
A light ray is an incident on a transparent sphere of the index\[ = \sqrt 2 \], at an angle of incidence \[ = {45^ \circ }\]. What is the deviation of a tiny fraction of the ray, which enters the sphere, undergoes two internal reflections, and then refracts out into the air?
A. \[{270^ \circ }\]
B. \[{240^ \circ }\]
C. \[{120^ \circ }\]
D. \[{180^ \circ }\]
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to determine the deviation of a tiny fraction of the ray such that it enters the sphere, undergoes two internal reflections, and then refracts out into the air. For this, we will use the different properties of reflection of light rays and total internal reflections.
Complete step by step answer:
The refractive index of the sphere \[{\mu _2} = \sqrt 2 \]
Angle of incidence \[i = {45^ \circ }\]
As the light ray enters the sphere from the air hence refractive index of the air \[{\mu _1} = 1\]
Now by using Snell’s law, we will find the angle of reflection
\[
{\mu _1}\sin i = {\mu _2}\sin r \\
1 \times \sin {45^ \circ } = \sqrt 2 \sin r \\
\sin r = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}}}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\]
Therefore the of reflection
\[
\sin r = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
r = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) \\
= {30^ \circ } \\
\]
Since the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of refraction, hence\[r = r' = {30^ \circ }\]
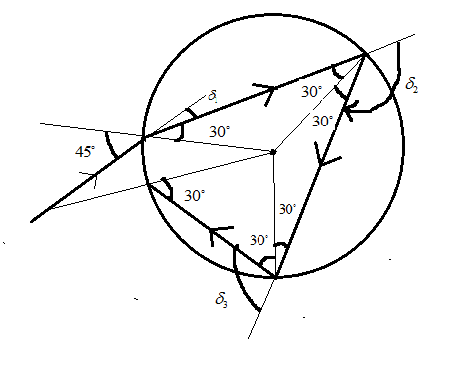
It is given that the light ray enters the sphere and undergoes two internal reflections, so the first angle of deviation will be
\[{\delta _1} = i - r' = 45 - 30 = {15^ \circ }\]
Now, when the light ray refracted from the surface of the sphere and touches the other face of the sphere, the light ray undergoes total internal reflection where the angle of incidence and reflection will be equal to \[{30^ \circ }\].
Therefore the second angle of deviation will be
\[{\delta _2} = 180 - 30 - 30 = {120^ \circ }\]
When the light ray goes the total internal reflection, then the light reflects back and it incident on the internal surface of a sphere where the light again goes to total internal reflection where the angle of incidence and reflection will be equal to\[{30^ \circ }\].
Therefore the third angle of deviation will be
\[{\delta _3} = 180 - 30 - 30 = {120^ \circ }\]
Now it is said that after light undergoes two internal reflections, the light refracts out into the air, so we will again use the Snell’s law to find the angle of the refraction
\[
{\mu _2}\sin i = {\mu _1}\sin r \\
\sqrt 2 \times \sin {30^ \circ } = 1\sin r \\
\sqrt 2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = \sin r \\
\sin r = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
\]
Therefore the of reflection
\[
\sin r = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
r = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \\
= {45^ \circ } \\
\]
So the fourth angle of deviation will be
\[{\delta _4} = 45 - 30 = {15^ \circ }\]
Hence the total angle of deviation will be
\[
\delta = {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} + {\delta _3} + {\delta _4} \\
= 15 + 120 + 120 + 15 \\
= {270^ \circ } \\
\]
So the deviation of a tiny fraction of the ray \[ = {270^ \circ }\]
Option 1 is correct.
Note:It is interesting to note here that when light enters into a medium at a certain angle then, the light rays cannot go out in the initial medium; then, the reflection is known as Total Internal Reflection.
Complete step by step answer:
The refractive index of the sphere \[{\mu _2} = \sqrt 2 \]
Angle of incidence \[i = {45^ \circ }\]
As the light ray enters the sphere from the air hence refractive index of the air \[{\mu _1} = 1\]
Now by using Snell’s law, we will find the angle of reflection
\[
{\mu _1}\sin i = {\mu _2}\sin r \\
1 \times \sin {45^ \circ } = \sqrt 2 \sin r \\
\sin r = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}}}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\]
Therefore the of reflection
\[
\sin r = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
r = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) \\
= {30^ \circ } \\
\]
Since the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of refraction, hence\[r = r' = {30^ \circ }\]

It is given that the light ray enters the sphere and undergoes two internal reflections, so the first angle of deviation will be
\[{\delta _1} = i - r' = 45 - 30 = {15^ \circ }\]
Now, when the light ray refracted from the surface of the sphere and touches the other face of the sphere, the light ray undergoes total internal reflection where the angle of incidence and reflection will be equal to \[{30^ \circ }\].
Therefore the second angle of deviation will be
\[{\delta _2} = 180 - 30 - 30 = {120^ \circ }\]
When the light ray goes the total internal reflection, then the light reflects back and it incident on the internal surface of a sphere where the light again goes to total internal reflection where the angle of incidence and reflection will be equal to\[{30^ \circ }\].
Therefore the third angle of deviation will be
\[{\delta _3} = 180 - 30 - 30 = {120^ \circ }\]
Now it is said that after light undergoes two internal reflections, the light refracts out into the air, so we will again use the Snell’s law to find the angle of the refraction
\[
{\mu _2}\sin i = {\mu _1}\sin r \\
\sqrt 2 \times \sin {30^ \circ } = 1\sin r \\
\sqrt 2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = \sin r \\
\sin r = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
\]
Therefore the of reflection
\[
\sin r = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
r = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \\
= {45^ \circ } \\
\]
So the fourth angle of deviation will be
\[{\delta _4} = 45 - 30 = {15^ \circ }\]
Hence the total angle of deviation will be
\[
\delta = {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} + {\delta _3} + {\delta _4} \\
= 15 + 120 + 120 + 15 \\
= {270^ \circ } \\
\]
So the deviation of a tiny fraction of the ray \[ = {270^ \circ }\]
Option 1 is correct.
Note:It is interesting to note here that when light enters into a medium at a certain angle then, the light rays cannot go out in the initial medium; then, the reflection is known as Total Internal Reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




