
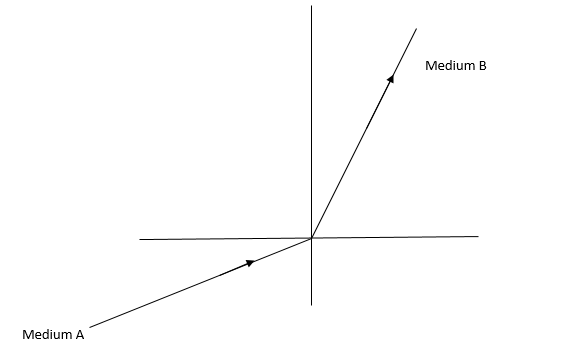
A light ray enters from medium \[A\] to \[B\] as shown in the figure. The refractive index of medium \[B\] relative to \[A\] will be:
A. Greater than unity
B. Less than unity
C. Equal to unity
D. Zero

Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Refraction is a phenomena of change in direction of a light ray when it passes from one medium to another.
Complete step by step answer:
Observe the diagram.
$PQ$ is the place separating two mediums, medium $A$ and $B$.
$XY$ is perpendicular to $PQ$ and it is called normal to the plane $AB$.
Rarer Medium: Rarer medium is a medium where molecules and medium are away from each other compared to the other medium.
Denser Medium: Denser medium is a medium where molecules of medium are closer to each other compared to the other medium.
For example: In case of water and air, air which will act as a rarer medium and water will act as a denser medium.
Now, when light passes from rarer to denser medium, then it beards towards the normal.
And when light passes from denser to rarer medium, then it bards away from the normal.
Refractive index $(\mu )$ is the measure of bending of a ray of light when it passes from one medium to another.
Clearly, the refractive index of the rarer medium is greater than the refractive index of the denser medium.
Now, by observing the diagram, we can clearly conclude the medium $B$ is rarer medium and medium $A$ is denser medium.
Let ${\mu _A}$ be the refractive index of medium $A$.
${\mu _B}$ be the refractive index of medium $B$.
And ${\mu _{BA}}$be the refractive index of medium $B$ relative to $A$.
$\therefore {\mu _B} > {\mu _A}$
Dividing both the sides of ${\mu _A}$, we get
$\dfrac{{{\mu _B}}}{{{\mu _A}}} > 1(\therefore \mu > 0)$ . . . (1)
Also ,${\mu _{BA}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _B}}}{{{\mu _A}}}$ . . . (2)
Therefore, from the equation (1) and (2), we get
${\mu _{BA}} > 1$.
Note:
Observe the diagram very carefully to solve such questions.
A medium can be denser in some cases but the same medium can be rarer for some other cases.
For Example: water is a denser medium when compared to air. But it is a rarer medium when compared to glass slab
Complete step by step answer:
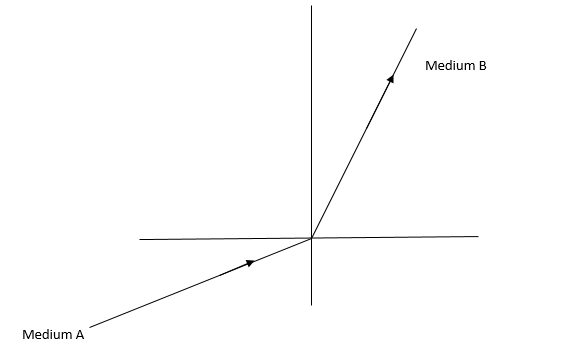
Observe the diagram.

$PQ$ is the place separating two mediums, medium $A$ and $B$.
$XY$ is perpendicular to $PQ$ and it is called normal to the plane $AB$.
Rarer Medium: Rarer medium is a medium where molecules and medium are away from each other compared to the other medium.
Denser Medium: Denser medium is a medium where molecules of medium are closer to each other compared to the other medium.
For example: In case of water and air, air which will act as a rarer medium and water will act as a denser medium.
Now, when light passes from rarer to denser medium, then it beards towards the normal.
And when light passes from denser to rarer medium, then it bards away from the normal.
Refractive index $(\mu )$ is the measure of bending of a ray of light when it passes from one medium to another.
Clearly, the refractive index of the rarer medium is greater than the refractive index of the denser medium.
Now, by observing the diagram, we can clearly conclude the medium $B$ is rarer medium and medium $A$ is denser medium.
Let ${\mu _A}$ be the refractive index of medium $A$.
${\mu _B}$ be the refractive index of medium $B$.
And ${\mu _{BA}}$be the refractive index of medium $B$ relative to $A$.
$\therefore {\mu _B} > {\mu _A}$
Dividing both the sides of ${\mu _A}$, we get
$\dfrac{{{\mu _B}}}{{{\mu _A}}} > 1(\therefore \mu > 0)$ . . . (1)
Also ,${\mu _{BA}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _B}}}{{{\mu _A}}}$ . . . (2)
Therefore, from the equation (1) and (2), we get
${\mu _{BA}} > 1$.
Note:
Observe the diagram very carefully to solve such questions.
A medium can be denser in some cases but the same medium can be rarer for some other cases.
For Example: water is a denser medium when compared to air. But it is a rarer medium when compared to glass slab
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




