
Account for the following:
(i) Primary amines ($R-{ NH }_{ 2 }$) have higher boiling point than tertiary amines (${ R }_{ 3 }N$).
(ii) Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(iii) ${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 2 }NH$ is more basic than ${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 3 }N$ in an aqueous solution.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: Primary and secondary amines undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding due to the presence of two and one hydrogen atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom in the amino group respectively. $ Al{ Cl }_{ 3 }$ is used in the Friedel-Crafts reaction as a Lewis acid.
Complete answer:
(i) Let us look at the first part.
Primary and secondary amines undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding due to the presence of two and one hydrogen atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom in the amino group respectively. Since tertiary amines do not have any hydrogen atom bonded to the nitrogen atom of their amino group therefore they cannot undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Due to the presence of the intermolecular hydrogen bonding in primary and secondary amines, the molecules are held together weakly and more temperature will be required to break this hydrogen bonding than in the case of tertiary amines and hence the boiling point of primary amines is higher than that of tertiary amines.
(ii) $ Al{ Cl }_{ 3 }$ is used in the Friedel-Crafts reaction as a Lewis acid. Aniline is a Lewis base and hence it reacts with $ Al{ Cl }_{ 3 }$ and forms a salt. The reaction is given below:
$ \begin{matrix} { AlCl }_{ 3 } \\ Lewis\quad acid \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 5 }{ NH }_{ 2 } \\ Aniline(Lewis\quad base) \end{matrix}\rightarrow \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 5 }\overset { + }{ { NH }_{ 2 } } Al{ Cl }_{ 3 }^{ - } \\ Salt \end{matrix}$
Due to the formation of the salt, the nitrogen atom of the amino group acquires a positive charge due to which it acts as a strong electron withdrawing group thereby reducing the electron density in the benzene ring. Hence aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(iii) In accordance with the Inductive effect ${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 3 }N$ should be more basic than ${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 2 }NH$ and it is so in the gaseous phase but in aqueous phase other factors beside the inductive effect also determine the basicity of an amine. These factors include (a) stability of their conjugate acids due to hydrogen bonding and (b) steric effects of the alkyl groups.
Greater the number of the hydrogen atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom of the amino group, more will be the number of hydrogen bonds with water molecules and hence more stable will be the conjugate acid. The conjugate acid of secondary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 2 }NH$) forms two hydrogen bonds with the water molecules while the conjugate acid of the tertiary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 3 }N$) forms only one hydrogen bond with the water molecules. This is shown below:
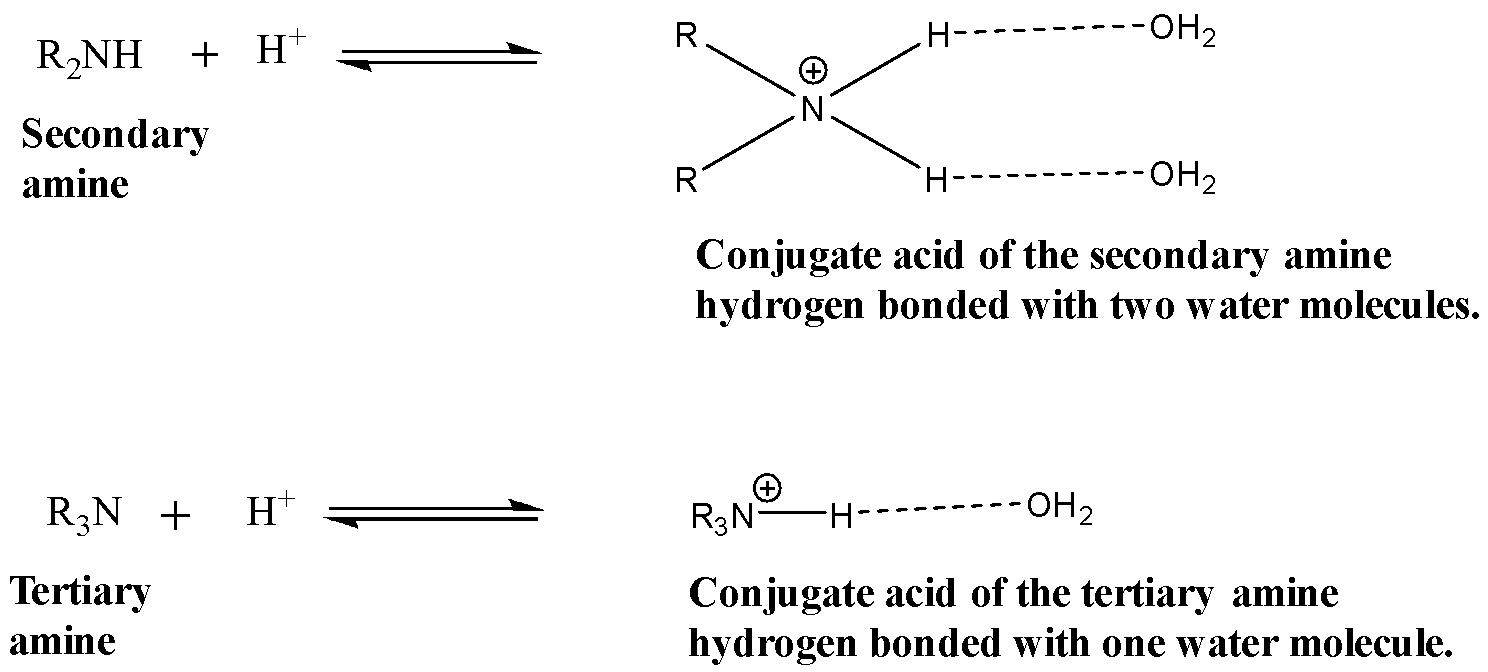
Because of the presence of three alkyl groups in the tertiary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 3 }N$) the hydrogen bonding between the water molecule and the conjugate acid will further decrease due to steric hindrance.
