
Assertion:
Hydrolysis of sucrose brings about a change in sign of rotation from laevo.
Reason:
Hydrolysis always changes the optical rotation of a compound.
A.)Both Assertion and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
B.) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
C.)Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D.)Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Answer
599.4k+ views
Hint: Sucrose is dextrorotatory and its specific rotation is \[ + 66.5\% \] and the specific rotation of dextrorotatory glucose is $ + 53$ and the fructose has a large negative rotation ${[a]_D} = - 92.4$ .
Complete step by step answer:
When hydrolysis of sucrose takes place, there is a change in the sign of rotation from dextro to laevo, because of this there is a change of optical rotation.
On hydrolysis sucrose gives equal parts of glucose and fructose due to the presence of optical isomers of mixture of glucose and fructose sugar, the angle of specific rotation of plane polarized light changes. The angle becomes negative from a positive value.
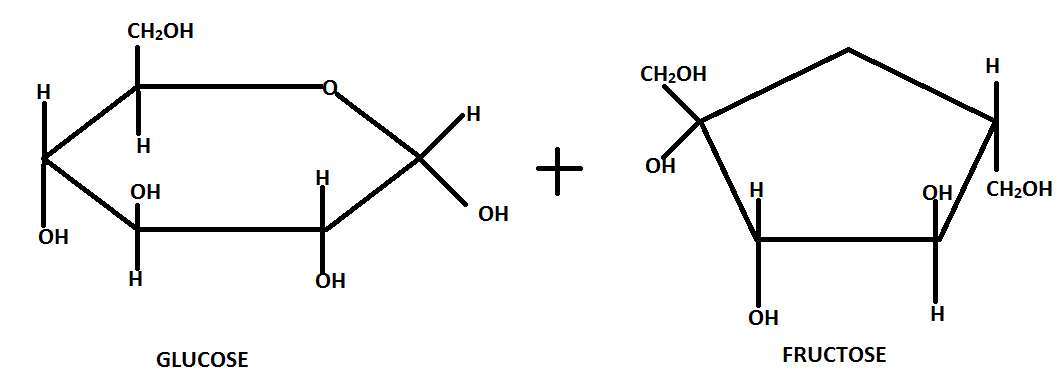
The glucose and fructose units are joined by an acetal oxygen bridge.
Sucrose is dextrorotatory in nature and on hydrolysis it gives dextrorotatory glucose and laevorotatory fructose.
Specific rotation of sucrose= \[ + 66.5\% \]
Dextrorotatory glucose’s specific rotation is ${[a]_D} = + 53$
Laevorotatory fructose has a large negative rotation ${[a]_D} = - 92.4$ because of the very high value of laevorotatory fructose the resulting mixture is laevorotatory.
So option-C is correct.
Note:
Hydrolysis of sucrose brings a change in sign of rotation. The sign changes from dextro to laevo and the resulting compound is known as invert sugar.
Complete step by step answer:
When hydrolysis of sucrose takes place, there is a change in the sign of rotation from dextro to laevo, because of this there is a change of optical rotation.
On hydrolysis sucrose gives equal parts of glucose and fructose due to the presence of optical isomers of mixture of glucose and fructose sugar, the angle of specific rotation of plane polarized light changes. The angle becomes negative from a positive value.

The glucose and fructose units are joined by an acetal oxygen bridge.
Sucrose is dextrorotatory in nature and on hydrolysis it gives dextrorotatory glucose and laevorotatory fructose.
Specific rotation of sucrose= \[ + 66.5\% \]
Dextrorotatory glucose’s specific rotation is ${[a]_D} = + 53$
Laevorotatory fructose has a large negative rotation ${[a]_D} = - 92.4$ because of the very high value of laevorotatory fructose the resulting mixture is laevorotatory.
So option-C is correct.
Note:
Hydrolysis of sucrose brings a change in sign of rotation. The sign changes from dextro to laevo and the resulting compound is known as invert sugar.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




