
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image – distance $(v)$ with object – distance $(u)$ in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations:
a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
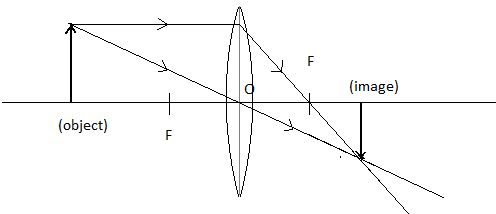
c) Select an approximate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2. Also give the approximate value of magnification.
S.No. Object Distance (cm) $(u)$ Image distance (cm) $v$ 1 -100 +25 2 -60 +30 3 -40 +40 4 -30 +60 5 -25 +100 6 -15 +120
| S.No. | Object Distance (cm) $(u)$ | Image distance (cm) $v$ |
| 1 | -100 | +25 |
| 2 | -60 | +30 |
| 3 | -40 | +40 |
| 4 | -30 | +60 |
| 5 | -25 | +100 |
| 6 | -15 | +120 |
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint:Try to remember the various ray diagrams for a convex lens, the position of the object and its image for all cases. You will get a faint idea of the positions of object and image given in the questions and will be able to answer the given questions.
Formula Used:
Magnification, $m = \dfrac{v}{u}$ where, $v$ is the image distance and $u$ is the object distance
Complete Step by Step Solution:
For part (a), we will look at the given readings. We can see in the reading number 3 that the object and image distance are equal (when taken face value). Also, we know that in case of a convex lens, when the object is at centre of curvature, the image distance and object distance are equal. Therefore, the centre of curvature of the given lens is at $40cm$ . Since centre of curvature is always twice the focal length, we can say that the focal length of the given lens is $20cm$
For part (b), we have the focal length of the lens equal to $20cm$ therefore, it is clear that for reading 6, the object is kept between focus and the centre of lens, often called O. remember that in this case, the image formed is virtual and is on the left side of the lens. Hence, the image distance should be negative, but it is given to be positive. Hence, reading 6 is incorrect.
For part (c), we will consider the reading 2 as given in question and use the above-mentioned formula for magnification. We have, $v = 30cm$ and $u = - 60cm$
Therefore, $m = \dfrac{{30}}{{ - 60}} = - \dfrac{1}{2} = - 0.5$ (The minus sign indicates the image is inverted)
Hence, the image is real, inverted and diminished.
Note:You need to study all the cases of convex/concave lens/mirror to ace at questions like these. Studying all the cases will help you relate the given values and hence you will be able to find answers more quickly and efficiently.
Formula Used:
Magnification, $m = \dfrac{v}{u}$ where, $v$ is the image distance and $u$ is the object distance
Complete Step by Step Solution:
For part (a), we will look at the given readings. We can see in the reading number 3 that the object and image distance are equal (when taken face value). Also, we know that in case of a convex lens, when the object is at centre of curvature, the image distance and object distance are equal. Therefore, the centre of curvature of the given lens is at $40cm$ . Since centre of curvature is always twice the focal length, we can say that the focal length of the given lens is $20cm$
For part (b), we have the focal length of the lens equal to $20cm$ therefore, it is clear that for reading 6, the object is kept between focus and the centre of lens, often called O. remember that in this case, the image formed is virtual and is on the left side of the lens. Hence, the image distance should be negative, but it is given to be positive. Hence, reading 6 is incorrect.
For part (c), we will consider the reading 2 as given in question and use the above-mentioned formula for magnification. We have, $v = 30cm$ and $u = - 60cm$
Therefore, $m = \dfrac{{30}}{{ - 60}} = - \dfrac{1}{2} = - 0.5$ (The minus sign indicates the image is inverted)
Hence, the image is real, inverted and diminished.

Note:You need to study all the cases of convex/concave lens/mirror to ace at questions like these. Studying all the cases will help you relate the given values and hence you will be able to find answers more quickly and efficiently.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




