
Draw the structure of major monohalo products in the following structure.
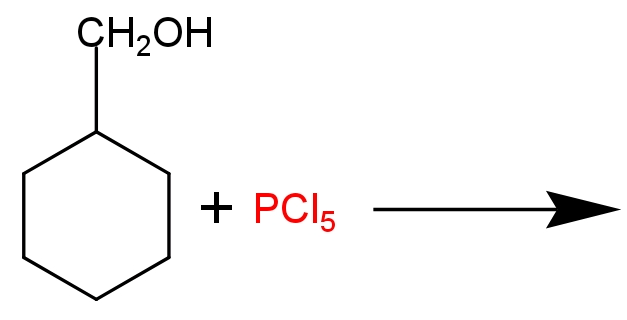

Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint in a multi- product reaction the most likely formed product will be the major product of the reaction, which will be the structurally most stable form of product. Phosphorus pentachloride acts as a halogenating agent. It reacts with alcohols at room temperature and produces alkyl halide and fumes of hydrogen chloride. Phosphorus pentachloride found in solid state in room temperature.
Stronger bases are a poor leaving group.
Complete Step by step solution-
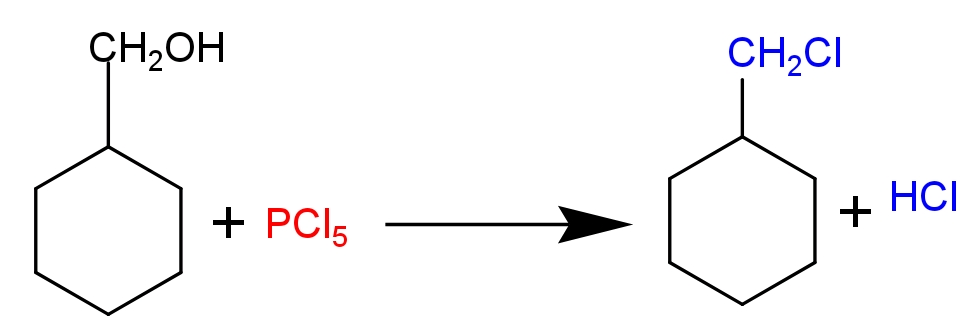
This reaction is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction (${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$). In this reaction $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ produces a nucleophile ($\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{\text{-}}}$ ion). It attacks alcoholic intermediates from the back side and substitutes the oxonium ion (electron deficient oxygen atom) and forms methyl cyclohexane chloride as a major product. Phosphoryl chloride ($\text{POC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$) and $\text{HCl}$ is formed as a bi-product.
Additional information -
In this reaction $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ act as an electrophile, because$\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ attached with five highly electronegative chlorine atoms. Alcoholic group of benzyl chloride donate its lone pair to the phosphorus atom and forms oxonium ion by the release of $\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{\text{-}}}$ ion. Formation of oxonium ion makes it a good leaving group. $\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{\text{-}}}$ Ion attacks in electron deficient alkyl carbocation by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ mechanism and forms benzyl chloride as a final product.
Note – ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$Reaction takes place through an intermediate transition state and back side attack of nucleophile occurs from the less hindered side.
Primary alkyl group and non-polar solvent favour the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ reaction.
Stronger bases are a poor leaving group.
Complete Step by step solution-
This reaction is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction (${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$). In this reaction $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ produces a nucleophile ($\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{\text{-}}}$ ion). It attacks alcoholic intermediates from the back side and substitutes the oxonium ion (electron deficient oxygen atom) and forms methyl cyclohexane chloride as a major product. Phosphoryl chloride ($\text{POC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$) and $\text{HCl}$ is formed as a bi-product.

Additional information -
In this reaction $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ act as an electrophile, because$\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ attached with five highly electronegative chlorine atoms. Alcoholic group of benzyl chloride donate its lone pair to the phosphorus atom and forms oxonium ion by the release of $\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{\text{-}}}$ ion. Formation of oxonium ion makes it a good leaving group. $\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{\text{-}}}$ Ion attacks in electron deficient alkyl carbocation by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ mechanism and forms benzyl chloride as a final product.
Note – ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$Reaction takes place through an intermediate transition state and back side attack of nucleophile occurs from the less hindered side.
Primary alkyl group and non-polar solvent favour the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




