of 10cm is ${{\phi }_{10}}$=25 V-m
$Q_{en}^{10}$ is charge enclosed within a radius of 10cm
$Q_{en}^{20}$is the charge enclosed within a radius of 20cm
${{\phi }_{20}}$ is the flux through a surface of 20cm
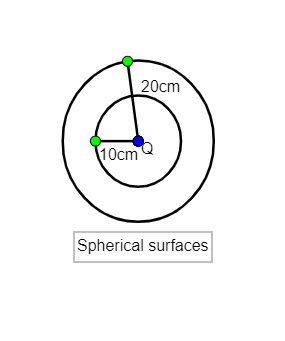
Using Gauss’s law, ${{\phi }_{10}}=\dfrac{Q_{en}^{10}}{{{\in }_{0}}}$
Or $Q_{en}^{10}=25{{\in }_{0}}$
Here for flux of radius 20cm, $Q_{en}^{20}=Q_{en}^{10}=25{{\in }_{0}}$
Thus, ${{\phi }_{20}}=\dfrac{25{{\in }_{0}}}{{{\in }_{0}}}=25$V-m.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
Laws of physics like the Gauss's law for magnetism and Gauss's law for gravity have a great mathematical similarity with the Gauss law. Any inverse-square law can be deducted to Gauss's law. For example, Gauss's law itself is quite equivalent to the inverse-square Coulomb's law and Gauss's law for gravity is quite equivalent to the inverse-square Newton's law of gravity.
Note:
Electric field passing through a given area at a particular time is known as electric flux. Electric flux is directly proportional to the number of electric field lines passing through that given area. If the electric field is uniform, the electric flux passing through a surface of vector area S is: \[\phi =E\cdot S=EScos\theta \], where E is the magnitude of the electric field having units of V/m, S is the area of the surface, and θ is the angle between the electric field lines and the normal to S. Electric flux is also related to Gauss law. Gauss Law states the net electric flux from a closed surface is equal to $\dfrac{1}{{{\in }_{0}}}$ times the net charge enclosed in that area. There are two forms of the Gauss law; the integral form and the differential form.
Complete answer:
Values given to us are flux through a surface of 10cm is ${{\phi }_{10}}$=25 V-m
$Q_{en}^{10}$ is charge enclosed within a radius of 10cm
$Q_{en}^{20}$is the charge enclosed within a radius of 20cm
${{\phi }_{20}}$ is the flux through a surface of 20cm

Using Gauss’s law, ${{\phi }_{10}}=\dfrac{Q_{en}^{10}}{{{\in }_{0}}}$
Or $Q_{en}^{10}=25{{\in }_{0}}$
Here for flux of radius 20cm, $Q_{en}^{20}=Q_{en}^{10}=25{{\in }_{0}}$
Thus, ${{\phi }_{20}}=\dfrac{25{{\in }_{0}}}{{{\in }_{0}}}=25$V-m.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
Laws of physics like the Gauss's law for magnetism and Gauss's law for gravity have a great mathematical similarity with the Gauss law. Any inverse-square law can be deducted to Gauss's law. For example, Gauss's law itself is quite equivalent to the inverse-square Coulomb's law and Gauss's law for gravity is quite equivalent to the inverse-square Newton's law of gravity.
Note:
Electric field passing through a given area at a particular time is known as electric flux. Electric flux is directly proportional to the number of electric field lines passing through that given area. If the electric field is uniform, the electric flux passing through a surface of vector area S is: \[\phi =E\cdot S=EScos\theta \], where E is the magnitude of the electric field having units of V/m, S is the area of the surface, and θ is the angle between the electric field lines and the normal to S. Electric flux is also related to Gauss law. Gauss Law states the net electric flux from a closed surface is equal to $\dfrac{1}{{{\in }_{0}}}$ times the net charge enclosed in that area. There are two forms of the Gauss law; the integral form and the differential form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




