
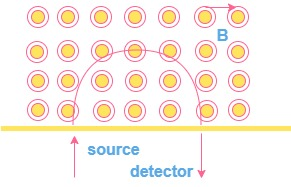
A uniform magnetic field with a slit system shown in fig. is to be used as a momentum filter for high energy charged particles. With a field B tesla, it is found that the filter transmits $ \alpha $ -particles each of energy $ 5\cdot 3 $ MeV. The magnetic field is increased to $ 2\cdot 3 $ B Tesla and deuterons are passed into the filter. The energy of each deuteron transmitted by the filter is…
(A) 5MeV
(B) 7MeV
(C) 14MeV
(D) 21MeV

Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint : The centripetal force required by the ion to move in a circular path is provided by the perpendicular magnetic field B.
$ qvB=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r} $
m is mass of charge particle to be accelerated, B is magnetic field, q is charge on particle, v is velocity of charge particle, r is radius of circular path.
The energy of particle is given $ E=\dfrac{{{p}^{2}}}{2m} $
p is the momentum of a particle.
Using the above formulas we will get the required result.
Complete step by step solution:
We have given, high energy charge particle in the magnetic field B Tesla.
Radius of charge particle is given by,
$ \begin{align}
& r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}=\dfrac{P}{qB} \\
& \therefore r=\dfrac{\sqrt{2Em}}{Bq} \\
\end{align} $
Radius in case of $ \alpha $ -particles
$ {{r}_{\alpha }}=\dfrac{{{\sqrt{2{{E}_{\alpha }}m}}_{\alpha }}}{B{{q}_{\alpha }}} $
Radius in case of deuteron –particle is given by
$ {{r}_{d}}=\dfrac{{{\sqrt{2{{E}_{d}}m}}_{d}}}{2.3B{{q}_{d}}} $
Since the radius for both the particle is same
$ \dfrac{{{\sqrt{2{{E}_{\alpha }}m}}_{\alpha }}}{B{{q}_{\alpha }}}=\dfrac{{{\sqrt{2{{E}_{d}}m}}_{d}}}{2\cdot 3B{{q}_{d}}} $
Squaring on both sides
$ \dfrac{2{{E}_{\alpha }}{{m}_{\alpha }}}{{{q}_{\alpha }}^{2}}=\dfrac{2{{E}_{d}}{{m}_{d}}}{{{\left( 2\cdot 3 \right)}^{2}}{{q}_{d}}^{2}} $ ---- (1)
Since,
$ \dfrac{{{q}_{d}}}{{{q}_{\alpha }}}=\dfrac{e}{2e}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
qd is charge on deuteron, $ {{q}_{\alpha }} $ is charge on $ \alpha $ -particle
$ \dfrac{{{m}_{\alpha }}}{{{m}_{d}}}=\dfrac{4}{2}=2 $
$ {{m}_{\alpha }} $ is mass of $ \alpha $ -particle, $ {{m}_{d}} $ is mass of deuteron
$ {{E}_{\alpha }} $ (energy of $ \alpha $ -particle = 5.3 MeV
Put all in eq. (1)
$ \begin{align}
& {{\left( 2.3 \right)}^{2}}\times {{\left( \dfrac{{{q}_{d}}}{{{q}_{\alpha }}} \right)}^{2}}\dfrac{{{E}_{\alpha }}{{m}_{\alpha }}}{{{m}_{d}}}={{E}_{d}} \\
& {{\left( 2.3 \right)}^{2}}\times {{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}\times 5.3MeV(2)={{E}_{d}} \\
\end{align} $
Energy of deuteron particle is given by,
$ \begin{align}
& {{E}_{d}}={{\dfrac{\left( 2.3 \right)}{4}}^{2}}\times 2\times 5.3MeV \\
& {{E}_{d}}=14.01MeV \\
\end{align} $ .
Note:
Motion of charge particle in magnetic field explained below:
Then the centripetal force acquired by charged particle to move in circular path is provided by perpendicular magnetic field B is given by
$ {{F}_{e}}=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r} $ --- (1)
$ {{F}_{b}}=qvB $ --- (2)
From eq (1) and (2)
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}=qvB \\
& \dfrac{mv}{r}=Bq \\
\end{align} $
$ r=\dfrac{mv}{qB} $ This is the radius of circular path.
