
Why are transistors used in making NOT gates?
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: NOT gates are the logical gates which gives the negation of the input value as output. It is the basic logic gate among all the gates. A true input will produce a false output. This characteristic of NOT is widely used in electronics.
Complete answer:
A transistor, also known as a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), is a n-p-n or p-n-p device which has three terminals which can be used flexibly according to the user’s requirement. A transistor is a basic switch or amplifier. The switch property of a transistor is employed for NOT gates.
Let us consider a Common-emitter (CE configuration) type transistor. The CE transistors are well-known for their compatibility with low power and low frequency signals.
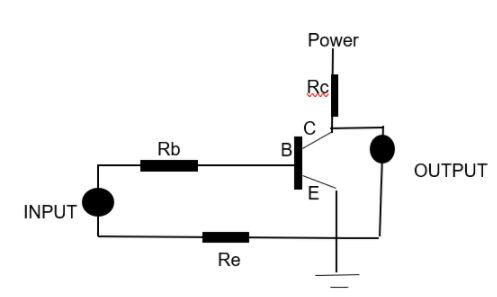
When we observe the output from such a CE transistor, we will notice that the output has high power when a lower power input is given. This is due to a phase shift that takes place in this configuration. A phase shift of a half cycle or 180degrees takes place in this type of transistor configuration. Such a phase shift has the ability to make a negated output always.
i.e., a high input power will give a low output and vice versa.
This property of transistors helps in switching operations in electronic devices and thus transistors are used as a NOT gate.
Additional Information:
The phase change is developed due to the reverse saturation current developed in the base-collector region even when the input is zero.
Note:
The base-collector region and base-emitter junction are reverse biased even when there is no input correct. This is due to the reverse saturation current developed in the base-collector region. In this case, there is no current flow from collector to emitter and it acts as an open switch. This allows the input current to directly reach the power supply through Rc.
Complete answer:
A transistor, also known as a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), is a n-p-n or p-n-p device which has three terminals which can be used flexibly according to the user’s requirement. A transistor is a basic switch or amplifier. The switch property of a transistor is employed for NOT gates.
Let us consider a Common-emitter (CE configuration) type transistor. The CE transistors are well-known for their compatibility with low power and low frequency signals.

When we observe the output from such a CE transistor, we will notice that the output has high power when a lower power input is given. This is due to a phase shift that takes place in this configuration. A phase shift of a half cycle or 180degrees takes place in this type of transistor configuration. Such a phase shift has the ability to make a negated output always.
i.e., a high input power will give a low output and vice versa.
This property of transistors helps in switching operations in electronic devices and thus transistors are used as a NOT gate.
Additional Information:
The phase change is developed due to the reverse saturation current developed in the base-collector region even when the input is zero.
Note:
The base-collector region and base-emitter junction are reverse biased even when there is no input correct. This is due to the reverse saturation current developed in the base-collector region. In this case, there is no current flow from collector to emitter and it acts as an open switch. This allows the input current to directly reach the power supply through Rc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




