
: A metal crystallises in face centred cubic structure. If the edge of its unit cell is ‘a’, the closest approach between two atoms in metallic crystal will be:
(A) ${\rm{2}}\sqrt {{\rm{2a}}} $
(B) $\sqrt {{\rm{2a}}} $
(C) $\dfrac{{\rm{a}}}{{\sqrt {\rm{2}} }}$
(D) ${\rm{2a}}$
Answer
527.8k+ views
Hint: We know that, in the face centred cubic structure the number of atoms present in it is four. Generally, the one atom is present or exists in the center and three atoms present at the corner of the FCC structure. The FCC is one of the abbreviations used for representing the face centred cubic.
Complete step-by-step solution:As we all know, for FCC crystal or face cubic structure, the closet method between two atoms in metallic crystal will be equal to the half the length of the face diagonal. It generally be represented as $\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\rm{length}}\;{\rm{of}}\;{\rm{diagonal}}......\left( 1 \right)$.
But the length of the face diagonal of the face cubic structure is $\sqrt {{\rm{2a}}} ......\left( 2 \right)$.
Where, ‘a’ is the edge of the unit cell.
So, equating the equations (1) and (2), for getting the closet value between the atoms in a metallic crystal as shown below.
$\dfrac{1}{2} \times \sqrt {{\rm{2a}}} = \dfrac{{\rm{a}}}{{\sqrt {\rm{2}} }}$
Thus, for “a metal crystallises in face centred cubic structure. If the edge of its unit cell is ‘a’, the closet approach between two atoms in metallic crystal” will be $\dfrac{{\rm{a}}}{{\sqrt {\rm{2}} }}$ as shown in the image below:
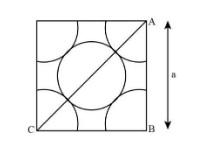
Hence, the correct option for this question is C that is $\dfrac{{\rm{a}}}{{\sqrt {\rm{2}} }}$.
Note:Usually, the crystals are divided into seven main types. Generally, it is divided on the basis of the number of atoms present in the crystals at the corner and at the center and the arrangement of atoms or ions in the crystal. The process is normally termed as crystallography.
Complete step-by-step solution:As we all know, for FCC crystal or face cubic structure, the closet method between two atoms in metallic crystal will be equal to the half the length of the face diagonal. It generally be represented as $\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\rm{length}}\;{\rm{of}}\;{\rm{diagonal}}......\left( 1 \right)$.
But the length of the face diagonal of the face cubic structure is $\sqrt {{\rm{2a}}} ......\left( 2 \right)$.
Where, ‘a’ is the edge of the unit cell.
So, equating the equations (1) and (2), for getting the closet value between the atoms in a metallic crystal as shown below.
$\dfrac{1}{2} \times \sqrt {{\rm{2a}}} = \dfrac{{\rm{a}}}{{\sqrt {\rm{2}} }}$
Thus, for “a metal crystallises in face centred cubic structure. If the edge of its unit cell is ‘a’, the closet approach between two atoms in metallic crystal” will be $\dfrac{{\rm{a}}}{{\sqrt {\rm{2}} }}$ as shown in the image below:

Hence, the correct option for this question is C that is $\dfrac{{\rm{a}}}{{\sqrt {\rm{2}} }}$.
Note:Usually, the crystals are divided into seven main types. Generally, it is divided on the basis of the number of atoms present in the crystals at the corner and at the center and the arrangement of atoms or ions in the crystal. The process is normally termed as crystallography.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




