
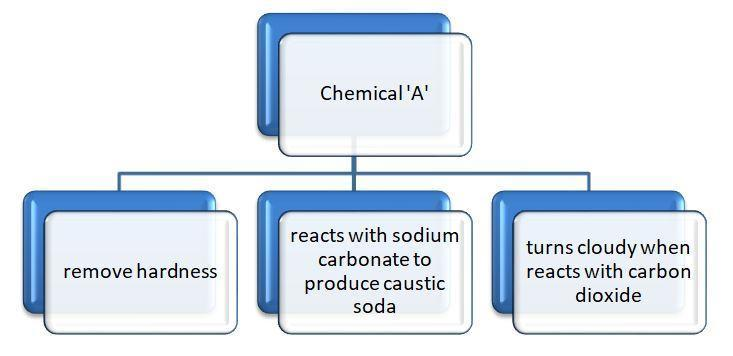
Chemical A is used for softening of water to remove temporary hardness. A reacts with sodium carbonate to produce caustic soda, when $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$ is bubbled through ‘A’, it turns cloudy. Chemically ‘A’ is:
A. $\text{CaO}$
B. $\text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}$
C. $\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{HC}{{\text{O}}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}$
D. $\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}$
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: The question can be easily solved when we will draw a step by step chart or flowchart of this question.
Hardness of water is the measure of calcium and magnesium bicarbonates whose hardness can be removed by converting these bicarbonate salts into carbonates.
On reaction with sodium carbonate, it gives its corresponding carbonate.
The milkiness in the solution is due to white coloured precipitate of metal carbonate.
Complete answer: Let us see the properties of chemical ‘A’ to find the common features shown by the chemical.
Property (1)- Use to remove temporary hardness: The hardness in the water is due to high concentrations of magnesium and calcium carbonates, chlorides, bicarbonates and sulphates.
Temporary hardness (bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium) can be removed by boiling and by Clarke’s method:
Clarke's reagent is calcium hydroxide. It removes water hardness by converting bicarbonates to carbonates. The reaction is $\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}+\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{HC}{{\text{O}}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}\to 2\text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\downarrow +2{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}$.
Property (2)- Turns solution milky when reacts with $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$ : When carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water, it turns milky because of the formation of calcium carbonate. The reaction is $\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}\left( \text{aq}\text{.} \right)+\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\left( \text{g} \right)\to \text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\downarrow \left( \text{s} \right)+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}\left( \text{l} \right)$.
Property (3)- Reacts with sodium carbonate to form caustic soda: Caustic soda is $\text{NaOH}$. The reaction is $\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}+\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\to 2\text{NaOH}+\text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}$.
The answer to this question is ‘d’. Calcium hydroxide is used to remove temporary hardness of water, reacts with sodium carbonate to form sodium hydroxide and the lime water turns milky when reacts with $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$.
Additional Information:
Uses of calcium hydroxide:
(1) Used as a flocculant in sewage treatment plants.
(2) Used as acid neutralizer because it is a weak base and used as a pH regulator in soil.
(3) Used as filler material in rubber and plastics.
Note: The options given in the question are little confusing inter-related, as all the options are the different compounds of calcium. The point is to remember the chemical used to remove temporary hardness. The answer will be much clearer from that only. The temporary hardness is removed by slaked lime ($\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}$) only.

Hardness of water is the measure of calcium and magnesium bicarbonates whose hardness can be removed by converting these bicarbonate salts into carbonates.
On reaction with sodium carbonate, it gives its corresponding carbonate.
The milkiness in the solution is due to white coloured precipitate of metal carbonate.
Complete answer: Let us see the properties of chemical ‘A’ to find the common features shown by the chemical.
Property (1)- Use to remove temporary hardness: The hardness in the water is due to high concentrations of magnesium and calcium carbonates, chlorides, bicarbonates and sulphates.
Temporary hardness (bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium) can be removed by boiling and by Clarke’s method:
Clarke's reagent is calcium hydroxide. It removes water hardness by converting bicarbonates to carbonates. The reaction is $\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}+\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{HC}{{\text{O}}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}\to 2\text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\downarrow +2{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}$.
Property (2)- Turns solution milky when reacts with $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$ : When carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water, it turns milky because of the formation of calcium carbonate. The reaction is $\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}\left( \text{aq}\text{.} \right)+\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\left( \text{g} \right)\to \text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\downarrow \left( \text{s} \right)+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}\left( \text{l} \right)$.
Property (3)- Reacts with sodium carbonate to form caustic soda: Caustic soda is $\text{NaOH}$. The reaction is $\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}+\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\to 2\text{NaOH}+\text{CaC}{{\text{O}}_{3}}$.
The answer to this question is ‘d’. Calcium hydroxide is used to remove temporary hardness of water, reacts with sodium carbonate to form sodium hydroxide and the lime water turns milky when reacts with $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$.
Additional Information:
Uses of calcium hydroxide:
(1) Used as a flocculant in sewage treatment plants.
(2) Used as acid neutralizer because it is a weak base and used as a pH regulator in soil.
(3) Used as filler material in rubber and plastics.
Note: The options given in the question are little confusing inter-related, as all the options are the different compounds of calcium. The point is to remember the chemical used to remove temporary hardness. The answer will be much clearer from that only. The temporary hardness is removed by slaked lime ($\text{Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{2}}$) only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




