
Compound (A) and (C) in the following reaction are:
$C{H_3}CHO\xrightarrow[{{H_2}O}]{{C{H_3}MgBr}}A\xrightarrow{{{H_2}S{O_{4,}}\Delta }}B\xrightarrow{{Hydroboration\,\,\,oxidation}}C$
A. Identical
B. Positional isomer
C. Functional isomer
D. Optical isomer
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The first reaction with $C{H_3}MgBr$ which is a Grignard reagent will lead to the formation of secondary alcohol. Then with ${H_2}S{O_4}$ there is dehydration and alkene is formed. On further reaction with $B{H_3}$ known as hydroboration, we will get primary alcohol. Compare the two types of alcohol with respect to the carbon number at which the alcohol group is attached. Positional isomers have the same functional group but the functional group is attached at a different carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction given to us in the question is a compound reaction and hence lets break it down into individual reactions. The first reaction is of acetaldehyde with Grignard reagent, $C{H_3}MgBr$
This reaction will give rise to secondary alcohol formation. This is compound A
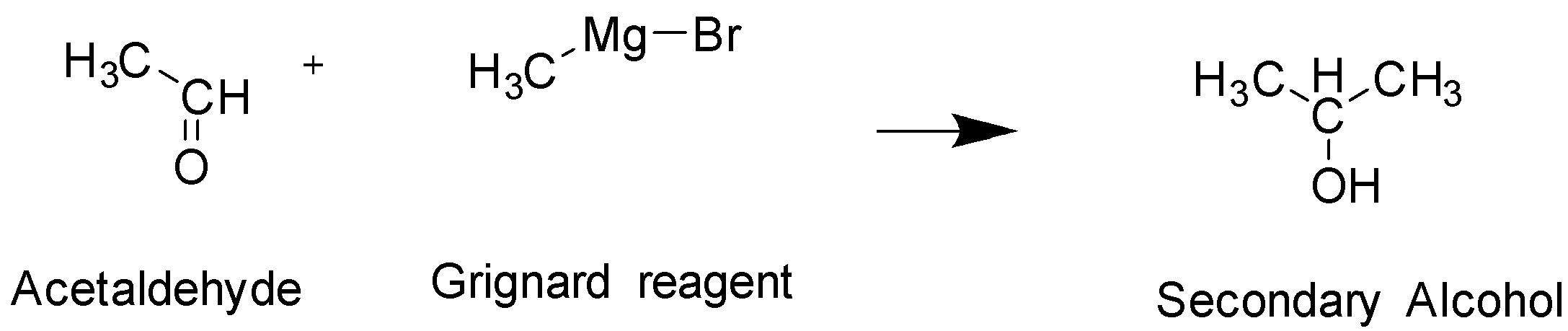 (Self-made diagram)
(Self-made diagram)
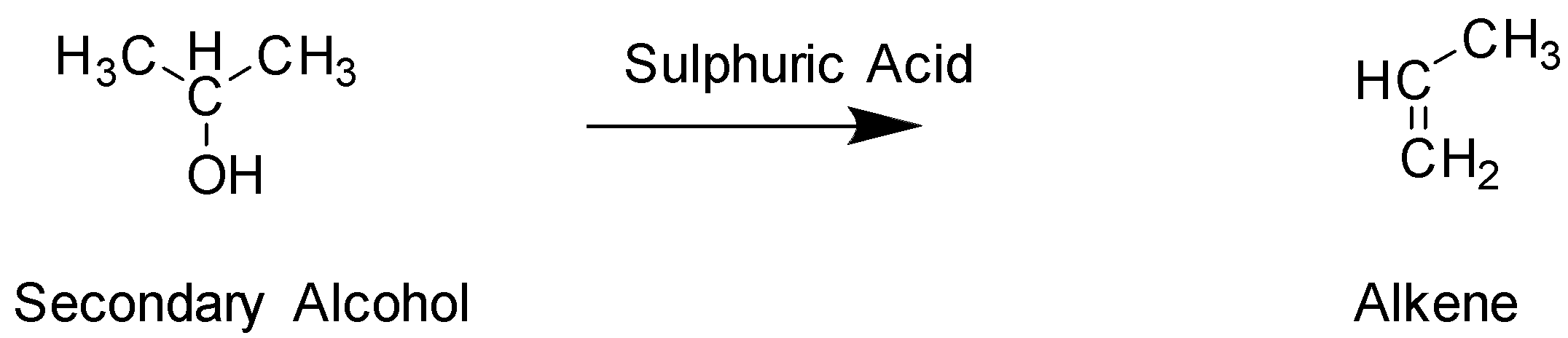
The next reaction with ${H_2}S{O_4}$ will lead to dehydrogenation and lead to the formation of alkene. This is compound B
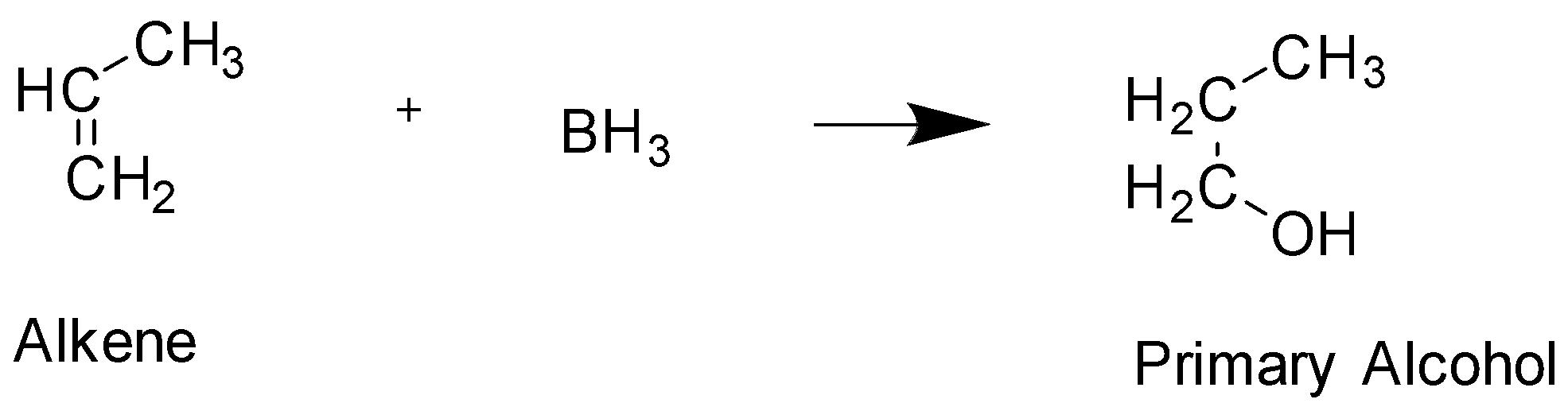
The next reaction is known as Hydroboration and it will lead to the formation of primary alcohol. This is compound C
From the above reactions, we can see that the starting product given to us is an aldehyde and the product in the end is a primary alcohol. In the question we have been asked to identify the relationship between A and C.

