
An ideal dipole of dipole moment $$\vec p$$ is placed in front of an uncharged conducting sphere of radius $R$ as shown:
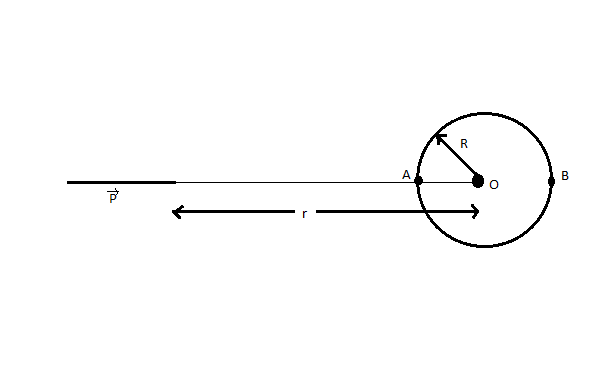
A. The potential at point A is $\dfrac{{KP}}{{{{\left( {r - R} \right)}^2}}}$
B. The potential at point A is $\dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$
C. The potential due to dipole at point B is $\dfrac{{KP}}{{{{\left( {r + R} \right)}^2}}}$
D. The potential due to dipole at point B is $\dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Here, we will let the sphere as an uncharged conductor and the dipole is placed in front of this sphere. A dipole is defined as the pair of equal and opposite charged material or magnetized material that are separated by a certain distance.
Complete step by step answer:
Potential is defined as the ability or power required for something to happen.
In the case of an uncharged sphere, the potential at the surface is equal to the potential inside the sphere i.e. ${V_A} = {V_0}$
Where ${V_A}$ is the potential at the surface of the sphere and ${V_0}$ is the potential inside the sphere.
Now, potential inside the sphere, ${V_0} = $potential at the center O due to the dipole + potential at the center O due to the sphere
Now, the potential at the center O due to the dipole is, $\dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where, $K$ is the constant, $P$ is the dipole, and $r$ is the distance of dipole from the center of the sphere.
Also, in the case of an uncharged sphere, the potential at O due to the sphere is zero.
Therefore, ${V_0} = \dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}} + 0$
$ \Rightarrow \,{V_0} = \dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$
As we know, the potential at the surface of the sphere is equal to the potential inside the sphere, therefore,
${V_A} = {V_0} = \dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$
Therefore, the potential at A is $\dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$.
Hence, option B is the correct option.
Note: The potential at any point throughout the volume of a charged conductor is constant and the value of the potential at the surface of the charged conductor is equal to the potential at that point inside the volume of the conductor.
Also, the electric field inside the conductor is zero at all the points, therefore the potential difference inside the conductor will remain constant throughout the volume of the conductor.
Complete step by step answer:
Potential is defined as the ability or power required for something to happen.
In the case of an uncharged sphere, the potential at the surface is equal to the potential inside the sphere i.e. ${V_A} = {V_0}$
Where ${V_A}$ is the potential at the surface of the sphere and ${V_0}$ is the potential inside the sphere.
Now, potential inside the sphere, ${V_0} = $potential at the center O due to the dipole + potential at the center O due to the sphere
Now, the potential at the center O due to the dipole is, $\dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where, $K$ is the constant, $P$ is the dipole, and $r$ is the distance of dipole from the center of the sphere.
Also, in the case of an uncharged sphere, the potential at O due to the sphere is zero.
Therefore, ${V_0} = \dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}} + 0$
$ \Rightarrow \,{V_0} = \dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$
As we know, the potential at the surface of the sphere is equal to the potential inside the sphere, therefore,
${V_A} = {V_0} = \dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$
Therefore, the potential at A is $\dfrac{{KP}}{{{r^2}}}$.
Hence, option B is the correct option.
Note: The potential at any point throughout the volume of a charged conductor is constant and the value of the potential at the surface of the charged conductor is equal to the potential at that point inside the volume of the conductor.
Also, the electric field inside the conductor is zero at all the points, therefore the potential difference inside the conductor will remain constant throughout the volume of the conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




