
All are membrane-bound cell organelles except
A. Mitochondria
B. Spherosomes
C.Ribosomes
D. Lysosomes
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Most of the cell organelles are enclosed by a semipermeable membrane, although there are some membrane-less organelles too within the cell.
The membrane-less cell organelle among the given options are macromolecules that contain both RNA and proteins and are extremely crucial in the process of translation.
Complete answer: Ribosomes are free-floating membrane-less cell organelles in the cytoplasm. They can be divided into two subunits which are different in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
The lack of membrane is a strategic plan in order to facilitate the process of translation where a long chain of amino acids is produced.
During the process of translation, they are bound to the ER membrane but during the rest period, they can float freely in the cytoplasm which helps them to pick up translational RNA which are essentially released from the nucleus. It also enables them to grab free amino acids and later produce long protein chains hence they have dual adaptation.
Being a non-membrane bound organelle, they are more solid in nature and are not fluid-filled along with ribosomes, cell organelles like the lysosomes, peroxisomes, Golgi bodies, and vacuoles.
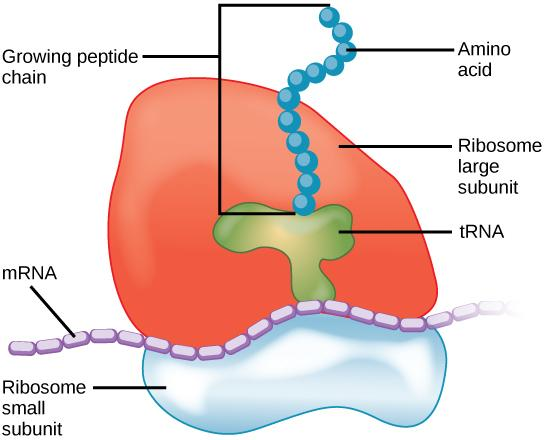
So, the correct answer is option C. Ribosomes.
Note: During the extensive process of translation, the two ribosomal subunits join together just like a sandwich on the messenger RNA strand and attract the tRNA molecules. A long chain of amino acids called polypeptide chains (after undergoing post-translational processing) emerges as the ribosome decodes the mRNA sequence.
The membrane-less cell organelle among the given options are macromolecules that contain both RNA and proteins and are extremely crucial in the process of translation.
Complete answer: Ribosomes are free-floating membrane-less cell organelles in the cytoplasm. They can be divided into two subunits which are different in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
The lack of membrane is a strategic plan in order to facilitate the process of translation where a long chain of amino acids is produced.
During the process of translation, they are bound to the ER membrane but during the rest period, they can float freely in the cytoplasm which helps them to pick up translational RNA which are essentially released from the nucleus. It also enables them to grab free amino acids and later produce long protein chains hence they have dual adaptation.
Being a non-membrane bound organelle, they are more solid in nature and are not fluid-filled along with ribosomes, cell organelles like the lysosomes, peroxisomes, Golgi bodies, and vacuoles.

So, the correct answer is option C. Ribosomes.
Note: During the extensive process of translation, the two ribosomal subunits join together just like a sandwich on the messenger RNA strand and attract the tRNA molecules. A long chain of amino acids called polypeptide chains (after undergoing post-translational processing) emerges as the ribosome decodes the mRNA sequence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




