
A group of $13$ elements if added in small amounts to $Ge$ , then the type of semiconductor formed is :
A . n-type semiconductor
B . p-type semiconductor
C . super semiconductor
D . both A and B
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint : We know that when a small amount of foreign impurity is added to a crystal then this process is called doping. Doping increases electrical conductivity of the crystal. We have learned about two types of semiconductor i.e. extrinsic semiconductors and intrinsic semiconductors. The pure semiconductor which does not go through the process of doping is called intrinsic semiconductor and an extrinsic semiconductor is one that has been doped.
Complete answer:
- We know about two types of doping agents which result in two types of semiconductor .
- When the donor is an electron donor atom then it is called n-type semiconductor while when the dopant is electron acceptor it is called p-type semiconductor. The majority charge carriers in p-type semiconductors and n-type semiconductors are holes and electrons respectively. Extrinsic semiconductors are used as the components of many semiconductor devices.
- Group $13$ elements in the periodic table are the boron family. The members of group $13$ are boron, aluminium, gallium ,indium, thallium. Elements of this group $13$ have three valence electrons. So these elements will give electrons when we add them in pure semiconductor. Germanium ($Ge$) has a similar nature like silicon and is used to make semiconductor devices. So a group of $13$ elements if added in small amounts to $Ge$ , then the type of semiconductor formed is p-type semiconductor. Hence option B is correct
.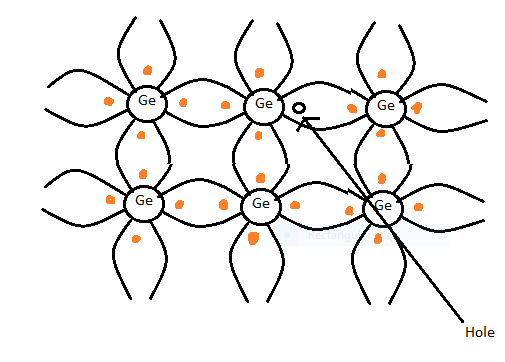
Note : Here we have approached this problem with the help of concept that when trivalent impurity atom is added to germanium it becomes p-type semiconductor so here option B is correct that is p-type semiconductor .In the above diagram we can see that there is bonding between germanium and trivalent impurity atoms.
Complete answer:
- We know about two types of doping agents which result in two types of semiconductor .
- When the donor is an electron donor atom then it is called n-type semiconductor while when the dopant is electron acceptor it is called p-type semiconductor. The majority charge carriers in p-type semiconductors and n-type semiconductors are holes and electrons respectively. Extrinsic semiconductors are used as the components of many semiconductor devices.
- Group $13$ elements in the periodic table are the boron family. The members of group $13$ are boron, aluminium, gallium ,indium, thallium. Elements of this group $13$ have three valence electrons. So these elements will give electrons when we add them in pure semiconductor. Germanium ($Ge$) has a similar nature like silicon and is used to make semiconductor devices. So a group of $13$ elements if added in small amounts to $Ge$ , then the type of semiconductor formed is p-type semiconductor. Hence option B is correct
.

Note : Here we have approached this problem with the help of concept that when trivalent impurity atom is added to germanium it becomes p-type semiconductor so here option B is correct that is p-type semiconductor .In the above diagram we can see that there is bonding between germanium and trivalent impurity atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




