
\[1-Bromo-3-chloro\text{ }cyclobutane\] when treated with 2-equivalents of Na in presence of ether, which of the following products will be formed?
(A)
(B)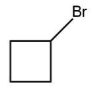
(C)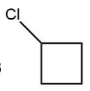
(D)

Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: When two equivalent sodium metals react with two alkyl halides in the presence of dry ether condition, this reaction is known as the Wurtz reaction (coupling reaction). In this reaction, sodium metal is used so that it can donate its electron to halogen and contribute to the formation of a radical. In this question, in place of two alkyl halides, \[1-Bromo-3-chloro\text{ }cyclobutane\]is given. In this case, an internal Wurtz reaction will take place.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the first step, \[N{{a}_{2}}\]break into two equivalent sodium metal, and in the second step, the bromine halogen of \[1-Bromo-3-chloro\text{ }cyclobutane\], makes a bond with one sodium metal leaving a radical of cyclobutane behind such as
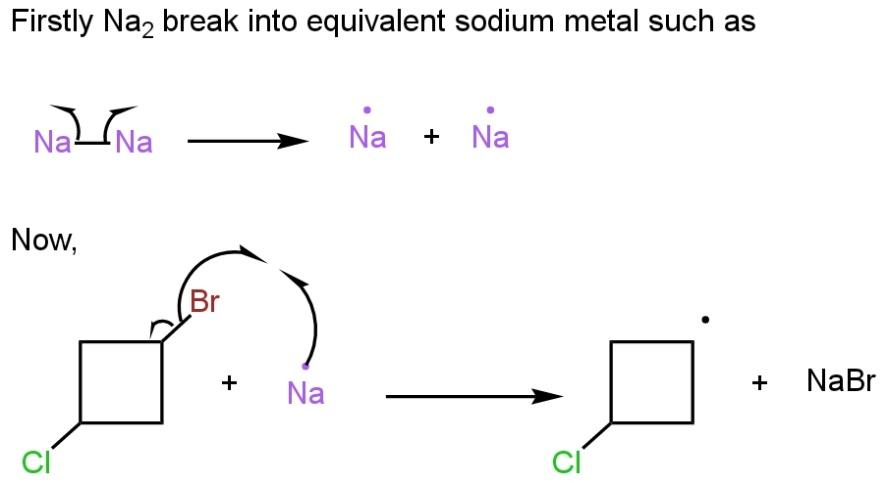
In the third step, the second equivalent of sodium metal give an electron to the radical compound to form a sodium salt of \[1-Bromo-3-chloro\text{ }cyclobutane\]. Now in the last step, the negative charge on the ring attracted by carbon bonded to chlorine atom as chlorine is a good leaving group such as
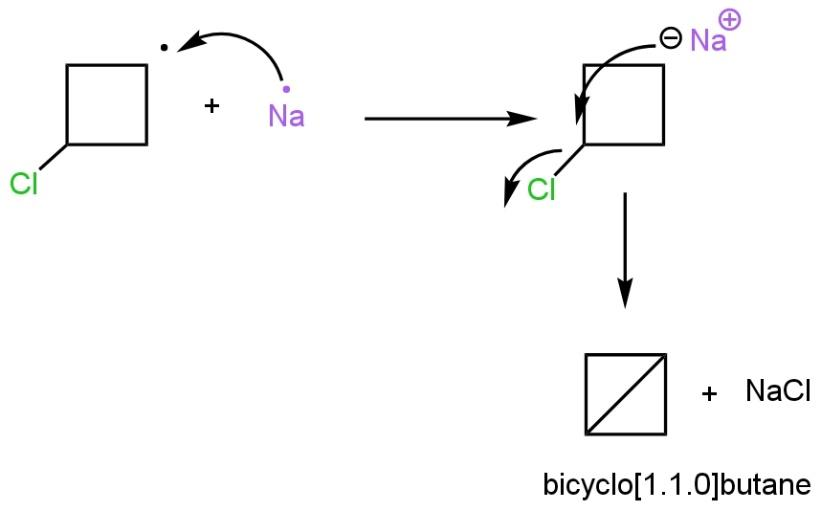
The resultant compound formed is a bicycle compound (two cycle formed), named bicycle\[\left[ 1.1.0 \right]\]butane.
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note: Both Chlorine and Bromine are good leaving groups (halogens are good leaving groups because of high electronegativity and stability). But the size of bromine halogen is large as compared to chlorine so due to this, it can easily leave the compound as compared to chlorine. This is the reason why bromine is attacked first by sodium.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the first step, \[N{{a}_{2}}\]break into two equivalent sodium metal, and in the second step, the bromine halogen of \[1-Bromo-3-chloro\text{ }cyclobutane\], makes a bond with one sodium metal leaving a radical of cyclobutane behind such as

In the third step, the second equivalent of sodium metal give an electron to the radical compound to form a sodium salt of \[1-Bromo-3-chloro\text{ }cyclobutane\]. Now in the last step, the negative charge on the ring attracted by carbon bonded to chlorine atom as chlorine is a good leaving group such as

The resultant compound formed is a bicycle compound (two cycle formed), named bicycle\[\left[ 1.1.0 \right]\]butane.
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note: Both Chlorine and Bromine are good leaving groups (halogens are good leaving groups because of high electronegativity and stability). But the size of bromine halogen is large as compared to chlorine so due to this, it can easily leave the compound as compared to chlorine. This is the reason why bromine is attacked first by sodium.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




