
An object A of mass 1kg is projected vertically upward with a speed of$20m/s$. At the same moment another object B of mass 3kg, which is initially above the object A, is dropped from a height h=20m. The two point-like objects (A and B) collide and stick to each other. The kinetic energy is K (in J) of the combined mass just after collision, find the value of$\dfrac{K}{25}$ .
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: You could apply equations of motion separately for both the given objects and thus find the time taken to collide and also their velocities just before collision. Now you could apply the law of conservation of momentum to the given collision and then find the velocity of the combined mass after collision. Now you could substitute this velocity in the expression for kinetic energy and then get required value.
Formulae used:
Equations of motion,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}$
${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
$v=u+at$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question, we are given an object A of mass 1kg that is projected upwards at $20m/s$ and another object B of mass 3kg that was initially above A is dropped from h=20m. These two objects are said to stick together after colliding with each other. We are asked to find the value of $\dfrac{K}{25}$ if K is the kinetic energy of the combined mass after collision.
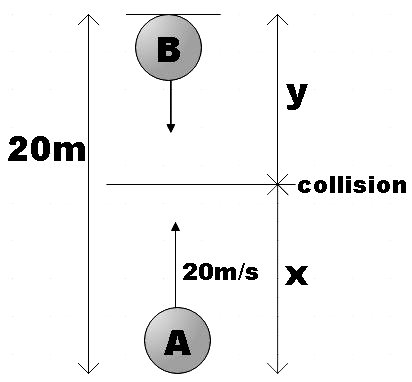
Let us assume that object A reaches a height x just before collision and object B travels a distance y downwards just before the collision. Let t be the time at which collision takes place, then,
For the case of object B,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}$
$y=0.5g{{t}^{2}}$ ……………………………………… (1)
Let us take, $g=10m{{s}^{-2}}$
$y=5m$ ……………………………………… (2)
Now for the case of object A,
$x=20t-0.5g{{t}^{2}}$
From (1),
$x=20t-y$
$x+y=20t$ …………………………. (3)
But sum of x and y will be the total height 20m, that is,
$x+y=20$ ……………………………………….. (4)
Comparing this with (3) we get,
$t=1s$ ……………………………………………… (5)
Therefore, we found the time taken for collision to be 1s.
Also, by substituting (2) in (4) gives,
$x=20-5=15m$ ………………………………….. (6)
Now, we have the equation of motion given by,
${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
As the object B is dropped B’s initial velocity will be zero, so,
$u=0$
$\Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}-0=2\times 10\times 5$
$\Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=100$
$\therefore {{v}_{B}}=10m{{s}^{-1}}$
We have another equation of motion given by,
$v=u+at$
So for object A,
$v=20-10\times 1$
$\therefore {{v}_{A}}=10m{{s}^{-1}}$
On applying law of conservation of angular momentum for the collision,
${{m}_{A}}{{v}_{A}}-{{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}=\left( {{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}} \right)v$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{{{m}_{A}}{{v}_{A}}-{{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}}{{{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}}}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{1\times 10-3\times 10}{1+3}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{-20}{4}$
$\therefore v=-5m{{s}^{-1}}$
So the velocity of the combined mass is found to be $-5m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Now let us find the kinetic energy of the combined mass after collision.
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}} \right){{v}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow K=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 4 \right){{5}^{2}}$
$\therefore K=50J$
But we are asked to find the value of $\dfrac{K}{25}$ .
$\dfrac{K}{25}=\dfrac{50}{25}$
$\therefore \dfrac{K}{25}=2J$
Note:
Though solving numerical problems for one dimensional motion is pretty easy, one should be careful with the directions and hence the sign. Also, after collision both objects are said to stick together and hence we have the substitute accordingly for the law of conservation of momentum. And we have taken $g=10m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Formulae used:
Equations of motion,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}$
${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
$v=u+at$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question, we are given an object A of mass 1kg that is projected upwards at $20m/s$ and another object B of mass 3kg that was initially above A is dropped from h=20m. These two objects are said to stick together after colliding with each other. We are asked to find the value of $\dfrac{K}{25}$ if K is the kinetic energy of the combined mass after collision.

Let us assume that object A reaches a height x just before collision and object B travels a distance y downwards just before the collision. Let t be the time at which collision takes place, then,
For the case of object B,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}$
$y=0.5g{{t}^{2}}$ ……………………………………… (1)
Let us take, $g=10m{{s}^{-2}}$
$y=5m$ ……………………………………… (2)
Now for the case of object A,
$x=20t-0.5g{{t}^{2}}$
From (1),
$x=20t-y$
$x+y=20t$ …………………………. (3)
But sum of x and y will be the total height 20m, that is,
$x+y=20$ ……………………………………….. (4)
Comparing this with (3) we get,
$t=1s$ ……………………………………………… (5)
Therefore, we found the time taken for collision to be 1s.
Also, by substituting (2) in (4) gives,
$x=20-5=15m$ ………………………………….. (6)
Now, we have the equation of motion given by,
${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
As the object B is dropped B’s initial velocity will be zero, so,
$u=0$
$\Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}-0=2\times 10\times 5$
$\Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=100$
$\therefore {{v}_{B}}=10m{{s}^{-1}}$
We have another equation of motion given by,
$v=u+at$
So for object A,
$v=20-10\times 1$
$\therefore {{v}_{A}}=10m{{s}^{-1}}$
On applying law of conservation of angular momentum for the collision,
${{m}_{A}}{{v}_{A}}-{{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}=\left( {{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}} \right)v$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{{{m}_{A}}{{v}_{A}}-{{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}}{{{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}}}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{1\times 10-3\times 10}{1+3}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{-20}{4}$
$\therefore v=-5m{{s}^{-1}}$
So the velocity of the combined mass is found to be $-5m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Now let us find the kinetic energy of the combined mass after collision.
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}} \right){{v}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow K=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 4 \right){{5}^{2}}$
$\therefore K=50J$
But we are asked to find the value of $\dfrac{K}{25}$ .
$\dfrac{K}{25}=\dfrac{50}{25}$
$\therefore \dfrac{K}{25}=2J$
Note:
Though solving numerical problems for one dimensional motion is pretty easy, one should be careful with the directions and hence the sign. Also, after collision both objects are said to stick together and hence we have the substitute accordingly for the law of conservation of momentum. And we have taken $g=10m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