The +I effect, the stability of the conjugate acid due to hydrogen bonding and steric factors are all in favour of the secondary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 2 }NH$) and hence it is stronger base than the tertiary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 3 }N$).
Note: Among the different types of amines, the secondary amines are the strongest bases in the aqueous medium. If the alkyl group attached to the amino group is small i.e. it is a methyl group then the stability of the conjugate acid due to hydrogen bonding in the case of primary amines will dominate over the strong +I effect in tertiary amines and hence such a primary amine (Methylamine) will be more basic than the tertiary amine (Trimethylamine). But if the alkyl group is bulky i.e. ethyl or any other alkyl then there will be steric hindrance to the hydrogen bonding due to which the +I effect of the tertiary amine will dominate over the stability of the conjugate acid of the primary amine due to hydrogen bonding. Therefore in this case, the tertiary amine will be more basic than the primary amine.
Complete answer:
(i) Let us look at the first part.
Primary and secondary amines undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding due to the presence of two and one hydrogen atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom in the amino group respectively. Since tertiary amines do not have any hydrogen atom bonded to the nitrogen atom of their amino group therefore they cannot undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Due to the presence of the intermolecular hydrogen bonding in primary and secondary amines, the molecules are held together weakly and more temperature will be required to break this hydrogen bonding than in the case of tertiary amines and hence the boiling point of primary amines is higher than that of tertiary amines.
(ii) $ Al{ Cl }_{ 3 }$ is used in the Friedel-Crafts reaction as a Lewis acid. Aniline is a Lewis base and hence it reacts with $ Al{ Cl }_{ 3 }$ and forms a salt. The reaction is given below:
$ \begin{matrix} { AlCl }_{ 3 } \\ Lewis\quad acid \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 5 }{ NH }_{ 2 } \\ Aniline(Lewis\quad base) \end{matrix}\rightarrow \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 5 }\overset { + }{ { NH }_{ 2 } } Al{ Cl }_{ 3 }^{ - } \\ Salt \end{matrix}$
Due to the formation of the salt, the nitrogen atom of the amino group acquires a positive charge due to which it acts as a strong electron withdrawing group thereby reducing the electron density in the benzene ring. Hence aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(iii) In accordance with the Inductive effect ${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 3 }N$ should be more basic than ${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 2 }NH$ and it is so in the gaseous phase but in aqueous phase other factors beside the inductive effect also determine the basicity of an amine. These factors include (a) stability of their conjugate acids due to hydrogen bonding and (b) steric effects of the alkyl groups.
Greater the number of the hydrogen atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom of the amino group, more will be the number of hydrogen bonds with water molecules and hence more stable will be the conjugate acid. The conjugate acid of secondary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 2 }NH$) forms two hydrogen bonds with the water molecules while the conjugate acid of the tertiary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 3 }N$) forms only one hydrogen bond with the water molecules. This is shown below:

Because of the presence of three alkyl groups in the tertiary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 3 }N$) the hydrogen bonding between the water molecule and the conjugate acid will further decrease due to steric hindrance.
The +I effect, the stability of the conjugate acid due to hydrogen bonding and steric factors are all in favour of the secondary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 2 }NH$) and hence it is stronger base than the tertiary amine (${ (C{ H }_{ 3 }) }_{ 3 }N$).
Note: Among the different types of amines, the secondary amines are the strongest bases in the aqueous medium. If the alkyl group attached to the amino group is small i.e. it is a methyl group then the stability of the conjugate acid due to hydrogen bonding in the case of primary amines will dominate over the strong +I effect in tertiary amines and hence such a primary amine (Methylamine) will be more basic than the tertiary amine (Trimethylamine). But if the alkyl group is bulky i.e. ethyl or any other alkyl then there will be steric hindrance to the hydrogen bonding due to which the +I effect of the tertiary amine will dominate over the stability of the conjugate acid of the primary amine due to hydrogen bonding. Therefore in this case, the tertiary amine will be more basic than the primary amine.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




