
At low temperatures, the slow addition of molecular bromine to \[C{{H}_{2}}=CH-C{{H}_{2}}-C\equiv CH\] gives
A.\[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - CBr = CHBr\]
B.\[BrC{H_2} - CHBr - C{H_2} - C \equiv CH\]
C.\[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CB{r_3}\]
D.\[C{H_3} - CB{r_2} - C{H_2} - C \equiv CH\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Molecular bromines get added to alkenes and alkynes using carbon tetrachloride as the common solvent. Alkenes are more reactive than reactive towards electrophilic addition reactions.
This reactivity depends on the reaction conditions.
Complete answer:The addition of molecular bromine is electrophilic.
Alkenes carry double bonds thus treatment with molecular bromine form 1,2-dibromides.
The bromine atoms get added to each carbon atom of the double bond.
Alkynes undergo a similar kind of electrophilic addition as alkenes with molecular bromine.
But in this addition, the halogen may be added one time or twice relying on the quantity of the halogen utilized in the reaction.
Here in this question, we are given a compound that contains both double and triple bonds.
Dihalo alkene is formed in this reaction.
Alkynes are usually less reactive than alkenes in electrophilic addition reactions as the pi-electrons are held extra tightly in triple bonds than in double bonds.
It is because triple bonds are stronger than double bonds.
It is also more sterically hard to construct a bromonium ion from an alkyne than from an alkene. This is because in the case of alkene carbocation is formed which is a 3-member ring with a double bond.
The organic reaction is either kinetically regulated or thermodynamically regulated.
For a kinetically controlled reaction, alkene would have undergone electrophilic addition first. This reaction would have happened faster.
The electrophilic addition of alkynes is slower than that of alkenes.
As the reaction is slow and at a low temperature, the product in which bromine gets added to the triple group will be formed.
This reaction is exothermic due to the strong nature of the triple bond.
So, it is a thermodynamically controlled product.
The reaction will happen as follows:-
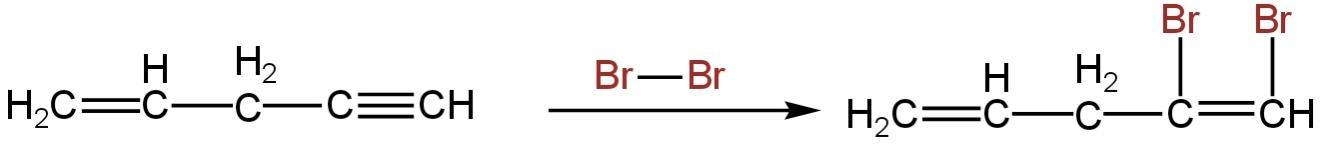
So, the product formed is \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - CBr = CHBr\].
So, option A is correct.
Note: Generally, addition reactions with alkynes are more exothermic than addition reactions with alkenes.
There are additional pi-electrons involved with the triple bond. The sp-hybridized alkyne carbons are highly electronegative as the s-character in sp-hybridization is 50 percent which is the highest.
So, carbon atoms exercise a powerful attraction for their pi-electrons, which are thus bound more tightly to the functional group than the pi-electrons of a double bond.
This reactivity depends on the reaction conditions.
Complete answer:The addition of molecular bromine is electrophilic.
Alkenes carry double bonds thus treatment with molecular bromine form 1,2-dibromides.
The bromine atoms get added to each carbon atom of the double bond.
Alkynes undergo a similar kind of electrophilic addition as alkenes with molecular bromine.
But in this addition, the halogen may be added one time or twice relying on the quantity of the halogen utilized in the reaction.
Here in this question, we are given a compound that contains both double and triple bonds.
Dihalo alkene is formed in this reaction.
Alkynes are usually less reactive than alkenes in electrophilic addition reactions as the pi-electrons are held extra tightly in triple bonds than in double bonds.
It is because triple bonds are stronger than double bonds.
It is also more sterically hard to construct a bromonium ion from an alkyne than from an alkene. This is because in the case of alkene carbocation is formed which is a 3-member ring with a double bond.
The organic reaction is either kinetically regulated or thermodynamically regulated.
For a kinetically controlled reaction, alkene would have undergone electrophilic addition first. This reaction would have happened faster.
The electrophilic addition of alkynes is slower than that of alkenes.
As the reaction is slow and at a low temperature, the product in which bromine gets added to the triple group will be formed.
This reaction is exothermic due to the strong nature of the triple bond.
So, it is a thermodynamically controlled product.
The reaction will happen as follows:-
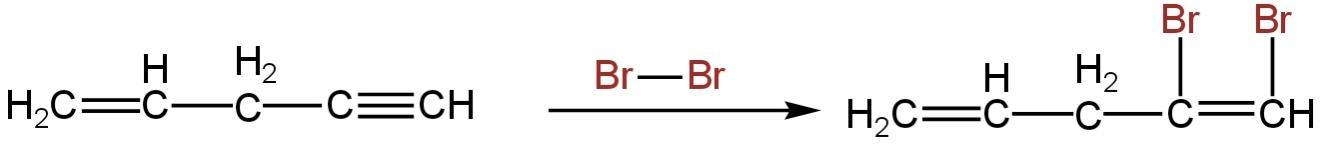
So, the product formed is \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - CBr = CHBr\].
So, option A is correct.
Note: Generally, addition reactions with alkynes are more exothermic than addition reactions with alkenes.
There are additional pi-electrons involved with the triple bond. The sp-hybridized alkyne carbons are highly electronegative as the s-character in sp-hybridization is 50 percent which is the highest.
So, carbon atoms exercise a powerful attraction for their pi-electrons, which are thus bound more tightly to the functional group than the pi-electrons of a double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




