
A block of mass 50 Kg can slide on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is 0.6. The least force of pull acting at an angle of ${30^0}$ to the upward drawn vertical which causes the block to just slide is:
A. 29.43 N
B. 219.6 N
C. 21.96 N
D. 294.3 N
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:Here we first need to find the frictional force that will cause the block to slide. For this first we have to find the horizontal and the vertical component of the force given. Also the angle for the force is also given. Then equate the horizontal component of the force with the frictional force in order to get the required answer.
Formula used:
1. Reaction force, $R = mg - F\cos \theta $
2. Frictional force, $f = \mu R$
Where, $\mu $is the coefficient of frictional force.
Complete step by step solution:
The free body diagram can be drawn as
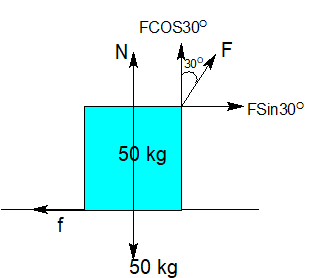
Let the force applied on the body at the given angle be F.
Given angle, $\theta = {30^0}$.
This force will consist of horizontal and vertical components.
Vertical component of force will be $F\cos \theta = F\cos {30^0}$.
Horizontal component of force will be $F\sin \theta = F\sin {30^0}$.
Reactional force will be:
$R = mg - F\cos \theta $
Putting the values from the question, we get:
$R = 50 \times 10 - F\cos {30^0}$
By solving;
$R = 500 - F\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
Now, frictional force is given as follows:
$f = \mu R$ (equation 1)
Also f will be equal to horizontal component of force:
$f = F\sin {30^0}$ (equation 2)
Equating equation 1 and 2, we get;
$\dfrac{F}{2} = \left[ {(500 - F\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)} \right]\mu $
By solving;
$F = (1000 - F\sqrt 3 )0.6$
$\therefore F = 294.3\,N$
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: Here the vertical component of force balances the mg force applied on the body in downward vertical direction and the horizontal component balances the frictional force applied on the body. Reactional force will be resultant of all the vertical forces applied on the given body. Then finally multiplying it with the frictional coefficient we will get the final answer.
Formula used:
1. Reaction force, $R = mg - F\cos \theta $
2. Frictional force, $f = \mu R$
Where, $\mu $is the coefficient of frictional force.
Complete step by step solution:
The free body diagram can be drawn as

Let the force applied on the body at the given angle be F.
Given angle, $\theta = {30^0}$.
This force will consist of horizontal and vertical components.
Vertical component of force will be $F\cos \theta = F\cos {30^0}$.
Horizontal component of force will be $F\sin \theta = F\sin {30^0}$.
Reactional force will be:
$R = mg - F\cos \theta $
Putting the values from the question, we get:
$R = 50 \times 10 - F\cos {30^0}$
By solving;
$R = 500 - F\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
Now, frictional force is given as follows:
$f = \mu R$ (equation 1)
Also f will be equal to horizontal component of force:
$f = F\sin {30^0}$ (equation 2)
Equating equation 1 and 2, we get;
$\dfrac{F}{2} = \left[ {(500 - F\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)} \right]\mu $
By solving;
$F = (1000 - F\sqrt 3 )0.6$
$\therefore F = 294.3\,N$
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: Here the vertical component of force balances the mg force applied on the body in downward vertical direction and the horizontal component balances the frictional force applied on the body. Reactional force will be resultant of all the vertical forces applied on the given body. Then finally multiplying it with the frictional coefficient we will get the final answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




