
How will you convert Benzene to acetophenone?
Answer
520.5k+ views
Hint: Acetophenone is a carbonyl compound in which the ketone group is attached to the benzene ring. The catalyst used in the production of acetophenone is anhydrous aluminium chloride. The reaction is a type of electrophilic substitution reaction.
Complete answer:
Benzene (having chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$) can be converted to acetophenone (has chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COC{{H}_{3}}$), which is a methylphenyl ketone by Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction.
There are two primary types of Friedel-Crafts reaction, which are alkylation and acylation reactions. Friedel-Crafts acylation is one of the most convenient and widely used methods for the preparation of aromatic ketone, in which the ketonic group is directly attached to at least one aromatic ring. The reaction involves the treatment of an aromatic hydrocarbon with an acid halide in the presence of a Lewis acid such as aluminium chloride.
Here, when benzene is reacted with an acyl halide in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride, it will give an acyl benzene as a product. This reaction is a type of electrophilic substitution reaction. Firstly, ethanoyl chloride reacts with aluminium chloride and produces an electrophile. Then this electrophile reacts with benzene which will actually undergo the electrophilic substitution reaction to form acetophenone. Following is the reaction shown for the production of acetophenone:
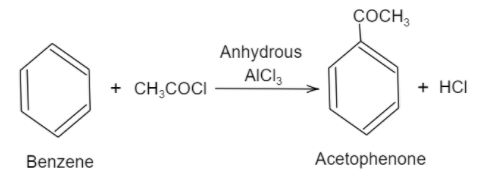
Hence, from the above discussion, it can be seen that benzene is converted into acetophenone by Friedel-Craft acylation reaction.
Note: Possibly you may get confused with Friedel-Craft alkylation but Friedel-Craft alkylation reaction involves reaction of benzene with alkyl halides in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst like anhydrous aluminium chloride to form alkyl benzene (otherwise called an arenes).
Complete answer:
Benzene (having chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$) can be converted to acetophenone (has chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COC{{H}_{3}}$), which is a methylphenyl ketone by Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction.
There are two primary types of Friedel-Crafts reaction, which are alkylation and acylation reactions. Friedel-Crafts acylation is one of the most convenient and widely used methods for the preparation of aromatic ketone, in which the ketonic group is directly attached to at least one aromatic ring. The reaction involves the treatment of an aromatic hydrocarbon with an acid halide in the presence of a Lewis acid such as aluminium chloride.
Here, when benzene is reacted with an acyl halide in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride, it will give an acyl benzene as a product. This reaction is a type of electrophilic substitution reaction. Firstly, ethanoyl chloride reacts with aluminium chloride and produces an electrophile. Then this electrophile reacts with benzene which will actually undergo the electrophilic substitution reaction to form acetophenone. Following is the reaction shown for the production of acetophenone:

Hence, from the above discussion, it can be seen that benzene is converted into acetophenone by Friedel-Craft acylation reaction.
Note: Possibly you may get confused with Friedel-Craft alkylation but Friedel-Craft alkylation reaction involves reaction of benzene with alkyl halides in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst like anhydrous aluminium chloride to form alkyl benzene (otherwise called an arenes).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




