
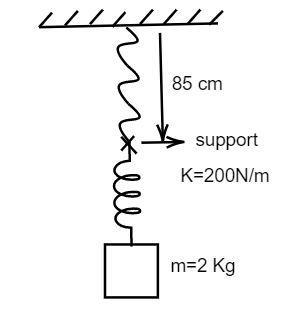
Block is at rest in equilibrium. Now suddenly support is removed so that upper end of spring is only connected with one end of spring having length $88\,cm$ , If acceleration of block and tension $i$ string just after removing the support is $a$ and $T$ ,
then-
(A) $a = Zero,\,T = 14$
(B) $a = 3\,m/{s^2},\,T = 14$
(C) $a = 3\,m/{s^2},\,T = 0$
(D) $T = 20\,N,\,a = Zero$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The spring is the elastic object that does not have deformation under a certain limit. It can withstand certain force and after releasing return back to its original position. Use the formula of the restoring force and calculate it. Apply this value in the formula of the tension, to find the value of tension of spring.
Useful formula:
The formula of the restoring force of the spring is given by
$F = kx$
Where $F$ is the restoring force of the spring, $k$ is the spring tension and the $x$ is the displacement of the spring.
(2) The tension of the string is given by
$T = W - F$
Where $T$ is the tension of the string and $W$ is the weight of the block suspended.
Complete step by step answer
It is given that the
Sum of the length of the spring and the string, $L = 88\,cm$
Length of the string, $l = 85\,cm$
Tension when the support is connected, $K = 200\,N{m^{ - 1}}$
Mass of the block, $m = 2\,Kg$
The length of the spring is obtained by subtracting the length of the spring and the string and the length of the string.
$l = 88 - 85 = 3\,cm$
Since the spring does not undergo deformation, there will be no acceleration of the block. Hence the acceleration of the block is zero.
Using the formula of the restoring force,
$F = kx$
Substituting the known values in it,
$F = 200 \times 0.03 = 6\,N$
Using the formula of the tension,
$T = W - F$
Substituting the weight as the product of the mass and the acceleration due to gravity and the calculated restoring force in it.
$T = mg - 6$
$T = 2 \times 10 - 6 = 14\,N$
Hence the tension of the string is calculated as $14\,N$ .
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note: The spring connected at the end of the string balances the support connected in between. So when the support is suddenly removed, this change in the tension and the force is balanced by the spring itself, since it is an elastic body. So no change in velocity will take place by the block. Hence its acceleration is zero and remains equilibrium.
Useful formula:
The formula of the restoring force of the spring is given by
$F = kx$
Where $F$ is the restoring force of the spring, $k$ is the spring tension and the $x$ is the displacement of the spring.
(2) The tension of the string is given by
$T = W - F$
Where $T$ is the tension of the string and $W$ is the weight of the block suspended.
Complete step by step answer
It is given that the
Sum of the length of the spring and the string, $L = 88\,cm$
Length of the string, $l = 85\,cm$
Tension when the support is connected, $K = 200\,N{m^{ - 1}}$
Mass of the block, $m = 2\,Kg$
The length of the spring is obtained by subtracting the length of the spring and the string and the length of the string.
$l = 88 - 85 = 3\,cm$
Since the spring does not undergo deformation, there will be no acceleration of the block. Hence the acceleration of the block is zero.
Using the formula of the restoring force,
$F = kx$
Substituting the known values in it,
$F = 200 \times 0.03 = 6\,N$
Using the formula of the tension,
$T = W - F$
Substituting the weight as the product of the mass and the acceleration due to gravity and the calculated restoring force in it.
$T = mg - 6$
$T = 2 \times 10 - 6 = 14\,N$
Hence the tension of the string is calculated as $14\,N$ .
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note: The spring connected at the end of the string balances the support connected in between. So when the support is suddenly removed, this change in the tension and the force is balanced by the spring itself, since it is an elastic body. So no change in velocity will take place by the block. Hence its acceleration is zero and remains equilibrium.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




