
Among sodium phosphate, sodium sulphate and sodium chloride the solubility in water decreases as:
A.sulphate>phosphate>chloride
B.chloride>suphate>phosphate
C.chloride>phosphate>sulphate
D.phosphate>chloride>sulphate
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: We know that like dissolves like. If both the solute and solvent are polar in nature the solubility tends to be maximum. Above given compounds are ionic in nature hence in a polar solvent like water higher polarization will cause less solubility. The cation sodium is same in all the compounds it is the anions ($SO_4^{2 - },PO_4^{3 - },C{l^{2 - }}$ ) that will affect the trend of solubility.
Step by step answer:
As the size of anion increases hydration energy decreases. Hydration energy is the energy released when ions dissociate to undergo hydration. More the hydration energy more the solubility. Anion size decreases as one goes from left to right in the periodic table. Solubility decreases with increase of atomic number.
Polarization effect is explained by Fajan’s rule that says when a cation approaches an anion , the electron cloud of the anion is attracted towards the cation and hence gets distorted.
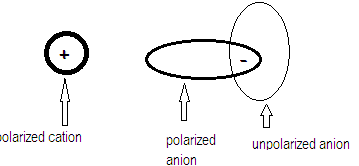
Larger the anion greater is the polarizability and greater the charge on anion more easily it gets polarized thereby imparting more covalent character to the compound leading to lesser solubility. Covalent character increase in the order:
$
NaCl < N{a_2}S{O_4} < N{a_3}P{O_4} \\
\\
$
Lattice energy is defined as the amount of the energy required to separate one mole of solid ionic compound into gaseous ions. Evidently greater the lattice energy lower is its solubility in water.
Hence the correct answer is option (A) sulphate>phosphate>chloride
Note: One must be careful while solving questions related to trends in solubility, enthalpy and ionization energy because a lot of factors go into determining it. Hence one should not hurry and analyze all the factors before coming to the conclusion. Periodic table also has a lot of exceptions such as the diagonal relationship between Li and Be so one should keep in mind all the exceptions as well.
Step by step answer:
As the size of anion increases hydration energy decreases. Hydration energy is the energy released when ions dissociate to undergo hydration. More the hydration energy more the solubility. Anion size decreases as one goes from left to right in the periodic table. Solubility decreases with increase of atomic number.
Polarization effect is explained by Fajan’s rule that says when a cation approaches an anion , the electron cloud of the anion is attracted towards the cation and hence gets distorted.

Larger the anion greater is the polarizability and greater the charge on anion more easily it gets polarized thereby imparting more covalent character to the compound leading to lesser solubility. Covalent character increase in the order:
$
NaCl < N{a_2}S{O_4} < N{a_3}P{O_4} \\
\\
$
Lattice energy is defined as the amount of the energy required to separate one mole of solid ionic compound into gaseous ions. Evidently greater the lattice energy lower is its solubility in water.
Hence the correct answer is option (A) sulphate>phosphate>chloride
Note: One must be careful while solving questions related to trends in solubility, enthalpy and ionization energy because a lot of factors go into determining it. Hence one should not hurry and analyze all the factors before coming to the conclusion. Periodic table also has a lot of exceptions such as the diagonal relationship between Li and Be so one should keep in mind all the exceptions as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




