
Calculate: $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint:To proceed with the solution first we will find out the sin value by using pythagoras theorem later we will use the properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions to find the value of the given expression.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the question. We have to find the value of $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \frac{3}{5}} \right)$
Now, to find the value of $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$
Let us assume that $
\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5} = \theta \\
\\
$
Then, $\dfrac{3}{5} = \sin \theta $
Or, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}....................(i)$
Now let us consider a right angled$\Delta ABC$, right angled at B.
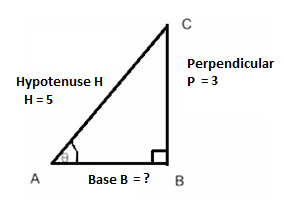
So, we know $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{hypotenuse}}....................(ii)$
So, comparing (i) and (ii) we get:
$\dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{hypotenuse}}$
That is, Perpendicular = 3 and Hypotenuse = 5.
Using Pythagoras Theorem:
$
{\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {base} \right)^2} + {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( 5 \right)^2} = {\left( {base} \right)^2} + {\left( 3 \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow 25 - 9 = {\left( {base} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {base} \right)^2} = 16 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {base} \right) = \sqrt {16} \\
\Rightarrow base = \pm 4 \\
$
Now, to find the value of $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$
Putting $\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5} = \theta $in $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$
It will now become as $\sin \left( {2\theta } \right)$
Now using the trigonometric formula for expanding $\sin \left( {2\theta } \right)$:
$\sin \left( {2\theta } \right) = 2\sin \theta \cos \theta $
So, using the values of the Right angled$\Delta ABC$,
We will get $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{hypotenuse}}$
So base=4 and hypotenuse = 5, putting these values we get
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}$,
So with $\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}$ and $\cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}$, the expression will now become:
$
\sin \left( {2\theta } \right) = 2\sin \theta \cos \theta \\
= 2 \times \dfrac{3}{5} \times \dfrac{4}{5} \\
= \dfrac{{24}}{{25}} \\
$
Hence, the value of $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{{24}}{{25}}$.
Note:While using the expansion for a trigonometric multiple angle like$\sin \left( {2\theta } \right)$, careful observation has to be made, if the trigonometric function taken is incorrect then the expansion will change and so will the corresponding solution. The expansion of trigonometric ratio is to be used depending on the trigonometric ratio mentioned in the term outside the arc trigonometric ratio. For example, instead of sin in $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$, if we have cos that is, $\cos \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$, then we will use the expansion of $\cos \left( {2\theta } \right)$,which is given as ${\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}\theta $ or $2{\cos ^2}\theta - 1$ or$1 - 2{\sin ^2}\theta $ .
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the question. We have to find the value of $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \frac{3}{5}} \right)$
Now, to find the value of $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$
Let us assume that $
\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5} = \theta \\
\\
$
Then, $\dfrac{3}{5} = \sin \theta $
Or, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}....................(i)$
Now let us consider a right angled$\Delta ABC$, right angled at B.

So, we know $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{hypotenuse}}....................(ii)$
So, comparing (i) and (ii) we get:
$\dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{hypotenuse}}$
That is, Perpendicular = 3 and Hypotenuse = 5.
Using Pythagoras Theorem:
$
{\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {base} \right)^2} + {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( 5 \right)^2} = {\left( {base} \right)^2} + {\left( 3 \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow 25 - 9 = {\left( {base} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {base} \right)^2} = 16 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {base} \right) = \sqrt {16} \\
\Rightarrow base = \pm 4 \\
$
Now, to find the value of $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$
Putting $\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5} = \theta $in $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$
It will now become as $\sin \left( {2\theta } \right)$
Now using the trigonometric formula for expanding $\sin \left( {2\theta } \right)$:
$\sin \left( {2\theta } \right) = 2\sin \theta \cos \theta $
So, using the values of the Right angled$\Delta ABC$,
We will get $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{hypotenuse}}$
So base=4 and hypotenuse = 5, putting these values we get
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}$,
So with $\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}$ and $\cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}$, the expression will now become:
$
\sin \left( {2\theta } \right) = 2\sin \theta \cos \theta \\
= 2 \times \dfrac{3}{5} \times \dfrac{4}{5} \\
= \dfrac{{24}}{{25}} \\
$
Hence, the value of $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{{24}}{{25}}$.
Note:While using the expansion for a trigonometric multiple angle like$\sin \left( {2\theta } \right)$, careful observation has to be made, if the trigonometric function taken is incorrect then the expansion will change and so will the corresponding solution. The expansion of trigonometric ratio is to be used depending on the trigonometric ratio mentioned in the term outside the arc trigonometric ratio. For example, instead of sin in $\sin \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$, if we have cos that is, $\cos \left( {2\arcsin \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)$, then we will use the expansion of $\cos \left( {2\theta } \right)$,which is given as ${\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}\theta $ or $2{\cos ^2}\theta - 1$ or$1 - 2{\sin ^2}\theta $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