The momentum of particle is given
$ P=mv $
And energy of particle is,
$ E=\dfrac{{{P}^{2}}}{2m} $
Or
$ P=\sqrt{2mE} $ ,
Radius of charge particle is given by
$ \begin{align}
& r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}=\dfrac{P}{qB} \\
& \therefore r=\dfrac{\sqrt{2Em}}{Bq} \\
\end{align} $.
$ qvB=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r} $
m is mass of charge particle to be accelerated, B is magnetic field, q is charge on particle, v is velocity of charge particle, r is radius of circular path.
The energy of particle is given $ E=\dfrac{{{p}^{2}}}{2m} $
p is the momentum of a particle.
Using the above formulas we will get the required result.
Complete step by step solution:
We have given, high energy charge particle in the magnetic field B Tesla.
Radius of charge particle is given by,
$ \begin{align}
& r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}=\dfrac{P}{qB} \\
& \therefore r=\dfrac{\sqrt{2Em}}{Bq} \\
\end{align} $
Radius in case of $ \alpha $ -particles
$ {{r}_{\alpha }}=\dfrac{{{\sqrt{2{{E}_{\alpha }}m}}_{\alpha }}}{B{{q}_{\alpha }}} $
Radius in case of deuteron –particle is given by
$ {{r}_{d}}=\dfrac{{{\sqrt{2{{E}_{d}}m}}_{d}}}{2.3B{{q}_{d}}} $
Since the radius for both the particle is same
$ \dfrac{{{\sqrt{2{{E}_{\alpha }}m}}_{\alpha }}}{B{{q}_{\alpha }}}=\dfrac{{{\sqrt{2{{E}_{d}}m}}_{d}}}{2\cdot 3B{{q}_{d}}} $
Squaring on both sides
$ \dfrac{2{{E}_{\alpha }}{{m}_{\alpha }}}{{{q}_{\alpha }}^{2}}=\dfrac{2{{E}_{d}}{{m}_{d}}}{{{\left( 2\cdot 3 \right)}^{2}}{{q}_{d}}^{2}} $ ---- (1)
Since,
$ \dfrac{{{q}_{d}}}{{{q}_{\alpha }}}=\dfrac{e}{2e}=\dfrac{1}{2} $
qd is charge on deuteron, $ {{q}_{\alpha }} $ is charge on $ \alpha $ -particle
$ \dfrac{{{m}_{\alpha }}}{{{m}_{d}}}=\dfrac{4}{2}=2 $
$ {{m}_{\alpha }} $ is mass of $ \alpha $ -particle, $ {{m}_{d}} $ is mass of deuteron
$ {{E}_{\alpha }} $ (energy of $ \alpha $ -particle = 5.3 MeV
Put all in eq. (1)
$ \begin{align}
& {{\left( 2.3 \right)}^{2}}\times {{\left( \dfrac{{{q}_{d}}}{{{q}_{\alpha }}} \right)}^{2}}\dfrac{{{E}_{\alpha }}{{m}_{\alpha }}}{{{m}_{d}}}={{E}_{d}} \\
& {{\left( 2.3 \right)}^{2}}\times {{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}\times 5.3MeV(2)={{E}_{d}} \\
\end{align} $
Energy of deuteron particle is given by,
$ \begin{align}
& {{E}_{d}}={{\dfrac{\left( 2.3 \right)}{4}}^{2}}\times 2\times 5.3MeV \\
& {{E}_{d}}=14.01MeV \\
\end{align} $ .
Note:
Motion of charge particle in magnetic field explained below:
Then the centripetal force acquired by charged particle to move in circular path is provided by perpendicular magnetic field B is given by
$ {{F}_{e}}=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r} $ --- (1)
$ {{F}_{b}}=qvB $ --- (2)
From eq (1) and (2)
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}=qvB \\
& \dfrac{mv}{r}=Bq \\
\end{align} $
$ r=\dfrac{mv}{qB} $ This is the radius of circular path.
The momentum of particle is given
$ P=mv $
And energy of particle is,
$ E=\dfrac{{{P}^{2}}}{2m} $
Or
$ P=\sqrt{2mE} $ ,
Radius of charge particle is given by
$ \begin{align}
& r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}=\dfrac{P}{qB} \\
& \therefore r=\dfrac{\sqrt{2Em}}{Bq} \\
\end{align} $.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




