
Consider two unlinked genes P and Q. A plant with genotype PPQQ was crossed with another plant with genotype ppqq to obtain F1 progeny. If the F1 progeny to test-crossed, the percentage of resultant plants with the genotype ppqq will be:
$
A.50\% \\
B.25\% \\
C.100\% \\
D.10\% \\
$
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint:When genes are found on different chromosomes or far apart on the same chromosome are said to be unlinked. The genes that are close together on the same chromosome, they are said to be linked.
The genotype is a complete set of heritable genes or the genes that can be passed down from parents to offspring.
Complete answer:
The cross between F1 progeny with homozygous recessive parents.
On test cross, the resultant genotypes are PpQq, Ppqq, ppQq, ppqq in the ratio $1:1:1:1$.
Hence percentage of resultant plants with the genotype ppqq will be $ \to \dfrac{1}{4} \times 100 = 25\% $
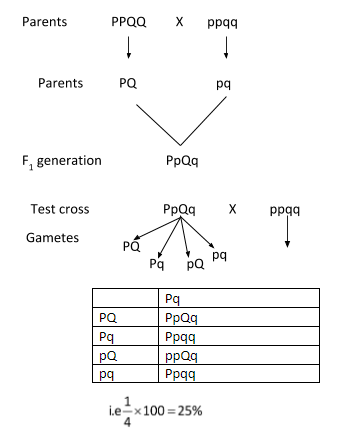
$i.e\,\dfrac{1}{4} \times 100 = 25\% $
Hence B $25\% $ is the correct option.
Note: Phenotypic ratio pertains to the relative number of offspring manifesting a particular trait or combination of traits. The genotypic ratios produce characteristic phenotypic ratios, according to the dominance relationships of the alleles involved.
The genotype is a complete set of heritable genes or the genes that can be passed down from parents to offspring.
Complete answer:
The cross between F1 progeny with homozygous recessive parents.
On test cross, the resultant genotypes are PpQq, Ppqq, ppQq, ppqq in the ratio $1:1:1:1$.
Hence percentage of resultant plants with the genotype ppqq will be $ \to \dfrac{1}{4} \times 100 = 25\% $

$i.e\,\dfrac{1}{4} \times 100 = 25\% $
Hence B $25\% $ is the correct option.
Note: Phenotypic ratio pertains to the relative number of offspring manifesting a particular trait or combination of traits. The genotypic ratios produce characteristic phenotypic ratios, according to the dominance relationships of the alleles involved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




