
How many diastereomers are there of glucose?
Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: The diastereomers are not mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable. The molecular formula of glucose is ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$. The maximum number of diastereomers present in a molecule is ${2^n} - 2$.
Complete step by step answer:
Diastereomers are the compounds which are not mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable in other hand the enantiomers are the mirror image of each other and are non-superimposable. The diastereomers and the enantiomers are commonly called stereoisomers which is the class of isomerism.
When two molecules are stereoisomers which means they possess the same molecular formula, same connectivity but different arrangement of atoms but are not enantiomers then they are considered as diastereomers.
As we know that the maximum optical isomerism can be ${2^n}$ where the n represents the number of chiral centers. The chiral centers are defined as the center where the atom is bonded to four different atoms or groups.
The glucose is the chemical compound with molecular formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$. The two enantiomers of glucose are D-glucose and L-Glucose.
The structure of glucose is shown below.
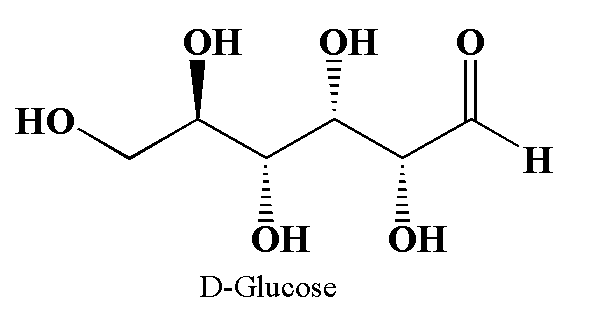
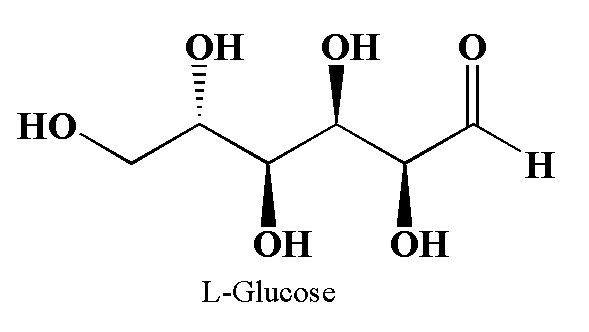
The above diagram is drawn using Chemdraw.
In D-glucose 4 stereocenters are present. So the number of optical isomers will be ${(2)^4}$= 16 which includes D-glucose.
In L-Glucose all the stereocenters are inverted as compared to the D-glucose.
As, the maximum number of diastereomers is ${2^n} - 2$, so the number of diastereoisomer is glucose is
$ \Rightarrow 16 - 2 = 14$
Therefore, 14 diastereomers are there of glucose.
Note: Diastereomers which differ from each other by one stereocenter out of two or more stereocenters are called epimers. D-galactose is one of the 14 diastereoisomers of glucose is the epimer along with D- glucose.
Complete step by step answer:
Diastereomers are the compounds which are not mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable in other hand the enantiomers are the mirror image of each other and are non-superimposable. The diastereomers and the enantiomers are commonly called stereoisomers which is the class of isomerism.
When two molecules are stereoisomers which means they possess the same molecular formula, same connectivity but different arrangement of atoms but are not enantiomers then they are considered as diastereomers.
As we know that the maximum optical isomerism can be ${2^n}$ where the n represents the number of chiral centers. The chiral centers are defined as the center where the atom is bonded to four different atoms or groups.
The glucose is the chemical compound with molecular formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$. The two enantiomers of glucose are D-glucose and L-Glucose.
The structure of glucose is shown below.


The above diagram is drawn using Chemdraw.
In D-glucose 4 stereocenters are present. So the number of optical isomers will be ${(2)^4}$= 16 which includes D-glucose.
In L-Glucose all the stereocenters are inverted as compared to the D-glucose.
As, the maximum number of diastereomers is ${2^n} - 2$, so the number of diastereoisomer is glucose is
$ \Rightarrow 16 - 2 = 14$
Therefore, 14 diastereomers are there of glucose.
Note: Diastereomers which differ from each other by one stereocenter out of two or more stereocenters are called epimers. D-galactose is one of the 14 diastereoisomers of glucose is the epimer along with D- glucose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




