
Why can aromatic primary amines not be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is a type of chemical reaction in which the primary alkyl halides are converted into the primary amines in the presence of ethanolic potassium hydroxide. In the primary alkyl halides the halogen atoms such as fluorine, chlorine etc. are attached with the primary carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
In this process the sodium and potassium salt of phthalimide is N-alkylated with a primary alkyl halide and produces its corresponding N-alkyl phthalimide. When the hydrolysis of acid takes place, the primary amine is released as the amine salt. This reaction can also take place with hydrazine.
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}(CO)NR+{{N}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}{{(CO)}_{2}}{{N}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}+RN{{H}_{2}}\]
Phthalhydrazine is precipitated in this reaction when phthalimide react with ethanolic potassium hydroxide. This helps the nitrogen atoms to easily attach with the R group. But this transformation only takes place with primary haloalkane.
If we try to conduct the reaction with secondary alkyl halide the result obtained would not be perfect. The Gabriel phthalimide synthesis fails with secondary alkyl halide.
Aromatic primary amine cannot be formed by this reaction as the aryl halide does not undergo the nucleophilic substitution with the salt formed by phthalimide as it can be produced from aliphatic primary amines. A reaction is shown below:
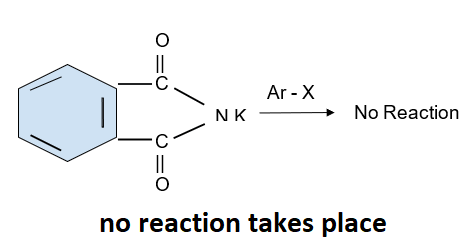
Note: In organic chemistry a nucleophilic substitution reaction is a fundamental reaction in which an electron rich compound which is the nucleophile replaces the leaving group in the compound. Nucleophile attacks on the positively charged species which is the electron deficient species.
Complete step by step answer:
In this process the sodium and potassium salt of phthalimide is N-alkylated with a primary alkyl halide and produces its corresponding N-alkyl phthalimide. When the hydrolysis of acid takes place, the primary amine is released as the amine salt. This reaction can also take place with hydrazine.
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}(CO)NR+{{N}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}{{(CO)}_{2}}{{N}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}+RN{{H}_{2}}\]
Phthalhydrazine is precipitated in this reaction when phthalimide react with ethanolic potassium hydroxide. This helps the nitrogen atoms to easily attach with the R group. But this transformation only takes place with primary haloalkane.
If we try to conduct the reaction with secondary alkyl halide the result obtained would not be perfect. The Gabriel phthalimide synthesis fails with secondary alkyl halide.
Aromatic primary amine cannot be formed by this reaction as the aryl halide does not undergo the nucleophilic substitution with the salt formed by phthalimide as it can be produced from aliphatic primary amines. A reaction is shown below:

Note: In organic chemistry a nucleophilic substitution reaction is a fundamental reaction in which an electron rich compound which is the nucleophile replaces the leaving group in the compound. Nucleophile attacks on the positively charged species which is the electron deficient species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