In The given structure , Primary Alcohol is Compound C In this structure the hydroxyl group $ - OH$ is added to the terminal carbon, whereas in Secondary alcohol which is compound A, The hydroxyl group is attached to the middle carbon. Hence, they are not identical. Both these alcohol have 3 carbons and the exact same molecular formula and only differ in the position of the functional group attached and hence they are positional isomers. The functional group in both these compounds is also alcohol, hence they cannot be functional isomers. They are not optical isomers since there is an absence of chiral carbon.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Functional isomerisation is only possible with two different functional groups. Alcoholic Organic compounds can show functional isomerisation with compounds with functional groups as ether. Aldehyde can show functional isomerism with Ketones.
Hydroboration reaction is used to form primary alcohol with alkenes. This reaction can be used to convert secondary alcohol to primary alcohol, even though the stability of secondary carbocation is more than primary carbocation.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction given to us in the question is a compound reaction and hence lets break it down into individual reactions. The first reaction is of acetaldehyde with Grignard reagent, $C{H_3}MgBr$
This reaction will give rise to secondary alcohol formation. This is compound A
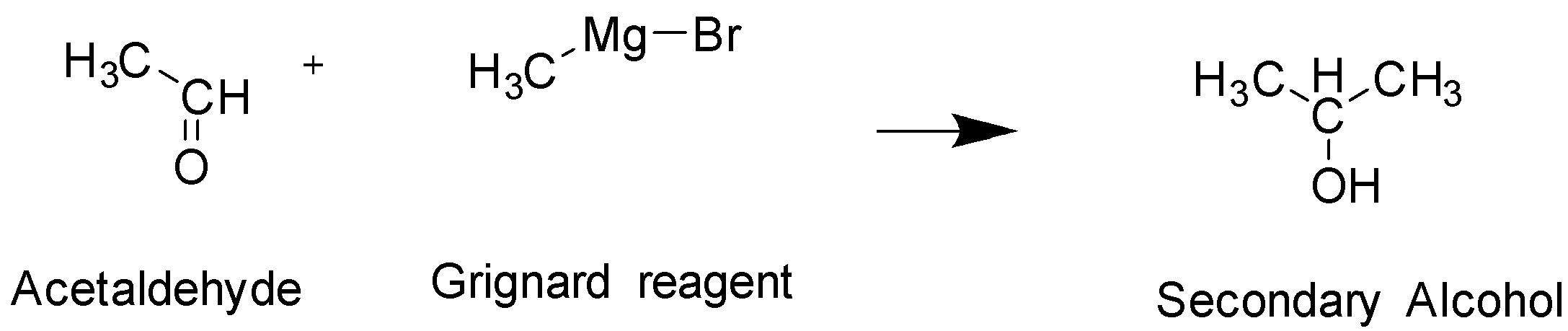
The next reaction with ${H_2}S{O_4}$ will lead to dehydrogenation and lead to the formation of alkene. This is compound B

The next reaction is known as Hydroboration and it will lead to the formation of primary alcohol. This is compound C

From the above reactions, we can see that the starting product given to us is an aldehyde and the product in the end is a primary alcohol. In the question we have been asked to identify the relationship between A and C.

In The given structure , Primary Alcohol is Compound C In this structure the hydroxyl group $ - OH$ is added to the terminal carbon, whereas in Secondary alcohol which is compound A, The hydroxyl group is attached to the middle carbon. Hence, they are not identical. Both these alcohol have 3 carbons and the exact same molecular formula and only differ in the position of the functional group attached and hence they are positional isomers. The functional group in both these compounds is also alcohol, hence they cannot be functional isomers. They are not optical isomers since there is an absence of chiral carbon.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Functional isomerisation is only possible with two different functional groups. Alcoholic Organic compounds can show functional isomerisation with compounds with functional groups as ether. Aldehyde can show functional isomerism with Ketones.
Hydroboration reaction is used to form primary alcohol with alkenes. This reaction can be used to convert secondary alcohol to primary alcohol, even though the stability of secondary carbocation is more than primary carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




