
How does image change when a face is slowly moved away from the inner face of a shining spoon?
Answer
553.5k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the type of reflecting surface formed by the inner surface of spoon in order to identify the possible image formations due to the object kept at different positions in front of it which will give the required solution here.
Complete answer:
We are given a shining spoon which is kept in front of the observer's face initially. The inner surface of the spoons are usually caved in thus forming a reflecting surface caved in known as the concave mirror. We need to understand how the reflections from the concave mirrors contribute to the image formations and thus find the nature of the image formed at different positions.
Initially, the face is kept in front of the mirror or the spoon so close that it is between the pole and the principal focus of the mirror. For a concave mirror, the image formed when the object is at this position is virtual and erect.
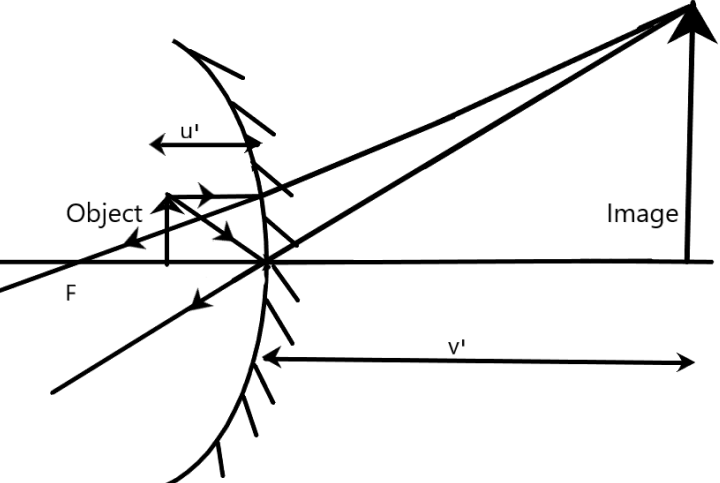
As the face is moved away, the size of the image diminishes and gets inverted at the focal point with a real nature at infinity. Now, when the face moves from the focus to the center of curvature, the image size increases to the original size at C forming a real and inverted image throughout.
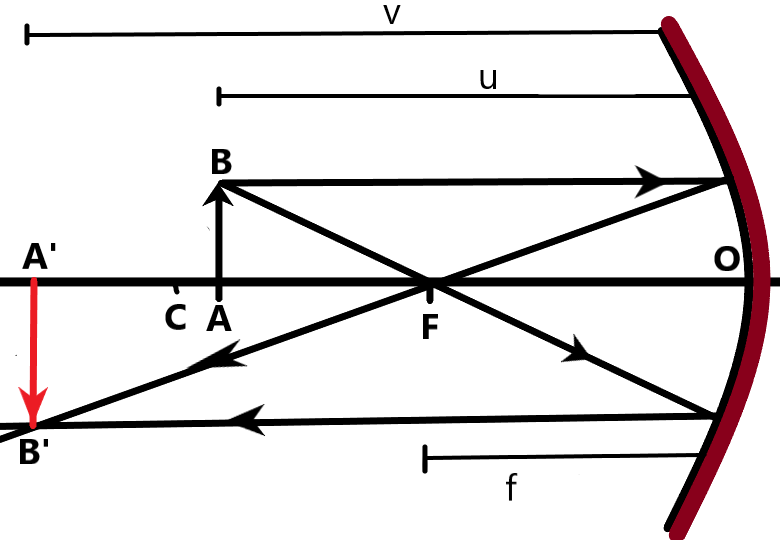
Once the face is moved beyond C, the image will form between the focus and C in real and inverted form itself. When the image is far enough the image will be formed at the focal point.
The image thus gets real and inverted when the object is moving away from the spoon.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The concave mirrors give virtual and erect mirrors only when the object is placed between the principal focus and the pole of the mirror. In all other situations the concave mirrors give the real and inverted image as we have discussed in this problem.
Complete answer:
We are given a shining spoon which is kept in front of the observer's face initially. The inner surface of the spoons are usually caved in thus forming a reflecting surface caved in known as the concave mirror. We need to understand how the reflections from the concave mirrors contribute to the image formations and thus find the nature of the image formed at different positions.
Initially, the face is kept in front of the mirror or the spoon so close that it is between the pole and the principal focus of the mirror. For a concave mirror, the image formed when the object is at this position is virtual and erect.

As the face is moved away, the size of the image diminishes and gets inverted at the focal point with a real nature at infinity. Now, when the face moves from the focus to the center of curvature, the image size increases to the original size at C forming a real and inverted image throughout.

Once the face is moved beyond C, the image will form between the focus and C in real and inverted form itself. When the image is far enough the image will be formed at the focal point.
The image thus gets real and inverted when the object is moving away from the spoon.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The concave mirrors give virtual and erect mirrors only when the object is placed between the principal focus and the pole of the mirror. In all other situations the concave mirrors give the real and inverted image as we have discussed in this problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




