
How many constitutional isomers of ${C_7}{H_{15}}Cl$ will form in the radical chain chlorination of 2, 4-dimethylpentane.
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint:Constitutional isomers also known as structural isomers are compounds which possess the same molecular formula but differ in their structural formula. In the compound ${C_7}{H_{15}}Cl$, three types of hydrogen bonding are present.
Complete step by step answer:Free radical halogenation reaction:
The free radical halogenation reaction is a type of halogenation reaction where single hydrogen of the alkane is replaced by the single halogen to form a haloalkane. This reaction takes place in presence of light.
This reaction has three steps.
Step 1: Initiation
In this step the halogen molecule breaks down in presence of light to give free radicals.
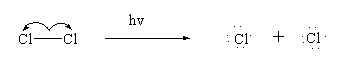
Step 2: Propagation
The propagation step is divided further in two steps. In the first propagation step, the chlorine radical attacks the hydrogen atom present in the methane and forms hydrochloric acid and a methyl radical.
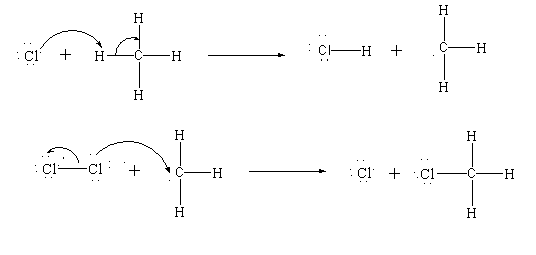
In the second propagation step more chlorine is added, out of which one chlorine atom becomes free radical and others get attached to the methyl radical.
Step 3: Termination
In the last step, the remaining free radicals combine with each other to generate new products like chloromethane and the two methyl radicals generate the by-product to form ethane.
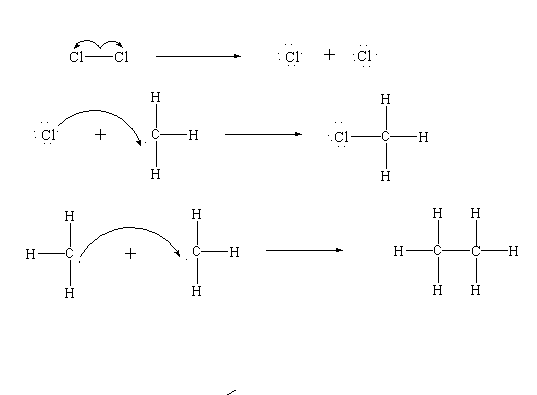
Note:
In free radical halogenation reaction, energy or light source is only needed in the first step that is initiation to break the halogen molecule into free radical. After that all the further reaction can be processed without any energy source.
Complete step by step answer:Free radical halogenation reaction:
The free radical halogenation reaction is a type of halogenation reaction where single hydrogen of the alkane is replaced by the single halogen to form a haloalkane. This reaction takes place in presence of light.
This reaction has three steps.
Step 1: Initiation
In this step the halogen molecule breaks down in presence of light to give free radicals.

Step 2: Propagation
The propagation step is divided further in two steps. In the first propagation step, the chlorine radical attacks the hydrogen atom present in the methane and forms hydrochloric acid and a methyl radical.

In the second propagation step more chlorine is added, out of which one chlorine atom becomes free radical and others get attached to the methyl radical.
Step 3: Termination
In the last step, the remaining free radicals combine with each other to generate new products like chloromethane and the two methyl radicals generate the by-product to form ethane.

Note:
In free radical halogenation reaction, energy or light source is only needed in the first step that is initiation to break the halogen molecule into free radical. After that all the further reaction can be processed without any energy source.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




